|
Princess Yaropolkovna Of Minsk
Princess Yaropolkovna of Minsk (1074 – 3 January 1158) was the daughter of prince Yaropolk Iziaslavich of Volhynia and Kunigunde von Orlamünde; the princess-consort of Gleb Vseslavich of Minsk ( 1090–1118); and, according to some scholarly interpretations, princess regnant of Minsk for about 40 years after her husband's death ( 1119–1158). According to one single unreliable source from the late 17th century, the ''Kievan Synopsis'' by Innokentii Gizel', her first name or Christian name was "Anastasia"; therefore, some earlier historians have called her "Anastasia Yaropolkovna", or "Anastasia of Minsk". Many modern historians no longer accept that as her probable first or Christian name, and instead call her "Gleb of Minsk's widow", "the Widow Princess of Minsk", or "unknown Yaropolkovna". Biography Encomium The sources mention this woman only once directly – in the ''Kievan Chronicle'', on the occasion of her death at age 84, ''sub anno'' 1158, where she is descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Of Anastasia,wife Of Gleb Vseslavich Of Minsk; Kunigunde Of Meissen, Mother Of Anastasia
Death is the end of life; the Irreversible process, irreversible cessation of all biological process, biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to Decomposition, decompose shortly after death. Some organisms, such as ''Turritopsis dohrnii'', are Biological immortality, biologically immortal; however, they can still die from means other than Senescence, aging. Death is generally applied to whole organisms; the equivalent for individual components of an organism, such as Cell (biology), cells or Tissue (biology), tissues, is necrosis. Something that is not considered an organism, such as a virus, can be physically destroyed but is not said ''to die'', as a virus is not considered alive in the first place. As of the early 21st century, 56 million people die per year. The most common reason is aging, followed by cardiovascular disease, which is a disease that af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vseslav Of Polotsk
Vseslav Bryachislavich ( 1029 – 24 April 1101; also known as ''Vseslav the Sorcerer'' or ''Vseslav the Seer'') was Prince of Polotsk (1044–1101) and Grand Prince of Kiev (1068–1069). Together with Rostislav Vladimirovich and voivode Vyshata, he created a coalition against the Yaroslaviches' triumvirate. Polotsk's Cathedral of Holy Wisdom, completed in the mid-11th century, is one of the most enduring monuments from his reign and the oldest stone building in Belarus. Biography Vseslav was the son of Bryachislav Izyaslavich, Prince of Polotsk and Vitebsk, and was thus the great-grandson of Vladimir I of Kiev and Rogneda of Polotsk. He was born in c. 1029–1030 in Polotsk (with Vasilii as his baptismal name) and married around 1060. He took the throne of Polotsk in 1044 upon his father's death, and although since 1093 he was the senior member of the Rurik dynasty for his generation, since his father had not been prince in Kiev, Vseslav was excluded ( izgoi) from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mstislav I Of Kiev
Mstislav I Vladimirovich Monomakh (; Christian name: ''Fedor''; February 1076 – 14 April 1132), also known as Mstislav the Great, was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1125 until his death in 1132. After his death, the state began to quickly disintegrate into rival principalities. He was the eldest son of Vladimir II Monomakh by Gytha of Wessex. He is figured prominently in the Norse Sagas under the name Harald, to allude to his grandfather, Harold II of England. Biography Mstislav was born in Turov. As his father's future successor, he reigned in Novgorod from 1088 to 1093 and (after a brief stint at Rostov) from 1095 to 1117. Thereafter, he was Monomakh's co-ruler in Belgorod Kievsky, and inherited the Kievan throne after his death. He built numerous churches in Novgorod, of which St. Nicholas Cathedral (1113), and the cathedral of St Anthony Cloister (1117) survive to the present day. Later, he would also erect important churches in Kiev, notably his family sepulchre at B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir II Monomakh
Vladimir II Monomakh (; Christian name: ''Vasily''; 26 May 1053 – 19 May 1125) was Grand Prince of Kiev from 1113 to 1125. He is considered a saint in the Eastern Orthodox Church and is celebrated on May 6 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics), May 6. Family background His father was Vsevolod I of Kiev, Vsevolod Yaroslavich, born 1030 as the fifth son of grand prince of Kiev Yaroslav the Wise (); he himself would go on to reign as grand prince Vsevolod I of Kiev from 1078 to 1093. In 1046, to seal an armistice in the Rus'–Byzantine War (1043) , Rus'–Byzantine War, Vsevolod Yaroslavich, then a junior member of the princely Rurikids of Kievan Rus', contracted a diplomatic marriage with a relative of the reigning Byzantine emperor Constantine IX Monomachos (), from whom Vladimir (born in 1053) likely inherited his sobriquet, ''Monomakh''. The name and ancestry of his mother are unknown; Byzantine sources do not mention the marriage at all, and the ''Primary Chronicle'' only says ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Izyaslavl
The Principality of Izyaslavl or Zaslawye () was a minor district of the former Principality of Polotsk, which it had split from in the 12th century. It split along with Polotsk, Minsk, Vitebsk, Drutsk and Logozhsk. These fragmented territories were ruled by Vseslav of Polotsk's many sons and grandsons. Later, there would be a failed attempt to unite the territory. See also * List of early East Slavic states The following is a list of tribes which dwelled and states which existed on the territories of contemporary Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine. Overview Clan cultures of the Stone Age and Bronze Age, up to the Late Antiquity period of the tribal soc ... References Former duchies Principalities of Kievan Rus' Former principalities {{Belarus-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lukoml
Lukoml (, ) is an agrotown in Chashniki District, Vitebsk Region, Belarus. It is situated by Lake Lukoml and serves as the administrative center of Lukoml selsoviet. History Early references to Lukoml in Russian chronicles are dated by 1078, when it was burned by Vladimir Monomakh. In 15-16th centuries it constituted a separate principality. In 1563, it was burned down by Russians. In the pre-1917 Russian Empire, it was a ''shtetl'' of about 1,000 inhabitants with one Orthodox church, one Catholic church, two synagogues, one school and 8 shops. There are remnants of ancient fortification A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Lati ...s by the village. Sources * {{coord, 54, 43, N, 29, 09, E, source:kolossus-plwiki, display=title Populated places in Vitebsk region Chas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Vitebsk
The Principality of Vitebsk () was a Ruthenian principality centered on the city of Vitebsk in modern Belarus, that existed from its founding in 1101 until it was nominally inherited into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1320. Vitebsk would later fall under the complete authority of Lithuania in 1508. History The area around Vitebsk was controlled by the Principality of Polotsk beginning from the 10th century. Following the death of Vseslav of Polotsk in 1101, Polotsk was divided into six smaller principalities each to be inherited by one of his six surviving sons. Vseslav's second-born son, Sviatoslav Vseslavich inherited the lands surrounding Vitebsk and started the Vitebsk branch of the princes of Polotsk. In 1106, Sviatoslav had partaken in a raid against the Baltic tribes in Semigallia with his brothers. In 1127, the prince of Kiev, Mstislav Vladimirovich, began a war with the princes of Polotsk over trade routes and pillaged several cities including Polotsk. Following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Drutsk
The Principality of Drutsk (; obsolete spelling: ''Druck'') was a small appanage of the Principality of Polotsk, centred in the city of Drutsk. It was located on a three way stick between Vitebsk, Minsk and Mogilev regions in modern Belarus. The appanage principality of Drutsk was established after the death of Vseslav, the Prince of Polotsk, in 1101 and the division of the Polatsk territory between Vseslav's sons. Drutsk was given to Rogvolod-Boris. Soon its territory was taken over by another appanage duchy of Polotsk, Principality of Minsk governed by Gleb Vseslavich. In 1116, the Principality of Drutsk was taken over by the Grand Principality of Kiev governed by Volodymyr Monomakh, but by 1150s it was returned to Principality of Minsk. Eventually Drutsk was entirely taken over by the Principality of Minsk in the second half of the 13th century and in early 14th century by another appanage duchy of Polotsk, Principality of Vitebsk. It is believed that Algirdas, Grand Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Polotsk
The Principality of Polotsk (obsolete spelling: ''Polock''; ; ), also known as the Duchy of Polotsk or Polotskian Rus', was a medieval principality. The origin and date of the establishment of the state are uncertain. Chronicles of Kievan Rus' mention Polotsk being conquered by Vladimir the Great, and thereafter it became associated with Kievan Rus' and its ruling Rurik dynasty. The principality was supposedly established around the town of Polotsk (now in Belarus) by the tribal union of Krivichs. In the second half of the 10th century, Polotsk was governed by its own dynasty; its first ruler mentioned in the chronicles was the semi-legendary Rogvolod (?–978), better known as the father of Rogneda. The principality was heavily involved in several succession crises of the 11th–12th centuries and a war with the Novgorod Land. By the 13th century, it was integrated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. At the time of its greatest extent, the principality stretched over large p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khlebnikov Codex F136v Sub Anno 1118 & 1119
{{surname ...
Khlebnikov, Khlebnikova () or Klebnikov is a Russian surname, meaning a maker of bread (, khleb), may refer to: * Aleksandr Khlebnikov (born 1984), Russian football player * Boris Khlebnikov * Paul Klebnikov (1963–2004), American journalist and historian * Sergey Khlebnikov (1955–1999), Russian Olympic speed skater * Sergey Khlebnikov (general) * Valery Khlebnikov (born 1981), Russian ice hockey player * Velimir Khlebnikov (1885–1922), Russian poet and playwright * Marina Khlebnikova (born 1965), Russian singer and actress, winner of a Golden Gramophone Award The Golden Gramophone Award () is a yearly national Russian music award, established by Russian Radio in 1996.p. 241, ''Pop culture Russia!: media, arts, and lifestyle'', Birgit Beumers, ABC-CLIO, 2005, . The awardee receives a gold-colored fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir The Great
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych (; Christian name: ''Basil''; 15 July 1015), given the epithet "the Great", was Prince of Novgorod from 970 and Grand Prince of Kiev from 978 until his death in 1015. The Eastern Orthodox Church canonization, canonised him as Saint Vladimir. Vladimir's father was Sviatoslav I of the Rurik dynasty. After the death of his father in 972, Vladimir, who was then the prince of Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod, was forced to flee abroad after his brother Yaropolk I of Kiev, Yaropolk murdered his other brother Oleg of Drelinia, Oleg in 977 to become the sole ruler of Rus'. Vladimir assembled a Varangian army and returned to depose Yaropolk in 978. By 980, Vladimir had consolidated his realm to the Baltic Sea and solidified the frontiers against incursions of Bulgarians, Baltic tribes and Eastern nomads. Originally a follower of Slavic paganism, Vladimir converted to Christianity in 988, and Christianization of Kievan Rus', Christianized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
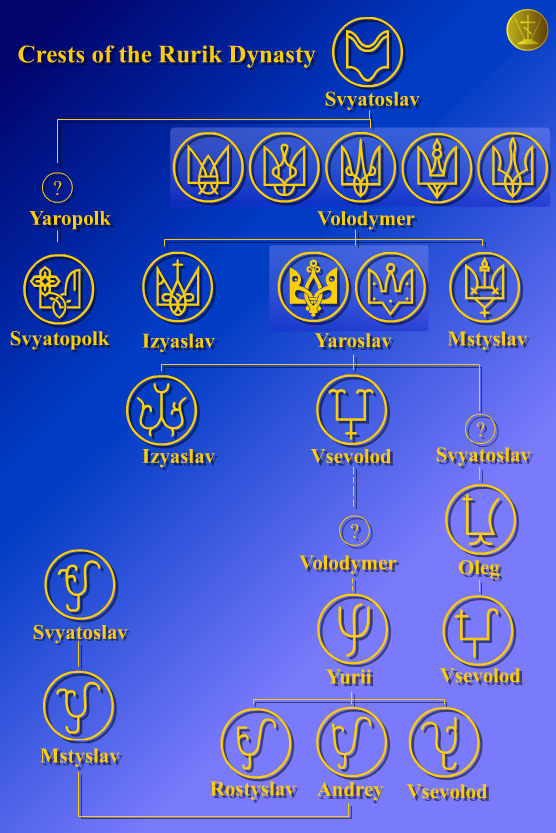
Rurikids
The Rurik dynasty, also known as the Rurikid or Riurikid dynasty, as well as simply Rurikids or Riurikids, was a noble lineage allegedly founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who, according to tradition, established himself at Novgorod in the year 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty of Kievan Rus' and its principalities following its disintegration. The ''Romanovichi'' ruled the southwestern territories, which were unified by Roman the Great and his son Daniel, who was in 1253 crowned by Pope Innocent IV as the king of Ruthenia. Galicia–Volhynia was eventually annexed by Poland and Lithuania. The northern and northeastern territories were unified by the ''Daniilovichi'' of Moscow; by the 15th century, Ivan III threw off the control of the Golden Horde and assumed the title of sovereign of all Russia. Ivan IV was crowned as the tsar of all Russia, where the Rurik line ruled until 1598, following which they were eventually succeeded by the House of Romanov. As a rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |