|
Progress 59
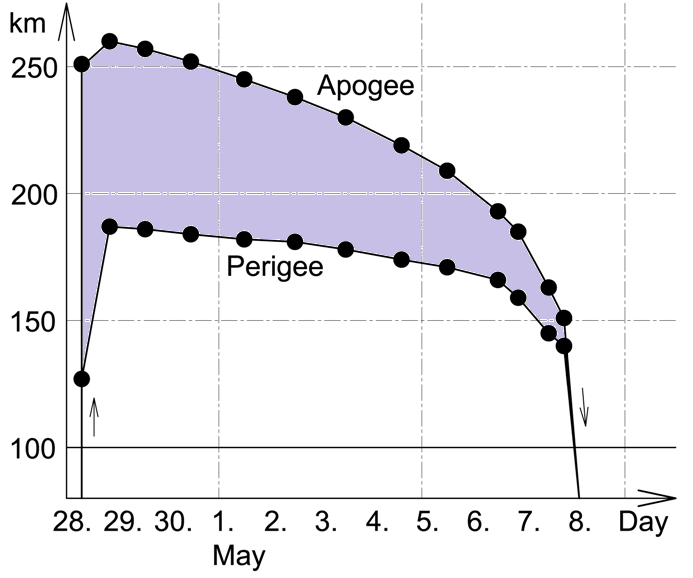
Progress M-27M (), identified by NASA as Progress 59P, was a Progress spacecraft used by Roscosmos in an unsuccessful attempt to resupply the International Space Station (ISS) in 2015. Launch Progress M-27M was the 27th Progress-M 11F615A60 spacecraft, with the serial number 427. It was built by RKK Energia and was operated by the Roscosmos. This was the second time the upgraded Soyuz-2.1a rocket was used for an ISS mission launch. The spacecraft was launched on 28 April 2015 at 07:09:50 UTC from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Progress M-27M was launched with a planned six-hour rendezvous profile to the ISS. During the launch the spacecraft achieved low Earth orbit, but a malfunction occurred near the end of the upper stage burn shortly before the separation of the Progress spacecraft, generating a debris field and leaving the spacecraft spinning and unable to be fully controlled. The spacecraft was deemed to be a total loss. Cargo The spacecraft carried of food, fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). As the largest space station ever constructed, it primarily serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in microgravity and studying the space environment. The station is divided into two main sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), developed by Roscosmos, and the US Orbital Segment (USOS), built by NASA, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. A striking feature of the ISS is the Integrated Truss Structure, which connect the station’s vast system of solar panels and Spacecraft thermal control, radiators to its pressurized modules. These modules support diverse functions, including scientific research, crew habitation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, peaking in number at an altitude around , while the farthest in LEO, before medium Earth orbit (MEO), have an altitude of 2,000 km, about one-third of the Earth radius, radius of Earth and near the beginning of the Van Allen radiation belt#Inner belt, inner Van Allen radiation belt. The term ''LEO region'' is used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. No human spaceflights other than the lunar missions of the Apollo program (1968-1972) have gone beyond L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as '' spacetime''. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. In the 19th and 20th centuries mathematicians began to examine geometries that are non-Euclidean, in which space is conceived as '' curved'', rather than '' flat'', as in the Euclidean space. According to Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, space around gravitational fields deviates from Euclidean space. Experimental tests of general relativity have confirmed that non-Euclidean geometries provide a bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Chile had a population of 17.5 million as of the latest census in 2017 and has a territorial area of , sharing borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. The country also controls several Pacific islands, including Juan Fernández Islands, Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas Islands, Desventuradas, and Easter Island, and claims about of Antarctica as the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The capital and largest city of Chile is Santiago, and the national language is Spanish language, Spanish. Conquest of Chile, Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Incas in Central Chile, Inca rule; however, they Arauco War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of the Americas. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Drake Passage; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. The Dutch Caribbean ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao) and Trinidad and Tobago are geologically located on the South-American continental shel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Entry
Atmospheric entry (sometimes listed as Vimpact or Ventry) is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. Atmospheric entry may be ''uncontrolled entry,'' as in the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides. It may be ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft that can be navigated or follow a predetermined course. Methods for controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass ( ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Objects have reentered with speeds ranging from 7.8 km/s for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its origins to 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established by transfer of personnel from the Army Air Forces with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in United States order of precedence, order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, airlift, rapid global mobility, Strategic bombing, global strike, and command and control. The United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the Air Force, which serves as the USAF's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
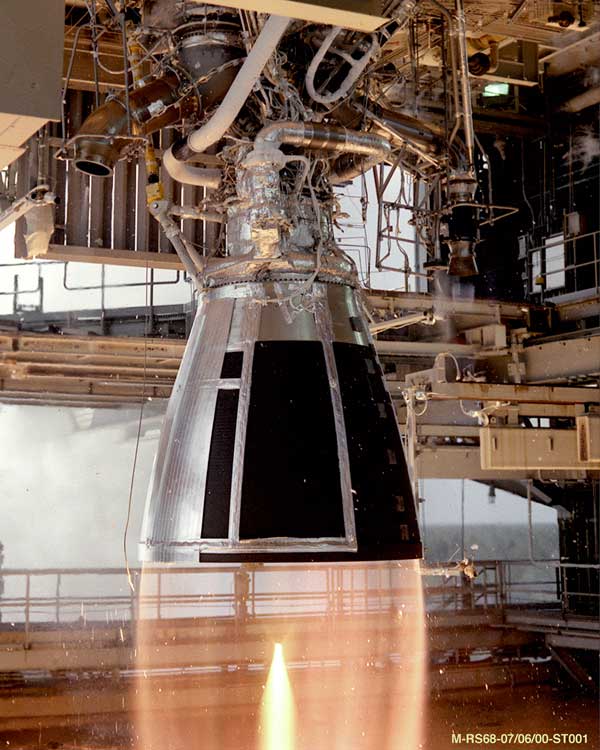
Rocket Engine
A rocket engine is a reaction engine, producing thrust in accordance with Newton's third law by ejecting reaction mass rearward, usually a high-speed Jet (fluid), jet of high-temperature gas produced by the combustion of rocket propellants stored inside the rocket. However, non-combusting forms such as cold gas thrusters and nuclear thermal rockets also exist. Rocket vehicles carry their own oxidiser, unlike most combustion engines, so rocket engines can be used in a vacuum, and they can achieve great speed, beyond escape velocity. Vehicles commonly propelled by rocket engines include missiles, Rocket-assisted projectile, artillery shells, ballistic missiles and rockets of any size, from tiny Rocket (firework), fireworks to Rocket (weapon), man-sized weapons to huge Space vehicle, spaceships. Compared to other types of jet engine, rocket engines are the lightest and have the highest thrust, but are the least propellant-efficient (they have the lowest specific impulse). The ideal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NORAD
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ; , CDAAN), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Canada and the continental United States. Headquarters for NORAD and the NORAD/ United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) center are located at Peterson Space Force Base in El Paso County, near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The nearby Cheyenne Mountain Complex has the Alternate Command Center. The NORAD commander and deputy commander are, respectively, a United States four-star general or equivalent and a Canadian lieutenant-general or equivalent. Command NORAD is headed by its commander, who is a four-star general or admiral in the United States Armed Forces. The deputy commander is a Royal Canadian Air Force lieutenant general. Prior to the 1968 unification of the Canadian Forces, the deputy commander was an RCAF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere Of Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by gravity of Earth, Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar irradiance, solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between daytime, day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the atmospheric chemistry, chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolution, evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurs (docking Navigation System)
Kurs () is an automated system for docking spacecraft used by the Soviet space program, Soviet and later the Russian space program. The system is primarily used by Progress (spacecraft), Progress cargo spacecraft, Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz spacecraft and to dock new modules to the Russian Orbital Segment of the International Space Station. The radio-based control system was developed by the Research Institute of Precision Instruments in Moscow before 1985 and initially manufactured by the Kiev Radio Factory. Kurs is now manufactured in Russia. History Kurs was the successor to the Igla (spacecraft docking system), Igla system and today provides navigation beaconing for Russian space vehicles including the Soyuz spacecraft and Progress spacecraft. The main difference between both systems is that Igla requires the space station to collaborate in the docking maneuver by reorienting itself to point the docking port to the spacecraft, while Kurs allows docking with a fully station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progres2015-024A-freefall
{{dab ...
Progres may refer to: * Progres, Kardzhali Province, a village in Momchilgrad Municipality, Kardzhali Province, Bulgaria * El Progrés, Badalona, Catalonia, Spain * Toyota ''Progrès'', a mid-sized Japanese luxury sedan * FC Progrès Niederkorn (aka ''Progrès''), Niederkorn, Luxembourg; a soccer team * PROGRES (Programme of Research on the Service Economy) * ''Le Progrès'', a daily newspaper from Lyon, Rhone, France * Le Progrès (Réunion), a political party * ' Progres 2', a Czech rock band See also * '' Haïti Progrès'', a daily U.S. newspaper focused on Haiti * '' Le Progrès Egyptien'', a daily French-language Egyptian newspaper * * Progress (other) Progress is advancement to a higher or more developed state. Progress or PROGRESS may also refer to: Architecture * Progress Energy Center for the Performing Arts, in Raleigh, North Carolina * Progress Energy Park, a baseball stadium in St. Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |