|
Principality Of Anhalt
The Principality of Anhalt () was a Imperial State, State of the Holy Roman Empire, located in Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany, in what is today part of the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt. Under the rule of the House of Ascania, the Anhalt territory was split off the German stem duchy of Duchy of Saxony, Saxony in 1212 and granted to Count Henry I, Count of Anhalt, Henry I, who was raised to the rank of a Princes of the Holy Roman Empire, Prince of the Holy Roman Empire in 1218. Ruled by Ascanian princes from the High Middle Ages to the Early modern period, Anhalt was divided several times amongst various lines of the dynasty until the dissolution of the Empire in 1806, when Napoleon elevated the remaining states of Anhalt-Bernburg, Anhalt-Dessau and Anhalt-Köthen to duchies. Geography The Anhalt territory stretched from the Harz mountain range in the west to the Elbe River and beyond to the Fläming Heath in the east. Upon the 1315 loss of Principality of An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial State
An Imperial Estate (; , plural: ') was an entity or an individual of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise significant rights and privileges and were "Imperial immediacy, immediate", meaning the only authority above them was that of the Holy Roman Emperor. They were thus able to rule their territories with a considerable degree of autonomy. The system of imperial states replaced the more regular division of Germany into stem duchy, stem duchies in the early medieval period. The old Carolingian Empire, Carolingian stem duchies were retained as the major divisions of Germany under the Salian dynasty, but they became increasingly obsolete during the early high medieval era, period under the Hohenstaufen, and they were finally abolished in 1180 by Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick Barbarossa in favour of more numerous territorial divisions. Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
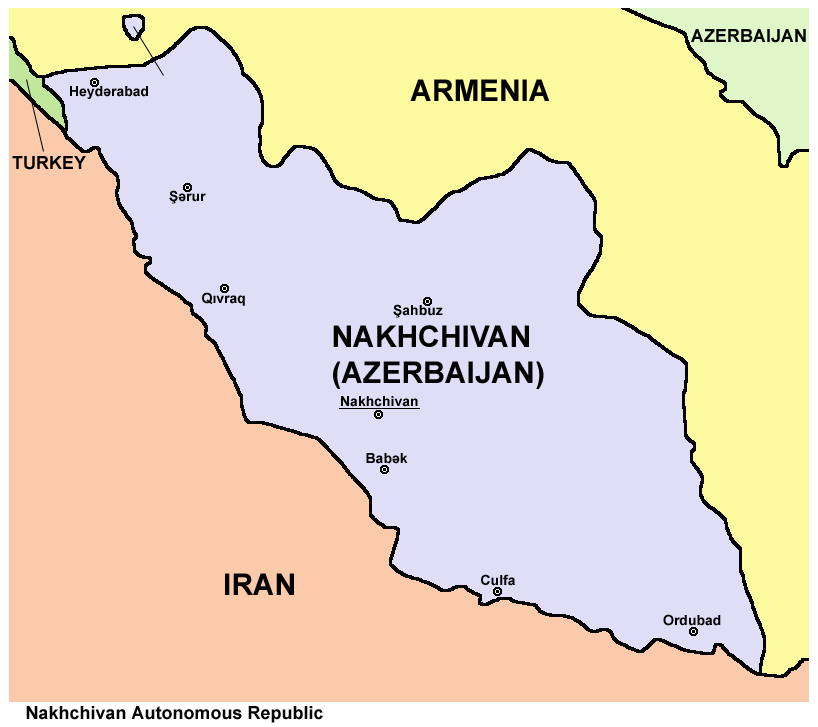
Enclave And Exclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to denote a territory that is only partly surrounded by another state. Enclaves that are not part of a larger territory are not exclaves, for example Lesotho (enclaved by South Africa), and San Marino and Vatican City (both enclaved by Italy) are enclaved sovereign states. An exclave is a portion of a state or district geographically separated from the main part, by some surrounding alien territory. Many exclaves are also enclaves, but an exclave surrounded by the territory of more than one state is not an enclave. The Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan is an example of an exclave that is not an enclave, as it borders Armenia, Iran, and Turkey. Semi-enclaves and semi-exclaves are areas that, except for possessing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Anhalt-Aschersleben
Anhalt-Aschersleben was a short-lived principality of the Holy Roman Empire ruled by the House of Ascania with its residence at Aschersleben in present-day Saxony-Anhalt. It emerged as a subdivision from the Principality of Anhalt from 1252 to 1315. History It was created when the Anhalt territory was divided among the sons of Prince Henry I into the Principalities of Anhalt-Aschersleben, Anhalt-Bernburg and Anhalt-Zerbst in 1252. Prince Henry II the Fat, the eldest son of Henry I, had been co-ruler of his father since 1244. In the course of the partition he chose the Anhalt ancestral homeland north of the Harz mountain range around the Ascanian residence of Aschersleben ''(Ascharia)'', which he granted town privileges in 1266. When in 1315 Henry's grandson Otto II died without male heirs, the principality — including the capital of Aschersleben — was seized as a fief by his cousin and creditor Bishop Albert of Halberstadt. Though Prince Bernhard II of Anhalt-Bernburg one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fläming Heath
The Fläming Heath () is a region and hill chain that reaches over 100 km from the Elbe river to the Dahme River in the German states Saxony-Anhalt and Brandenburg. Its highest elevation is the Hagelberg (201 m). The name Fläming originates from the 12th century, when Flemish colonists came to settle in the region from the overcrowded cities of Flanders. The Fläming Heath is a rural area, which benefits from its proximity to the Berlin metropolitan area. Tourism became an important economic sector. With its three nature parks ( High Fläming Nature Park, Fläming Nature Park, and Nuthe-Nieplitz Nature Park), the focus is on walking, cycling and recreation in nature. Another tourist attraction is Flaeming-Skate, which is one of the longest inline-skating tracks in Europe (190 km). The towns Ziesar, Bad Belzig, Niemegk, Treuenbrietzen, Jüterbog, Baruth/Mark, Dahme/Mark, Wittenberg, Loburg, Möckern, and Zerbst Zerbst () is a List of cities and towns in Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, northwest of Hamburg. Its total length is . The Elbe's major Tributary, tributaries include the rivers Vltava, Ohře, Saale, Havel, Mulde, and Schwarze Elster. The Elbe river basin, comprising the Elbe and its tributaries, has a catchment area of , the twelfth largest in Europe. The basin spans four countries; however, it lies almost entirely just in two of them, Germany (65.5%) and the Czech Republic (33.7%, covering about two thirds of the nation's territory). On its southeastern edges, the Elbe river basin also comprises small parts of Austria (0.6%) and Poland (0.2%). The Elbe catchment area is inhabited by 24.4 million people; its biggest cities are Berlin, Hamburg, Prague, Dresden a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harz
The Harz (), also called the Harz Mountains, is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German word ''Hardt'' or ''Hart'' (hill forest). The name ''Hercynia'' derives from a Celtic name and could refer to other mountain forests, but has also been applied to the geology of the Harz. The Brocken is the highest summit in the Harz with an elevation of above sea level. The Wurmberg () is the highest peak located entirely within the state of Lower Saxony. Geography Location and extent The Harz has a length of , stretching from the town of Seesen in the northwest to Eisleben in the east, and a width of . It occupies an area of , and is divided into the Upper Harz (''Oberharz'') in the northwest, which is up to 800 m high, apart from the 1,100 m high Brocken massif, and the Lower Harz (''Unterhar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon, a series of military campaigns across Europe during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars from 1796 to 1815. He led the French First Republic, French Republic as French Consulate, First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then ruled the First French Empire, French Empire as Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814, and briefly again in 1815. He was King of Italy, King of Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Italy from 1805 to 1814 and Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine, Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine from 1806 to 1813. Born on the island of Corsica to a family of Italian origin, Napoleon moved to mainland France in 1779 and was commissioned as an officer in the French Royal Army in 1785. He supported the French Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date that marks the beginning or end of the period and its extent may vary depending on the area of history being studied. In general, the early modern period is considered to have lasted from around the start of the 16th century to the start of the 19th century (about 1500–1800). In a European context, it is defined as the period following the Middle Ages and preceding the advent of modernity; but the dates of these boundaries are far from universally agreed. In the context of World history (field), global history, the early modern period is often used even in contexts where there is no equivalent "medieval" period. Various events and historical transitions have been proposed as the start of the early modern period, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention. Key historical trends of the High Middle Ages include the medieval demography, rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, and the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1350, the robust population increase had greatly benefited the European economy, which had reached levels that would not be seen again in some areas until the 19th century. That trend faltered in the early 14th century, as the result of numerous events which together comprised the crisis of the late Middle Ages—most notable among them being the Black Death, in addition to various regional wars and economic stagnation. From , Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Duchy
A stem duchy (, from '':wikt:Stamm, Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Baiuvarii, Bavarians and Alemanni, Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the Kingdom of Germany at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dynasty (death of Louis the Child in 911) and through the transitional period leading to the formation of the Ottonian dynasty. The Carolingians had dissolved the original tribal duchies of the Francia, Empire in the 8th century. As the Carolingian Empire declined, the old tribal areas assumed new identities. The five stem duchies (sometimes also called "younger stem duchies" in contrast to the pre-Carolingian tribal duchies) were duchy of Bavaria, Bavaria, duchy of Franconia, Franconia, duchy of Lotharingia, Lotharingia (Lorraine), duchy of Saxony, Saxony and duchy of Swabia, Swabia (Alemannia).See Donald C. Jackman, ''The Konradiner: A Study in Genealogical Methodology'', 1990p. 87 citing Hans-Werner Guetz, ''"Dux" und "Ducatus." Begriffs- un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Ascania
The House of Ascania () was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Principality of Anhalt, Anhalt. The Ascanians are named after Ascania (or Ascaria) Castle, known as ''Schloss Askanien'' in German, which was located near and named after Aschersleben. The castle was the seat of the County of Ascania, a title that was later subsumed into the titles of the princes of Anhalt. History File:Schloss Ballenstedt, Hofseite.JPG, Ballenstedt Castle File:Arms of the house of Ascania (ancient).svg, First coat of arms of the family Map of Anhalt (1747-1793).svg, Map of Anhalt (1747–1793) The earliest known member of the house, Esiko, Count of Ballenstedt, first appears in a document of 1036. Genealogists assume him to have been a grandson (through his mother) of Odo I, Margrave of the Saxon Ostmark (). From Odo, the Ascanians inherited large properties in the Saxon Eastern March. Esiko's grandson Otto, Count of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |