|
Propalaeotherium In Vienna
''Propalaeotherium'' was an early genus of perissodactyl endemic to Europe and Asia during the early Eocene. There are currently six recognised species within the genus, with ''P. isselanum'' as the type species (named by Georges Cuvier in 1824). Taxonomy ''Propalaeotherium'' was named by Paul Gervais; its name means "before ''Palaeotherium''". It was considered a member of Palaeotheriidae by Hooker (1986). A 2004 study found it to be an equid instead. A 2016 study lumped the genus back within the Palaeotheriidae. The species ''P. parvulum'' and ''P. messelensis'' have been alternately assigned to the equid genus ''Eurohippus''. Description ''Propalaeotherium'' was a small animal, ranging from 30–60 cm at the shoulder (2.9 to 5.9 hands), and weighing just . Despite being an early form of horse, it looked similar to small tapirs. It had no hooves, but instead several small nail-like hooflets. The well-preserved Messel fossils showed their herbivory, specifically t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypresian
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age (geology), age or lowest stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian is consistent with the Lower Eocene (Early Eocene). Events The Ypresian Age begins during the throes of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The Fur Formation in Denmark, the Messel shales in Germany, the Oise amber of France and Cambay amber of India are of this age. The Eocene Okanagan Highlands are an uplands subtropical to temperate series of lakes from the Ypresian. The Ypresian is additionally marked by another warming event called the Early Eocene Climatic Optimum (EECO). The EECO is the longest sustained warming event in the Cenozoic record, lasting about 2–3 million years between 53 and 50 Ma. The interval is characterized by low oxygen-18 isotopes, high levels of atmospheric pCO2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, '' Eohippus'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE in Central Asia, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, which are horses that have never been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior. Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Placental Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Mammals Of Europe
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Genus Extinctions
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Horses
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prehistoric Mammals
This is an incomplete list of prehistoric mammals. It does not include List of mammals, extant mammals or List of extinct mammals, recently extinct mammals. For extinct primate species, see: list of fossil primates.Mikko's Phylogeny Archiv Mammaliaformes ' *Genus †''Adelobasileus'' Lucas & Hunt 1990 *Genus †''Bocaconodon'' Montellano, Hopson & Clark 2008 *Genus †''Delsatia'' Sigogneau-Russell & Godefroit 1997 *Genus †''Tricuspes'' von Huene 1933 *Genus †''Hadrocodium'' Luo, Crompton & Sun 2001 *Genus †''Fruitafossor'' Luo & Wible 2005 Order †Dinnetheria *Family †Dinnetheriidae Averianov & Lopatin 2011 **Genus †''Dinnetherium'' Jenkins, Crompton & Downs 1983 Order †Siconodontiformes *Family †Siconodontidae Mills 1971 **Genus †''Sinoconodon'' Patterson & Olson 1961 Order †Morganucodonta ' *Genus †''Bridetherium'' Clemens 2011 *Genus †''Hallautherium'' Clemens 1980 *Genus †''Paceyodon'' Clemens 2011 *Genus †''Purbeckodon'' Butler et al. 2012 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of The Horse
The evolution of the horse, a mammal of the family Equidae, occurred over a geologic time scale of 50 million years, transforming the small, dog-sized, forest-dwelling '' Eohippus'' into the modern horse. Paleozoologists have been able to piece together a more complete outline of the evolutionary lineage of the modern horse than of any other animal. Much of this evolution took place in North America, where horses originated but became extinct about 10,000 years ago, before being reintroduced in the 15th century. The horse belongs to the order Perissodactyla ( odd-toed ungulates), the members of which one will share hooved feet and an odd number of toes on each foot, as well as mobile upper lips and a similar tooth structure. This means that horses share a common ancestry with tapirs and rhinoceroses. The perissodactyls arose in the late Paleocene, less than 10 million years after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. This group of animals appears to have been origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples of berries in the culinary sense are strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries, white currants, blackcurrants, and redcurrants. In Britain, soft fruit is a horticultural term for such fruits. The common usage of the term "berry" is different from the scientific or botanical definition of a berry, which refers to a fleshy fruit produced from the ovary of a single flower where the outer layer of the ovary wall develops into an edible fleshy portion( pericarp). The botanical definition includes many fruits that are not commonly known or referred to as berries, such as grapes, tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, bananas, and chili peppers. Fruits commonly considered berries but excluded by the botanical definition include strawberries, raspber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat non-vascular autotrophs such as mosses, algae and lichens, but do not include those feeding on decomposed plant matters (i.e. detritivores) or macrofungi (i.e. fungivores). As a result of their plant-based diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouth structures ( jaws or mouthparts) well adapted to mechanically break down plant materials, and their digestive systems have special enzymes (e.g. amylase and cellulase) to digest polysaccharides. Grazing herbivores such as horses and cattles have wide flat- crowned teeth that are better adapted for grinding grass, tree bark and other tougher lignin-containing materials, and many of them evolved rumination or cecotropic behaviors to better extract nutrients from plants. A larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messel Pit
The Messel Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in Hesse, central Germany, dating back to the Eocene Epoch (geology), epoch (about 47 Ma). Its geographic range is restricted to the Messel pit. There it unconformably overlies crystalline Variscan basement and its Permian cover (Rotliegend) as well as Eocene volcanic breccias derived from the basement rocks. The formation mainly comprises lacustrine laminated bituminous shale (‘oil shale’) renowned for its content of fossils in exceptional preservation, particularly plants, arthropods and vertebrates (e.g. ''Darwinius masillae''). Messel pit The Messel pit () is a disused quarry near the village of Messel (Landkreis Darmstadt-Dieburg, Hesse) about southeast of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Bituminous shale was mined there. Because of its abundance of well-preserved fossils of the Messel Formation dating from the middle of the Eocene, it has significant geological and scientific importance. Over 1400 taxa o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
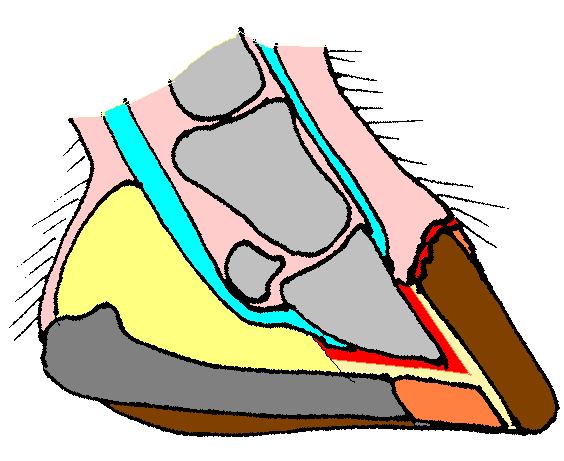
Hooves
The hoof (: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits; the ruminants with two digits are the most numerous, e.g. giraffe, deer, bison, cattle, goats, gazelles, pigs, and sheep. The feet of perissodactyl mammals have an odd number of toes, e.g. the horse, the rhinoceros, and the tapir. Although hooves are limb structures primarily found in placental mammals, hadrosaurs such as ''Edmontosaurus'' possessed hoofed forelimbs. The marsupial ''Chaeropus'' also had hooves. Description The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the distal phalanx, and the navicular bone. The hoof consists of the hoof wall, the bars of the hoof, the sole and frog and soft tissue shock absorption structures. The weight of the animal is normally borne by both the sole and the edge of the hoof wall. Hooves perform many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |