|
Probiotics In Pediatrics
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut flora. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria- host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is little evidence that probiotics bring the health benefits claimed for them. Health effects Diarrhea As many prevention methods for diarrhea have adverse effects (e.g. intestinal intussusception in the usage of rotavirus vaccine), scientists are now turning to probiotics in hope of using it as a supplement to treat acute diarrhea. In a review that covered 34 masked, randomized, placebo-controlled trials related to diarrhea and probiotics, it was concluded that there was an overall reduction of 52% in antibiotic associated diarrhea, an 8% reduction in traveller’s diarrhea, and a 34% reduction in other types of acute diarrhea. These numbers reflect a protective effect against diarr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is some evidence that probiotics are beneficial for some conditions, but there is little evidence for many of the health benefits claimed for them. The first discovered probiotic was a certain strain of bacillus in Bulgarian yoghurt, called ''Lactobacillus bulgaricus''. The discovery was made in 1905 by Bulgarian physician and microbiologist Stamen Grigorov. The modern-day theory is generally attributed to Russian Nobel laureate Élie Metchnikoff, who postulated around 1907 that yoghurt-consuming Bulgarian peasants lived longer. A growing probiotics market has led to the need for stricter requirements for scientific substantiation of putative benefits conferred by microorganisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic-associated Diarrhea
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) results from an imbalance in the colonic microbiota caused by antibiotics. Microbiotal alteration changes carbohydrate metabolism with decreased short-chain fatty acid absorption and an osmotic diarrhea as a result. Another consequence of antibiotic therapy leading to diarrhea is overgrowth of potentially pathogenic organisms such as '' Clostridium difficile''. It is defined as frequent loose and watery stools with no other complications. __TOC__ Cause ''Clostridium difficile'', also known more commonly as ''C. diff'', accounts for 10 to 20% of antibiotic-associated diarrhea cases, because the antibiotics administered for the treatment of certain disease processes such as inflammatory colitis also inadvertently kill a large portion of the gut flora, the normal flora that is usually present within the bowel. With this lower level of "healthy" bacteria present, the overgrowth of ''C. diff'' is then responsible "for elaborating the enterotoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and symptoms include fever, increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, and confusion. There may also be symptoms related to a specific infection, such as a cough with pneumonia, or painful urination with a kidney infection. The very young, old, and people with a weakened immune system may have no symptoms of a specific infection, and the body temperature may be low or normal instead of having a fever. Severe sepsis causes poor organ function or blood flow. The presence of low blood pressure, high blood lactate, or low urine output may suggest poor blood flow. Septic shock is low blood pressure due to sepsis that does not improve after fluid replacement. Sepsis is caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungemia
Fungemia is the presence of fungi or yeasts in the blood. The most common type, also known as candidemia, candedemia, or systemic candidiasis, is caused by '' Candida'' species; candidemia is also among the most common bloodstream infections of any kind. Infections by other fungi, including '' Saccharomyces'', '' Aspergillus'' and '' Cryptococcus'', are also called fungemia. It is most commonly seen in immunosuppressed or immunocompromised patients with severe neutropenia, cancer patients, or in patients with intravenous catheters. It has been suggested the otherwise immunocompetent patients taking infliximab may be at a higher risk for fungemia. Diagnosis is difficult, as routine blood cultures have poor sensitivity. Signs and symptoms Symptoms can range from mild to extreme—often described as extreme flu-like symptoms. Many symptoms may be associated with fungemia, including pain, acute confusion, chronic fatigue, and infections. Skin infections can include p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteremia
Bloodstream infections (BSIs), which include bacteremias when the infections are bacterial and fungemias when the infections are fungal, are infections present in the blood. Blood is normally a sterile environment, so the detection of microbes in the blood (most commonly accomplished by blood cultures) is always abnormal. A bloodstream infection is different from sepsis, which is the host response to bacteria. Bacteria can enter the bloodstream as a severe complication of infections (like pneumonia or meningitis), during surgery (especially when involving mucous membranes such as the gastrointestinal tract), or due to catheters and other foreign bodies entering the arteries or veins (including during intravenous drug abuse). Transient bacteremia can result after dental procedures or brushing of teeth. Bacteremia can have several important health consequences. The immune response to the bacteria can cause sepsis and septic shock, which has a high mortality rate. Bacteria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The term low and middle-income country (LMIC) is often used interchangeably but refers only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high, upper-middle, lower-middle, and low income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over this term's use, which some feel it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and "them". In 2015, the World Bank declared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucins
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins ( glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most gel-like secretions, serving functions from lubrication to cell signalling to forming chemical barriers. They often take an inhibitory role. Some mucins are associated with controlling mineralization, including nacre formation in mollusks, calcification in echinoderms and bone formation in vertebrates. They bind to pathogens as part of the immune system. Overexpression of the mucin proteins, especially MUC1, is associated with many types of cancer. Although some mucins are membrane-bound due to the presence of a hydrophobic membrane-spanning domain that favors retention in the plasma membrane, most mucins are secreted as principal components of mucus by mucous membranes or are secreted to become a component of saliva. Genes Human m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
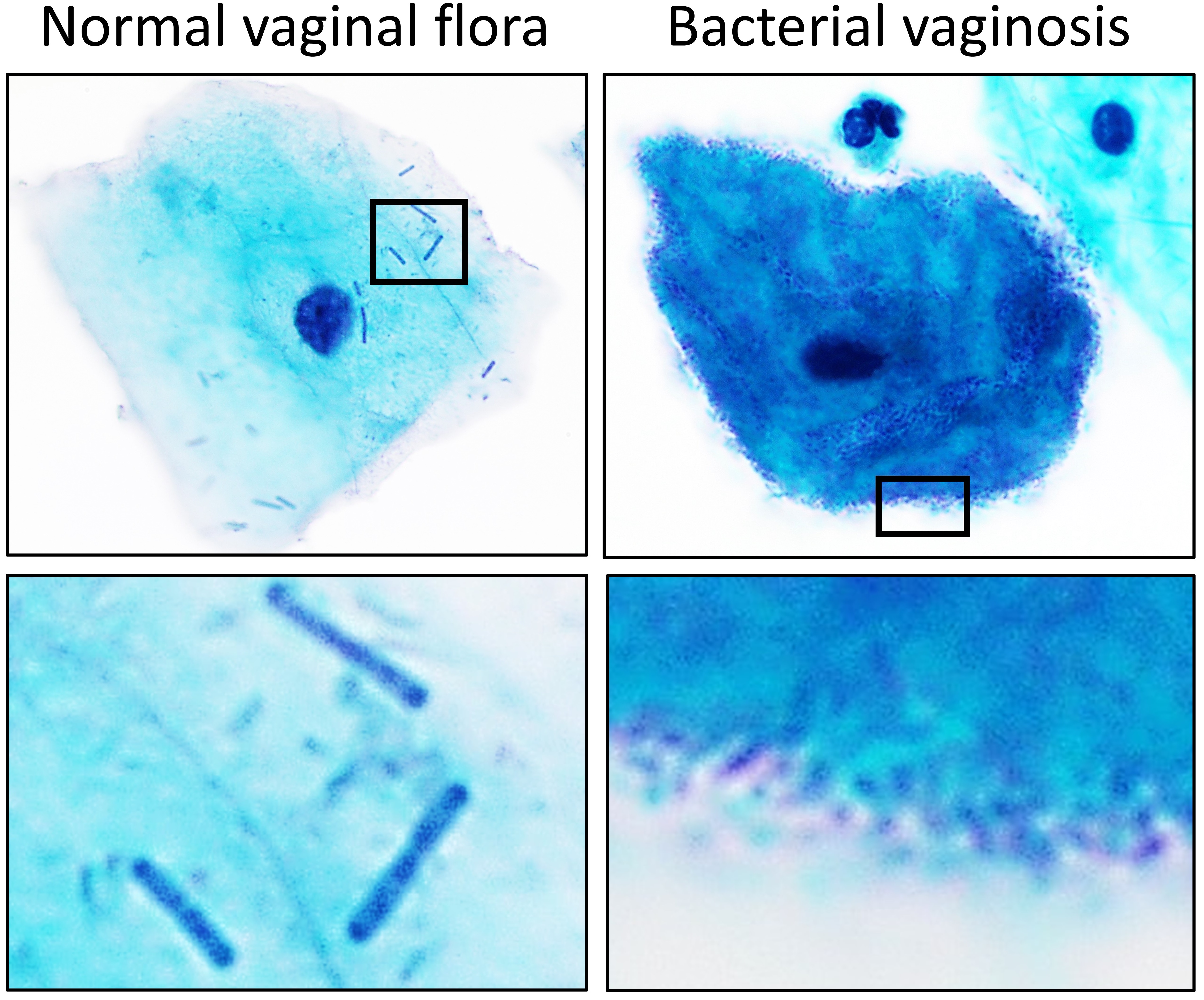
Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotavirus !
''Rotavirus'' is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family ''Reoviridae''. Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus at least once by the age of five. Immunity develops with each infection, so subsequent infections are less severe. Adults are rarely affected. There are nine species of the genus, referred to as A, B, C, D, F, G, H, I and J. ''Rotavirus A'', the most common species, causes more than 90% of rotavirus infections in humans. The virus is transmitted by the faecal-oral route. It infects and damages the cells that line the small intestine and causes gastroenteritis (which is often called "stomach flu" despite having no relation to influenza). Although rotavirus was discovered in 1973 by Ruth Bishop and her colleagues by electron micrograph images and accounts for approximately one third of hospitalisations for severe diarrhoea in infants and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
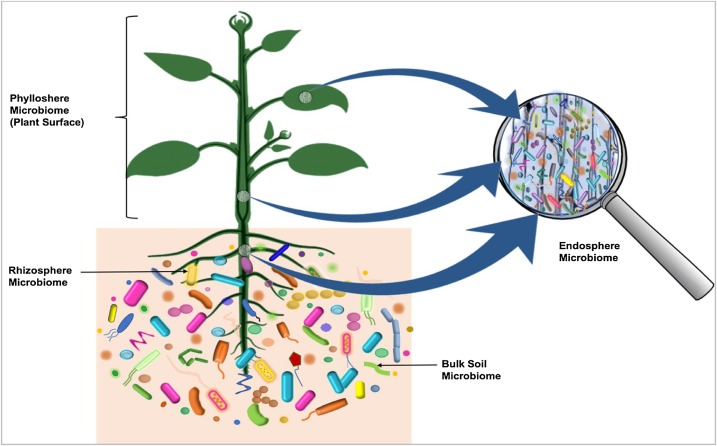
Microflora
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term '' microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or within the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product ( short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. Deep waters of the ocean are a common anoxic environment. First observation In his letter of 14 June 1680 to The Royal Society, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described an experiment he carried out by filling two identical glass tubes about halfway with crushed pepper powder, to which some clean rain water was added. Van Leeuwenhoek sealed one of the glass tubes using a flam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |