|
Prince Edward Of Saxe-Weimar
Prince William Augustus Edward of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, , PC(Ire) (11 October 1823 – 16 November 1902) was a British military officer of German descent. After a career in the Grenadier Guards, he became Major General commanding the Brigade of Guards and General Officer Commanding the Home District in 1870, General Officer Commanding Southern District in October 1878 and Commander-in-Chief, Ireland in October 1885. He was promoted to field marshal in 1897 despite his career including no great military achievements. Career Edward was born to Prince Bernhard of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach and Princess Ida of Saxe-Meiningen at Bushy House, the home of his mother's sister Adelaide and her husband the future William IV of the United Kingdom. After being naturalised as a British subject, Edward's military career began on 1 June 1841, when, having trained at the Royal Military College, Sandhurst, he joined the 67th (South Hampshire) Regiment of Foot as an ensign.Heathcote, p. 114 He wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Edward Of Saxe-Weimar
Princess Edward of Saxe-Weimar (born Lady Augusta Katherine Lennox; later Gordon-Lennox; 14 January 1827 – 3 April 1904) was a British aristocrat whose marriage to Prince Edward of Saxe-Weimar made her a relative of the British royal family. Biography Lady Augusta Katherine Lennox was born on 14 January 1827 at Goodwood House to Charles Lennox, 5th Duke of Richmond (1791–1860) and his wife Lady Caroline Paget (1796–1874), daughter of Henry Paget, 1st Marquess of Anglesey. She descended in the male line from Charles Lennox, 1st Duke of Richmond, the illegitimate son of King Charles II of England by his mistress Louise de Kérouaille. When her father inherited the Gordon estates from his uncle, the father took the surname Gordon-Lennox for himself and his descendants, by royal licence dated 9 August 1836. On 27 November 1851, Augusta Katherine married Prince Edward of Saxe-Weimar morganatically in London. He was a son of Prince Bernhard of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Military College, Sandhurst
The Royal Military College (RMC) was a United Kingdom, British military academy for training infantry and cavalry Officer (armed forces), officers of the British Army, British and British Indian Army, Indian Armies. It was founded in 1801 at Great Marlow and High Wycombe in Buckinghamshire, but moved in October 1812 to Sandhurst, Berkshire, Sandhurst, Berkshire. The RMC was reorganised at the outbreak of the World War II, Second World War, but some of its units remained operational at Sandhurst and Aldershot. In 1947, the Royal Military College was merged with the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, to form the present-day all-purpose Royal Military Academy Sandhurst. History Pre-dating the college, the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, had been established in 1741 to train artillery and engineer officers, but there was no such provision for training infantry and cavalry officers. The Royal Military College was conceived by Colonel John Le Marchant (British Army officer, bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inkermann
Inkerman (; ; ) is a city in the Crimean peninsula. It is '' de facto'' within the federal city of Sevastopol within the Russian Federation, but ''de jure'' within the Autonomous Republic of Crimea within Ukraine. It lies 5 kilometres (3 miles) east of Sevastopol, at the mouth of the Chernaya River which flows into Sevastopol Inlet (also called the North Inlet). Administratively, Inkerman was subordinate to the municipality of Sevastopol, but since September 2023 it ''de jure'' became a part of Bakhchysarai Raion of AR Crimea. Population: The name ''Inkerman'' is said to mean 'cave fortress' in Turkish. During the Soviet era, the area was known between 1976 and 1991 as ''Bilokamiansk'' () or ''Belokamensk'' (), which literally means 'white stone city', in reference to the soft white stone quarried in the area and commonly used for construction. In 1991 the Ukrainian authorities restored the pre-1976 name. History The area has been inhabited since ancient times. The cave mona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant Colonel (United Kingdom)
Lieutenant colonel (Lt Col), is a rank in the British Army and Royal Marines which is also used in many Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries. The rank is superior to Major (United Kingdom), major, and subordinate to Colonel (United Kingdom), colonel. The comparable Royal Navy rank is Commander (Royal Navy), commander, and the comparable rank in the Royal Air Force and many Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth air forces is Wing commander (rank), wing commander. The rank insignia in the British Army and Royal Marines, as well as many Commonwealth countries, is a crown above a Order of the Bath, four-pointed "Bath" star, also colloquially referred to as a British Army officer rank insignia, "pip". The crown has varied in the past with different monarchs; the current one being the Tudor Crown. Most other Commonwealth countries use the same insignia, or with the state emblem replacing the crown. In the modern British Armed forces, the established commander of a regiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
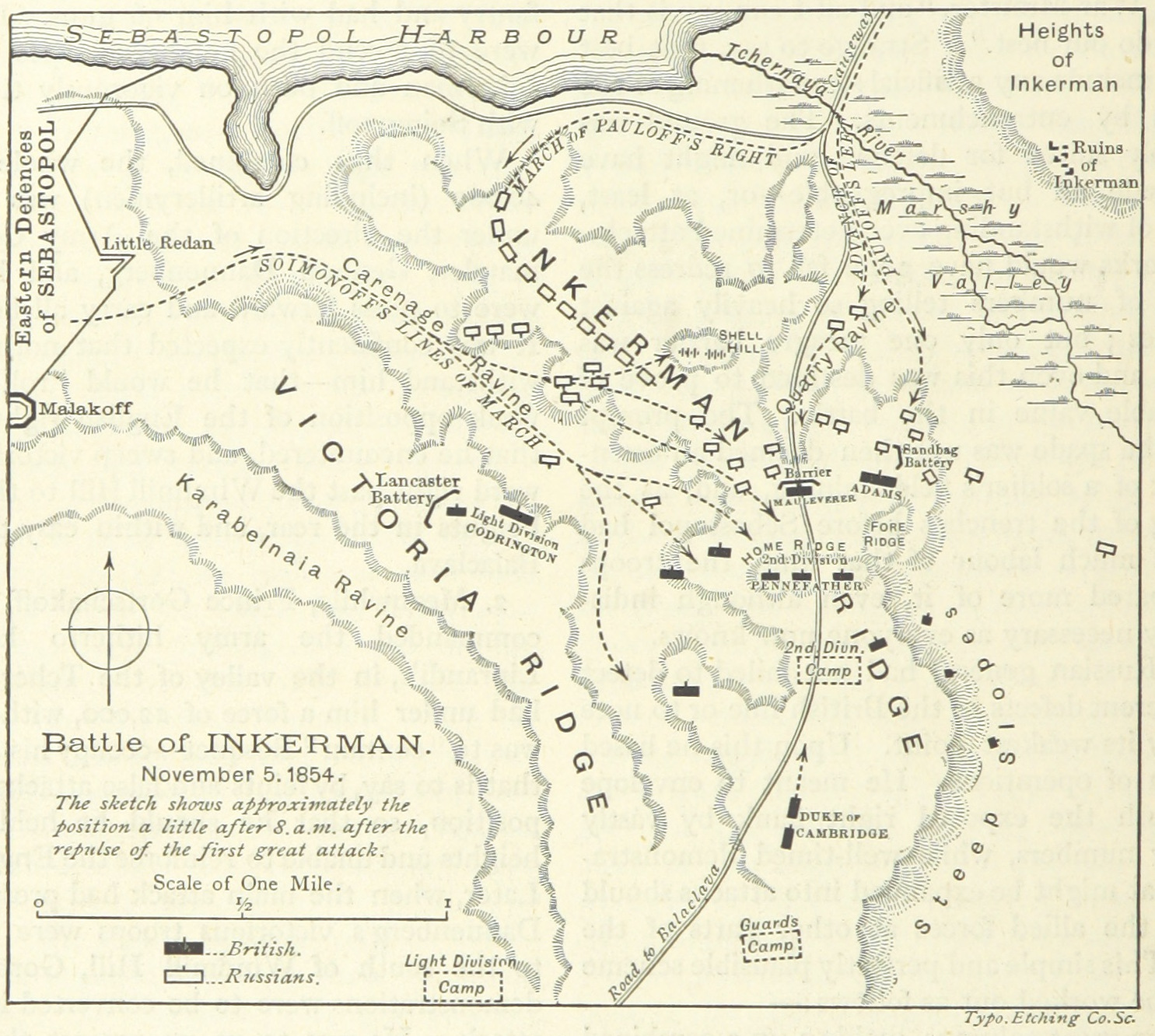
Battle Of Inkerman
The Battle of Inkerman was fought during the Crimean War on 5 November 1854 between the allied armies of Britain and France against the Imperial Russian Army. The battle broke the will of the Russian Army to defeat the allies in the field, and was followed by the Siege of Sevastopol. The role of troops fighting mostly on their own initiative due to the foggy conditions during the battle has earned the engagement the name "The Soldier's Battle." Prelude to the battle The allied armies of Britain, France, Sardinia, and the Ottoman Empire had landed on the west coast of Crimea on 14 September 1854, intending to capture the Russian naval base at Sevastopol. The allied armies fought off and defeated the Russian Army at the Battle of Alma, forcing them to retreat in some confusion toward the River Kacha. While the allies could have taken this opportunity to attack Sevastopol before Sevastopol could be put into a proper state of defence, the allied commanders, British general FitzRoy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Balaclava
The Battle of Balaclava, fought on 25 October 1854 during the Crimean War, was part of the Siege of Sevastopol (1854–55), an Allied attempt to capture the port and fortress of Sevastopol, Russian Empire, Russia's principal naval base on the Black Sea. The engagement followed the earlier Allied victory in September at the Battle of Alma, Battle of the Alma, where the Russian General Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov, Menshikov had positioned his army in an attempt to stop the Allies progressing south towards their strategic goal. Alma was the first major encounter fought in the Crimean Peninsula since the Allied landings at Kalamita Bay on 14 September, and was a clear battlefield success; but a tardy pursuit by the Allies failed to gain a decisive victory, allowing the Russians to regroup, recover and prepare their defence. The Russians split their forces. Defending within the allied siege lines was primarily the Navy manning the considerable static defenses of the city and threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Sevastopol (1854–55)
Siege of Sevastopol may refer to: * Siege of Sevastopol (1854–1855), during the Crimean War * Siege of Sevastopol (1941–1942), during the Second World War * ''Siege of Sevastopol'' (panorama), a 1904 painted panorama by Franz Roubaud See also * Sevastopol (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Alma
The Battle of the Alma (short for Battle of the Alma River) took place during the Crimean War between an allied expeditionary force (made up of French, British, and Ottoman forces) and Russian forces defending the Crimean Peninsula on 20September 1854. The allies had made a surprise landing in Crimea on 14September. The allied commanders, Marshal of France, Maréchal Jacques Leroy de Saint-Arnaud and FitzRoy Somerset, 1st Baron Raglan, Lord Raglan, then marched toward the strategically important port city of Sevastopol, away. Russian commander Prince Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov rushed his available forces to the last natural defensive position before the city, the Alma Heights, south of the Alma (Crimea), Alma River. The allies made a series of disjointed attacks. The French turned the Russian left flank with an attack up cliffs that the Russians had considered unscalable. The British initially waited to see the outcome of the French attack, then twice unsuccessfully assa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont from October 1853 to February 1856. Geopolitical causes of the war included the "Eastern question" (Decline and modernization of the Ottoman Empire, the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the "sick man of Europe"), expansion of Imperial Russia in the preceding Russo-Turkish wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the European balance of power, balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a dispute between France and Russia over the rights of Catholic Church, Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox minorities in Palestine (region), Palestine. After the Sublime Porte refused Nicholas I of Russia, Tsar Nicholas I's demand that the Empire's Orthodox subjects were to be placed unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevet (military)
In military terminology, a brevet ( or ) is a warrant which gives commissioned officers a higher military rank as a reward without necessarily conferring the authority and privileges granted by that rank. The promotion would be noted in the officer's title (for example, "Bvt. Maj. Gen. Joshua L. Chamberlain" or "Bvt. Col. Arthur MacArthur"). It is not to be confused with a '' Brevet d'état-major'' in Francophone European military circles, where it is an award, nor should it be confused with temporary commissions. France In France, ''brevet'' is a word with a very broad meaning, which includes every document giving a capacity to a person. For instance, the various military speciality courses, such as military parachutism, are ended by the award of a brevet. The more important brevet in the French military is that of the École de guerre (''lit''. "school of war"), the French Staff College. Between 1870 and 1940, an ''officier breveté'' was a graduate of the ''École ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Edward Of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, Vanity Fair, 1875-10-30
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". In a related sense, now not commonly used, all more or less sovereign rulers over a state, including kings, were "princes" in the language of international politics. They normally had another title, for example king or duke. Many of these were Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, ), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |