|
Probabilistic Soft Logic
Probabilistic Soft Logic (PSL) is a statistical relational learning (SRL) framework for modeling probabilistic and relational domains. It is applicable to a variety of machine learning problems, such as collective classification, entity resolution, link prediction, and ontology alignment. PSL combines two tools: first-order logic, with its ability to succinctly represent complex phenomena, and probabilistic graphical models, which capture the uncertainty and incompleteness inherent in real-world knowledge. More specifically, PSL uses "soft" logic as its logical component and Markov random fields as its statistical model. PSL provides sophisticated inference techniques for finding the most likely answer (i.e. the maximum a posteriori (MAP) state). The "softening" of the logical formulas makes inference a polynomial time operation rather than an NP-hard operation. Description The SRL community has introduced multiple approaches that combine graphical models and fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a High-level programming language, high-level, General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, Memory safety, memory-safe, object-oriented programming, object-oriented programming language. It is intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' (Write once, run anywhere, WORA), meaning that compiler, compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to Java bytecode, bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax (programming languages), syntax of Java is similar to C (programming language), C and C++, but has fewer low-level programming language, low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as Reflective programming, reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. Java gained popularity sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum A Posteriori Estimation
An estimation procedure that is often claimed to be part of Bayesian statistics is the maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimate of an unknown quantity, that equals the mode of the posterior density with respect to some reference measure, typically the Lebesgue measure. The MAP can be used to obtain a point estimate of an unobserved quantity on the basis of empirical data. It is closely related to the method of maximum likelihood (ML) estimation, but employs an augmented optimization objective which incorporates a prior density over the quantity one wants to estimate. MAP estimation is therefore a regularization of maximum likelihood estimation, so is not a well-defined statistic of the Bayesian posterior distribution. Description Assume that we want to estimate an unobserved population parameter \theta on the basis of observations x. Let f be the sampling distribution of x, so that f(x\mid\theta) is the probability of x when the underlying population parameter is \theta. Then t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
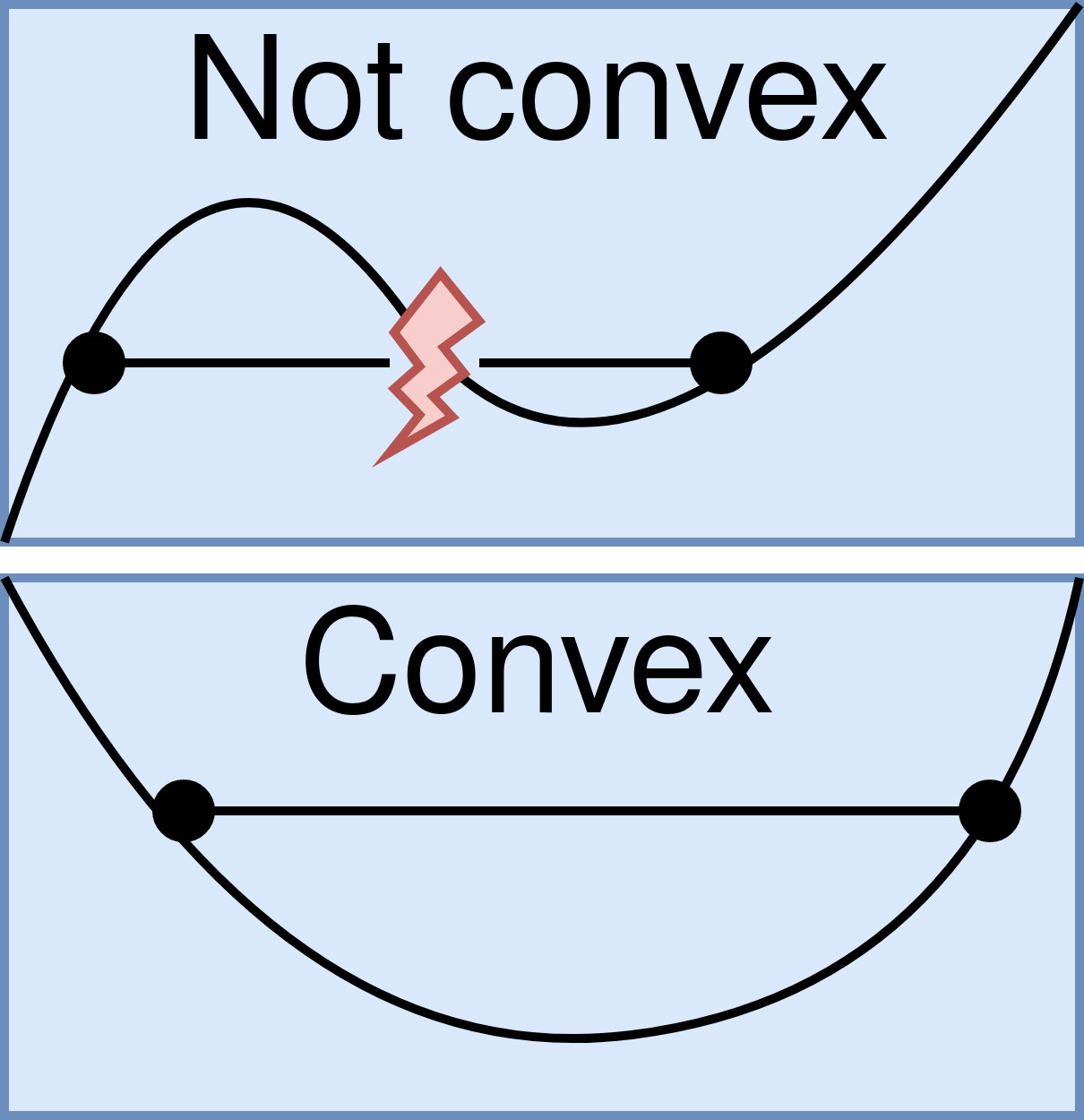
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two distinct points on the graph of the function lies above or on the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its ''epigraph'' (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. In simple terms, a convex function graph is shaped like a cup \cup (or a straight line like a linear function), while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include a linear function f(x) = cx (where c is a real number), a quadratic function cx^2 (c as a nonnegative real number) and an exponential function ce^x (c as a nonnegative real number). Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Combination
In mathematics, a linear combination or superposition is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results (e.g. a linear combination of ''x'' and ''y'' would be any expression of the form ''ax'' + ''by'', where ''a'' and ''b'' are constants). The concept of linear combinations is central to linear algebra and related fields of mathematics. Most of this article deals with linear combinations in the context of a vector space over a field, with some generalizations given at the end of the article. Definition Let ''V'' be a vector space over the field ''K''. As usual, we call elements of ''V'' ''vectors'' and call elements of ''K'' ''scalars''. If v1,...,v''n'' are vectors and ''a''1,...,''a''''n'' are scalars, then the ''linear combination of those vectors with those scalars as coefficients'' is :a_1 \mathbf v_1 + a_2 \mathbf v_2 + a_3 \mathbf v_3 + \cdots + a_n \mathbf v_n. There is some ambiguity in the use of the term "lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-order Logic
First-order logic, also called predicate logic, predicate calculus, or quantificational logic, is a collection of formal systems used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. First-order logic uses quantified variables over non-logical objects, and allows the use of sentences that contain variables. Rather than propositions such as "all humans are mortal", in first-order logic one can have expressions in the form "for all ''x'', if ''x'' is a human, then ''x'' is mortal", where "for all ''x"'' is a quantifier, ''x'' is a variable, and "... ''is a human''" and "... ''is mortal''" are predicates. This distinguishes it from propositional logic, which does not use quantifiers or relations; in this sense, propositional logic is the foundation of first-order logic. A theory about a topic, such as set theory, a theory for groups,A. Tarski, ''Undecidable Theories'' (1953), p. 77. Studies in Logic and the Foundation of Mathematics, North-Holland or a formal theory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command-line Interface
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternative to the non-interactive mode available with punched cards. For a long time, a CLI was the most common interface for software, but today a graphical user interface (GUI) is more common. Nonetheless, many programs such as operating system and software development utility software, utilities still provide CLI. A CLI enables automation, automating computer program, programs since commands can be stored in a scripting language, script computer file, file that can be used repeatedly. A script allows its contained commands to be executed as group; as a program; as a command. A CLI is made possible by command-line interpreters or command-line processors, which are programs that execute input commands. Alternatives to a CLI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Machine Learning Research
The ''Journal of Machine Learning Research'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering machine learning. It was established in 2000 and the first editor-in-chief was Leslie Kaelbling. The current editors-in-chief are Francis Bach (Inria) and David Blei (Columbia University). History The journal was established as an open-access alternative to the journal ''Machine Learning''. In 2001, forty editorial board members of ''Machine Learning'' resigned, saying that in the era of the Internet, it was detrimental for researchers to continue publishing their papers in expensive journals with pay-access archives. The open access model employed by the ''Journal of Machine Learning Research'' allows authors to publish articles for free and retain copyright, while archives are freely available online. Print editions of the journal were published by MIT Press until 2004 and by Microtome Publishing thereafter. From its inception, the journal received no revenue from the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lise Getoor
Lise Getoor is an American computer scientist who is a distinguished professor and Baskin Endowed chair in the Computer Science and Engineering department, at the University of California, Santa Cruz, and an adjunct professor in the Computer Science Department at the University of Maryland, College Park. Her primary research interests are in machine learning and reasoning with uncertainty, applied to graphs and structured data. She also works in data integration, social network analysis and visual analytics. She has edited a book on Statistical relational learning that is a main reference in this domain. She has published many highly cited papers in academic journals and conference proceedings. She has also served as action editor for the Machine Learning Journal, JAIR associate editor, and TKDD associate editor. She received her Ph.D. from Stanford University, her M.S. from UC Berkeley, and her B.S. from UC Santa Barbara. Prior to joining University of California, Santa Cruz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record Linkage
Record linkage (also known as data matching, data linkage, entity resolution, and many other terms) is the task of finding records in a data set that refer to the same entity across different data sources (e.g., data files, books, websites, and databases). Record linkage is necessary when joining different data sets based on entities that may or may not share a common identifier (e.g., database key, URI, National identification number), which may be due to differences in record shape, storage location, or curator style or preference. A data set that has undergone RL-oriented reconciliation may be referred to as being ''cross-linked''. Naming conventions "Record linkage" is the term used by statisticians, epidemiologists, and historians, among others, to describe the process of joining records from one data source with another that describe the same entity. However, many other terms are used for this process. Unfortunately, this profusion of terminology has led to few cross- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Network
A social network is a social structure consisting of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), networks of Dyad (sociology), dyadic ties, and other Social relation, social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities along with a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine dynamics of networks. For instance, social network analysis has been used in studying the spread of misinformation on social media platforms or analyzing the influence of key figures in social networks. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markov Logic Network
A Markov logic network (MLN) is a probabilistic logic which applies the ideas of a Markov network to first-order logic, defining probability distributions on possible worlds on any given domain. History In 2002, Ben Taskar, Pieter Abbeel and Daphne Koller introduced relational Markov networks as templates to specify Markov networks abstractly and without reference to a specific domain. Work on Markov logic networks began in 2003 by Pedro Domingos and Matt Richardson. Markov logic networks is a popular formalism for statistical relational learning. Syntax A Markov logic network consists of a collection of formulas from first-order logic, to each of which is assigned a real number, the weight. The underlying idea is that an interpretation is more likely if it satisfies formulas with positive weights and less likely if it satisfies formulas with negative weights. For instance, the following Markov logic network codifies how smokers are more likely to be friends with other sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |