|
Project DUMAND
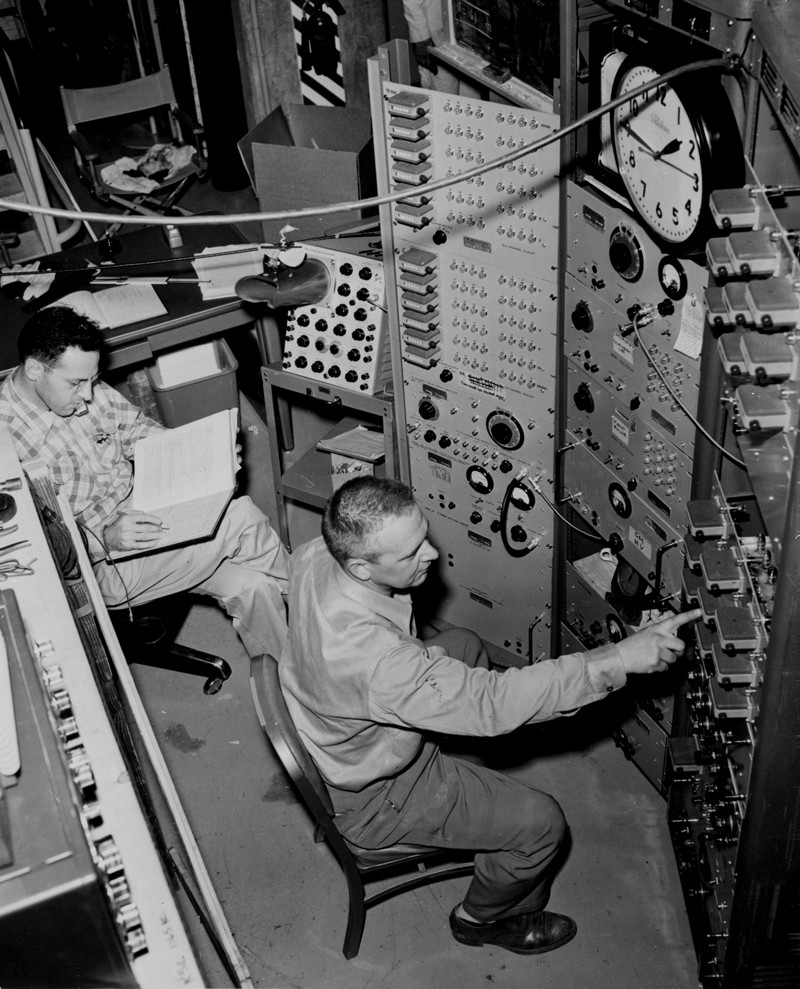
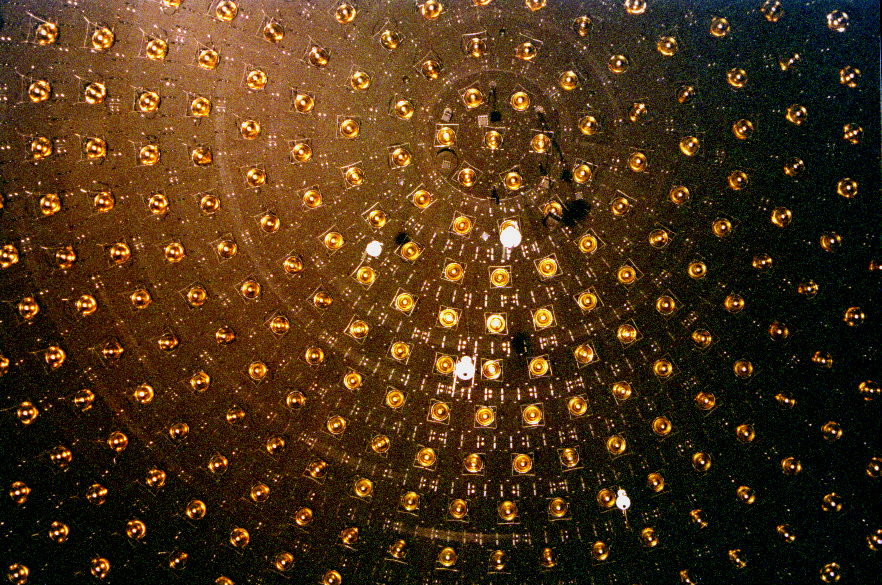
The DUMAND Project (Deep Underwater Muon And Neutrino Detector Project) was a proposed underwater neutrino telescope to be built in the Pacific Ocean, off the shore of the island of Hawaii, five kilometers beneath the surface. It would have included thousands of strings of instruments occupying a cubic kilometer of the ocean. The proposal called for two types of detectors: optical detectors to find the Cherenkov radiation emitted by secondary particles traveling faster than the speed of light in water, resulting from collisions by neutrinos, and hydrophones to listen for the acoustic signals generated by the interactions. Sophisticated signal processing would have combined the signals from many optical and acoustic sensors, allowing scientists to determine the direction from which the neutrino arrived, and to rule out false signals arising from other particles or acoustic sources. Because of the nature of the interaction between neutrinos and protons, DUMAND would have been m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino Telescope
A neutrino detector is a physics apparatus which is designed to study neutrinos. Because neutrinos only weakly interact with other particles of matter, neutrino detectors must be very large to detect a significant number of neutrinos. Neutrino detectors are often built underground, to isolate the detector from cosmic rays and other background radiation. The field of neutrino astronomy is still very much in its infancy – the only confirmed extraterrestrial sources are the Sun and the supernova 1987A in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud. Another likely source (three standard deviations) is the blazar TXS 0506+056 about 3.7 billion light years away. Neutrino observatories will "give astronomers fresh eyes with which to study the universe". Various detection methods have been used. Super Kamiokande is a large volume of water surrounded by phototubes that watch for the Cherenkov radiation emitted when an incoming neutrino creates an electron or muon in the water. The Sudbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subatomic Particle
In physics, a subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a baryon, like a proton or a neutron, composed of three quarks; or a meson, composed of two quarks), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, quarks; or electrons, muons, and tau particles, which are called leptons). Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Most force-carrying particles like photons or gluons are called bosons and, although they have quanta of energy, do not have rest mass or discrete diameters (other than pure energy wavelength) and are unlike the former particles that have rest mass and cannot overlap or combine which are called fermions. The W and Z bosons, however, are an exception to this rule and have relatively large rest masses at approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INSPIRE-HEP
INSPIRE-HEP is an open access digital library for the field of high energy physics (HEP). It is the successor of the Stanford Physics Information Retrieval System (SPIRES) database, the main literature database for high energy physics since the 1970s. History SPIRES was (in addition to the CERN Document Server (CDS), arXiv and parts of Astrophysics Data System) one of the main Particle Information Resources. A survey conducted in 2007 found that SPIRES database users wanted the portal to provide more services than the, at that time, already 30-year-old system could provide. On the second annual Summit of Information Specialists in Particle Physics and Astrophysics in May 2008, the physics laboratories CERN, DESY, SLAC and Fermilab therefore announced that they would work together to create a new Scientific Information System for high energy physics called INSPIRE. It interacts with other HEP service providers like arXiv.org, Particle Data Group, NASA The National A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as '' spacetime''. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. In the 19th and 20th centuries mathematicians began to examine geometries that are non-Euclidean, in which space is conceived as '' curved'', rather than '' flat'', as in the Euclidean space. According to Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, space around gravitational fields deviates from Euclidean space. Experimental tests of general relativity have confirmed that non-Euclidean geometries provide a bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NESTOR Project
The NESTOR Project (Neutrino Extended Submarine Telescope with Oceanographic Research Project) is an international scientific collaboration whose target is the deployment of a neutrino telescope on the sea floor off Pylos, Greece. Neutrino Neutrinos are elementary particles first detected in the 1950s, long after their theoretical prediction by theorist Wolfgang Pauli. Neutrinos (or anti-neutrinos) are created during certain nuclear reactions, where protons are transformed into neutrons and vice versa. Neutrinos do not interact with matter via either the electromagnetic, the strong nuclear, or gravitational forces, since they are electrically neutral leptons and their rest mass is very small. They interact with the nucleons (neutrons and protons) only via weak nuclear interactions. Since they do not interact with matter via the electromagnetic or gravitational forces, it is extremely difficult to detect them. Since their mass is very small (less than 14 eV) they travel with sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino Mediterranean Observatory
The Cubic Kilometre Neutrino Telescope, or KM3NeT, is a European research infrastructure located at the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea. It hosts water Cherenkov radiation, Cherenkov neutrino astronomy, neutrino telescopes designed to detect and study neutrinos from distant astrophysical sources as well as from our own atmosphere, contributing significantly to both astrophysics and particle physics knowledge. Arrays of thousands of optical sensor modules detect the faint Cherenkov light in the deep sea from charged particles originating from interactions of neutrinos in water or rock in the vicinity of the detector. The position and direction of the optical modules and the time of arrival of the light on the photomultipliers inside are recorded with high precision. Properties of the particles, like their trajectory and energy, are reconstructed from these measurements. The KM3NeT project foresees the construction of several of these detectors in the depths of the Mediterranean Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANTARES (telescope)
ANTARES (Astronomy with a Neutrino Telescope and Abyss environmental RESearch project) is a neutrino detector residing 2.5 km under the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Toulon, France. It is designed to be used as a directional neutrino telescope to locate and observe neutrino flux from cosmic origins in the direction of the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth, a complement to the South Pole neutrino detector IceCube that detects neutrinos from both hemispheres. The experiment is a recognized CERN experiment (RE6). Other neutrino telescopes designed for use in the nearby area include the Greek NESTOR telescope and the Italian NEMO telescope, which are both in early design stages. The data taking of ANTARES was finished in February 2022, after 16 years of continuous operation. Design The array contains a set of twelve separate vertical strings of photomultiplier tubes. Each one has 75 optical modules and is about 350 meters long. They are anchored at the bottom of the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Muon And Neutrino Detector Array
The Antarctic Muon And Neutrino Detector Array (AMANDA) was a neutrino telescope that was located beneath the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station. In 2005, after nine years of operation, AMANDA became part of its successor project, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory. AMANDA consisted of optical modules, each containing one photomultiplier tube, sunk in Antarctic ice cap at a depth of about 1500 to 1900 metres. In its latest development stage, known as AMANDA-II, AMANDA was made up of an array of 677 optical modules mounted on 19 separate strings that are spread out in a rough circle with a diameter of 200 metres. Each string had several dozen modules, that were put in place by "drilling" a hole in the ice using a hot-water hose, sinking the cable with attached optical modules in, and then letting the ice freeze around it. AMANDA detected very high energy neutrinos (50+ GeV) which pass through the Earth from the northern hemisphere and then react just as they are leaving upwards thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keahole Point
Keāhole Point is the westernmost point of the island of Hawaii. The Kona International Airport was moved here from directly north of the town of Kailua-Kona in 1970, when the previous smaller airstrip was converted into the Old Kona Airport State Recreation Area. The name comes from ''Ke āhole'' since the āhole fish (Kuhlia sandvicensis) was found nearby. Between the airport and the coast lies the Natural Energy Laboratory of Hawaii. Most of the land was formed in 1801 by the ''Huehue'' lava flow from Hualālai. This flow extended the shoreline out an estimated 1 mile, adding some 4 km2 of land to the island. The southern part of this point is sometimes referred to as Kalihi Point. The Ahupuaa (ancient name of the community in this area) was Kalaoa, still used by the census. The site includes a house platform, a walled enclosure, a debris pile with volcanic glass and marine shells, and a larger wall. Probably the home of a common family, an excavation in 1975 es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Neutrino
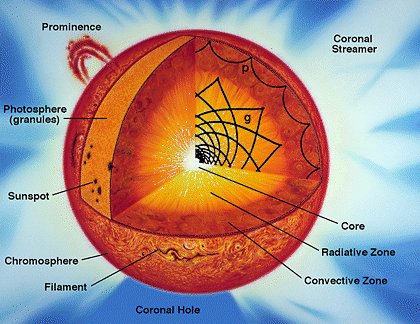
A solar neutrino is a neutrino originating from nuclear fusion in the Sun's core, and is the most common type of neutrino passing through any source observed on Earth at any particular moment. Neutrinos are elementary particles with extremely small rest mass and a neutral electric charge. They only interact with matter via weak interaction and gravity, making their detection very difficult. This has led to the now-resolved solar neutrino problem. Much is now known about solar neutrinos, but research in this field is ongoing. History and background Homestake experiment The timeline of solar neutrinos and their discovery dates back to the 1960s, beginning with the two astrophysicists John N. Bahcall and Raymond Davis Jr. The experiment, known as the Homestake experiment, named after the town in which it was conducted (Homestake, South Dakota), aimed to count the solar neutrinos arriving at Earth. Bahcall, using a solar model he developed, came to the conclusion that the mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is an elementary particle that interacts via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles (excluding massless particles). The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the electromagnetic interaction or the strong interaction. Consequently, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and with no detectable effect. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: # electron neutrino, # muon neutrino, # tau neutrino, Each flavor is associated with the correspondingly named charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |