|
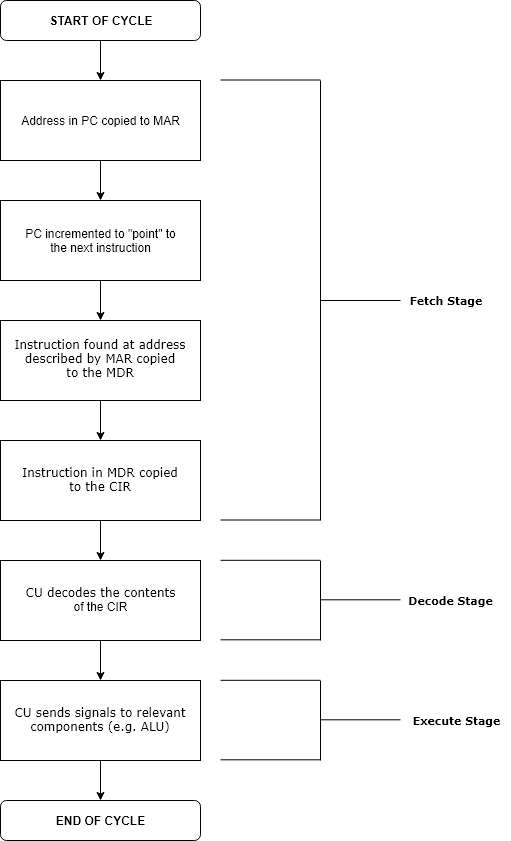
Processor Cycle
The instruction cycle (also known as the fetch–decode–execute cycle, or simply the fetch–execute cycle) is the cycle that the central processing unit (CPU) follows from boot-up until the computer has shut down in order to process instructions. It is composed of three main stages: the fetch stage, the decode stage, and the execute stage. In simpler CPUs, the instruction cycle is executed sequentially, each instruction being processed before the next one is started. In most modern CPUs, the instruction cycles are instead executed concurrently, and often in parallel, through an instruction pipeline: the next instruction starts being processed before the previous instruction has finished, which is possible because the cycle is broken up into separate steps. Role of components Program counter The program counter (PC) is a register that holds the memory address of the next instruction to be executed. After each instruction copy to the memory address register (MAR), the PC can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, CPU design, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic operation, arithmetic and Bitwise operation, logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the #Fetch, fetching (from memory), #Decode, decoding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrupt
In digital computers, an interrupt (sometimes referred to as a trap) is a request for the processor to ''interrupt'' currently executing code (when permitted), so that the event can be processed in a timely manner. If the request is accepted, the processor will suspend its current activities, save its state, and execute a function called an '' interrupt handler'' (or an ''interrupt service routine'', ISR) to deal with the event. This interruption is often temporary, allowing the software to resume normal activities after the interrupt handler finishes, although the interrupt could instead indicate a fatal error. Interrupts are commonly used by hardware devices to indicate electronic or physical state changes that require time-sensitive attention. Interrupts are also commonly used to implement computer multitasking and system calls, especially in real-time computing. Systems that use interrupts in these ways are said to be interrupt-driven. History Hardware interrupts wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycles Per Instruction
In computer architecture, cycles per instruction (aka clock cycles per instruction, clocks per instruction, or CPI) is one aspect of a processor's performance: the average number of clock cycles per instruction for a program or program fragment. It is the multiplicative inverse of instructions per cycle. Definition The average of Cycles Per Instruction in a given process () is defined by the following weighted average: : \mathrm := \frac = \frac Where \mathrm_i is the number of instructions for a given instruction type i, \mathrm_i is the clock-cycles for that instruction type and \mathrm=\Sigma_i(\mathrm_i) is the total instruction count. The summation sums over all instruction types for a given benchmarking process. Explanation Let us assume a classic RISC pipeline, with the following five stages: # Instruction fetch cycle (IF). # Instruction decode/Register fetch cycle (ID). # Execution/Effective address cycle (EX). # Memory access (MEM). # Write-back cycle (WB). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Instruction Set Computer
A complex instruction set computer (CISC ) is a computer architecture in which single instructions can execute several low-level operations (such as a load from memory, an arithmetic operation, and a memory store) or are capable of multi-step operations or addressing modes within single instructions. The term was retroactively coined in contrast to reduced instruction set computer (RISC) and has therefore become something of an umbrella term for everything that is not RISC, where the typical differentiating characteristic is that most RISC designs use uniform instruction length for almost all instructions, and employ strictly separate load and store instructions. Examples of CISC architectures include complex mainframe computers to simplistic microcontrollers where memory load and store operations are not separated from arithmetic instructions. Specific instruction set architectures that have been retroactively labeled CISC are System/360 through z/Architecture, the PDP-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic RISC Pipeline
In the history of computing hardware, history of computer hardware, some early reduced instruction set computer central processing units (RISC CPUs) used a very similar architectural solution, now called a classic RISC pipeline. Those CPUs were: MIPS architecture, MIPS, SPARC, Motorola Motorola 88000, 88000, and later the notional CPU DLX invented for education. Each of these classic scalar RISC designs fetches and tries to execute one Instructions per cycle, instruction per cycle. The main common concept of each design is a five-stage execution instruction pipeline. During operation, each pipeline stage works on one instruction at a time. Each of these stages consists of a set of flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops to hold state, and combinational logic that operates on the outputs of those flip-flops. The classic five stage RISC pipeline Instruction fetch The instructions reside in memory that takes one cycle to read. This memory can be dedicated to SRAM, or an Instructi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Slice
In computing, preemption is the act performed by an external scheduler — without assistance or cooperation from the task — of temporarily interrupting an executing task, with the intention of resuming it at a later time. This preemptive scheduler usually runs in the most privileged protection ring, meaning that interruption and then resumption are considered highly secure actions. Such changes to the currently executing task of a processor are known as context switching. User mode and kernel mode In any given system design, some operations performed by the system may not be preemptable. This usually applies to kernel functions and service interrupts which, if not permitted to run to completion, would tend to produce race conditions resulting in deadlock. Barring the scheduler from preempting tasks while they are processing kernel functions simplifies the kernel design at the expense of system responsiveness. The distinction between user mode and kernel mode, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stack (abstract Data Type)
In computer science, a stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection (abstract data type), collection of elements with two main operations: * Push, which adds an element to the collection, and * Pop, which removes the most recently added element. Additionally, a peek (data type operation), peek operation can, without modifying the stack, return the value of the last element added. The name ''stack'' is an analogy to a set of physical items stacked one atop another, such as a stack of plates. The order in which an element added to or removed from a stack is described as last in, first out, referred to by the acronym LIFO. As with a stack of physical objects, this structure makes it easy to take an item off the top of the stack, but accessing a Data, datum deeper in the stack may require removing multiple other items first. Considered a sequential collection, a stack has one end which is the only position at which the push and pop operations may occur, the ''top'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addressing Mode
Addressing modes are an aspect of the instruction set architecture in most central processing unit (CPU) designs. The various addressing modes that are defined in a given instruction set architecture define how the machine language instructions in that architecture identify the operand(s) of each instruction. An addressing mode specifies how to calculate the effective memory address of an operand by using information held in registers and/or constants contained within a machine instruction or elsewhere. In computer programming, addressing modes are primarily of interest to those who write in assembly languages and to compiler writers. For a related concept see orthogonal instruction set which deals with the ability of any instruction to use any addressing mode. Caveats There are no generally accepted names for addressing modes: different authors and computer manufacturers may give different names to the same addressing mode, or the same names to different addressing modes. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Decoder
In digital electronics, a binary decoder is a combinational logic circuit that converts binary information from the n coded inputs to a maximum of 2n unique outputs. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including instruction decoding, data multiplexing and data demultiplexing, seven segment displays, and as address decoders for memory and port-mapped I/O. There are several types of binary decoders, but in all cases a decoder is an electronic circuit with multiple input and multiple output signals, which converts every unique combination of input states to a specific combination of output states. In addition to integer data inputs, some decoders also have one or more "enable" inputs. When the enable input is negated (disabled), all decoder outputs are forced to their inactive states. Depending on its function, a binary decoder will convert binary information from n input signals to as many as 2n unique output signals. Some decoders have less than 2n output lines; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus (computing)
In computer architecture, a bus (historically also called a data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers Data (computing), data between components inside a computer or between computers. It encompasses both Computer hardware, hardware (e.g., wires, optical fiber) and software, including communication protocols. At its core, a bus is a shared physical pathway, typically composed of wires, traces on a circuit board, or busbars, that allows multiple devices to communicate. To prevent conflicts and ensure orderly data exchange, buses rely on a communication protocol to manage which device can transmit data at a given time. Buses are categorized based on their role, such as system buses (also known as internal buses, internal data buses, or memory buses) connecting the Central processing unit, CPU and Computer memory, memory. Expansion buses, also called peripheral buses, extend the system to connect additional devices, including peripherals. Examples of widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Bus
In computer architecture, a control bus is part of the system bus and is used by central processing unit, CPUs for communicating with other devices within the computer. While the address bus carries the information about the device with which the CPU is communicating and the Bus (computing), data bus carries the actual data being processed, the control bus carries commands from the CPU and returns status signals from the devices. For example, if the data is being read or written to the device the appropriate line (read or write) will be active (logic one). Lines The number and type of lines in a control bus varies but there are basic lines common to all microprocessors, such as: * Read (\overline ). A single line that when active (logic zero) indicates the device is being read by the CPU. * Write (\overline ). A single line that when active (logic zero) indicates the device is being written by the CPU. * Byte enable (\overline E). A group of lines that indicate the size of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, peripherals, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computerfrom cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. , Android (operating system), Android is the most popular operating system with a 46% market share, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |