|
Primula Borealis
''Primula borealis'', also known as the Northern primrose or slender primrose, is a species of flowering plant within the genus ''Primula'' and family Primulaceae. The species is a halophyte, inhabiting coastal saline habitats within subalpine and subarctic regions. Description ''Primula borealis'' is a small herbaceous perennial plant, typically measuring between 1 and 12 centimetres in height. It possesses thin and short rhizomes, that give rise to shoots. Due to the rhizomes ''P. borealis'' possesses a clumping growth habit. ''P. borealis'' possesses both diploid and polyploid individuals, with a chromosome count of 2n = 18 and 36. Leaves The leaves of ''Primula borealis'' are not aromatic and have indistinct petioles, which are narrowly winged. The leaf blade is variable in shape, ranging from spatulate to rhombic. It typically measures between 1 and 3.5 cm in length and 0.1 to 0.7 cm in width. The leaves are thin in texture and have smooth surfaces devoid of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit. The group was formerly called Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms are by far the most diverse group of Embryophyte, land plants with 64 Order (biology), orders, 416 Family (biology), families, approximately 13,000 known Genus, genera and 300,000 known species. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody Plant stem, stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of broad-leaved trees, shrubs and vines, and most aquatic plants. Angiosperms are distinguished from the other major seed plant clade, the gymnosperms, by having flowers, xylem consisting of vessel elements instead of tracheids, endosperm within their seeds, and fruits that completely envelop the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s westernmost territory and the smallest territory by land area. As of the 2021 Canadian census, 2021 census, Yukon is the middle territory in terms of population, but the most densely populated. Yukon has an estimated population of 47,126 as of 2025. Whitehorse, the territorial capital, is the largest settlement. Yukon was History of the Northwest Territories, split from the Northwest Territories by a federal statute in 1898 as the Yukon Territory. The current governing legislation is a new statute passed by the federal Parliament in 2002, the ''Yukon Act''. That act established Yukon as the territory's official name, although Yukon Territory remains in popular usage. Canada Post uses the territory's internationally approved postal abbrevia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Marsh
A salt marsh, saltmarsh or salting, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is dominated by dense stands of salt-tolerant plants such as herbs, grasses, or low shrubs. These plants are terrestrial in origin and are essential to the stability of the salt marsh in trapping and binding sediments. Salt marshes play a large role in the aquatic food web and the delivery of nutrients to coastal waters. They also support terrestrial animals and provide coastal protection. Salt marshes have historically been endangered by poorly implemented coastal management practices, with land reclaimed for human uses or polluted by upstream agriculture or other industrial coastal uses. Additionally, sea level rise caused by climate change is endangering other marshes, through erosion and submersion of otherwise tidal marshes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magadan Oblast
Magadan Oblast is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (an oblast) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Russian Far East, Far East region of the country, and is administratively part of the Far Eastern Federal District. Magadan Oblast has a population of 136,085 (Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census), making it the least populated oblast and the third-least populated federal subject in Russia. Magadan is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center, capital of Magadan Oblast with the majority of the oblast's inhabitants living in the city itself. The coastline has a less severe climate than the interiors, although both are very cold for its latitude. It borders Chukotka Autonomous Okrug in the north, Kamchatka Krai in the east, Khabarovsk Krai in the south and the Sakha Republic in the west. The economy is primarily based on mining, particularly gold, silver and other non-ferrous metals. History Magadan Oblast was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasnoyarsk Krai
Krasnoyarsk Krai (, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (a krai) of Russia located in Siberia. Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Krasnoyarsk, the second-largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk. Comprising half of the Siberian Federal District, Krasnoyarsk Krai is the largest krai in Russia, the list of subdivisions of Russia by area, second-largest federal subject in the country after neighboring Sakha Republic, Sakha, and the list of the largest country subdivisions by area, third-largest country subdivision by area in the world. The krai covers an area of , constituting roughly 13% of Russia's total area. Krasnoyarsk Krai has a population of 2,856,971 as of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census. Geography The krai lies in the middle of Siberia, and occupies nearly half of the Siberian Federal District, almost splitting it in half, stretching from the Sayan Mountains in the south along the Yenisei River to the Tay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khabarovsk Krai
Khabarovsk Krai (, ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (a krai) of Russia. It is located in the Russian Far East and is administratively part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The administrative centre of the krai is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Khabarovsk, which is home to roughly half of the krai's population and the largest city in the Russian Far East (just ahead of Vladivostok). Khabarovsk Krai is the fourth-largest federal subject by area, and had a population of 1,343,869 as of 2010. Being dominated by the Siberian High winter cold, the continental climates of the krai see extreme freezing for an area adjacent to the sea near the mid-latitudes, but also warm summers in the interior. The southern region lies mostly in the drainage basin, basin of the lower Amur River, with the River mouth, mouth of the river located at Nikolaevsk-on-Amur draining into the Strait of Tartary, which separates Khabarovsk Krai from the island of Sakha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench. The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and Karaginsky Island constitute Kamchatka Krai of the Russian Federation. The majority of the 322,079 inhabitants are ethnic Russians, with about 13,000 being Koryaks (2014). More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (179,526 in 2010) and nearby Yelizovo (38,980). The Kamchatka Peninsula contains the volcanoes of Kamchatka, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, that form part of the Ring of Fire. Geography Politically, the peninsula forms part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka. (Lopatka is Russian for spade.) The circular bay to the north of this on the Pacific side is Ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
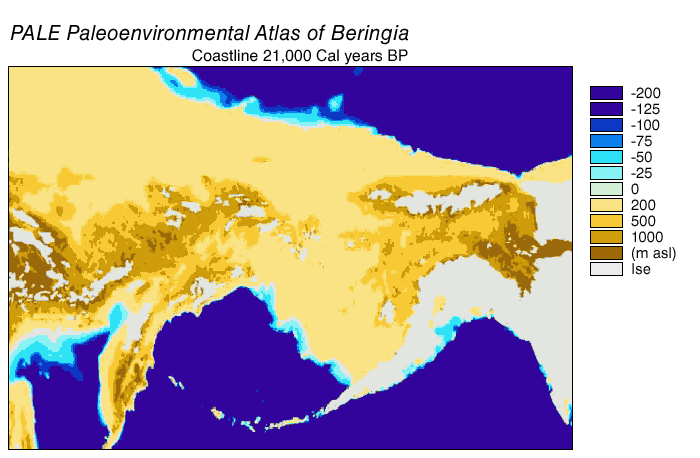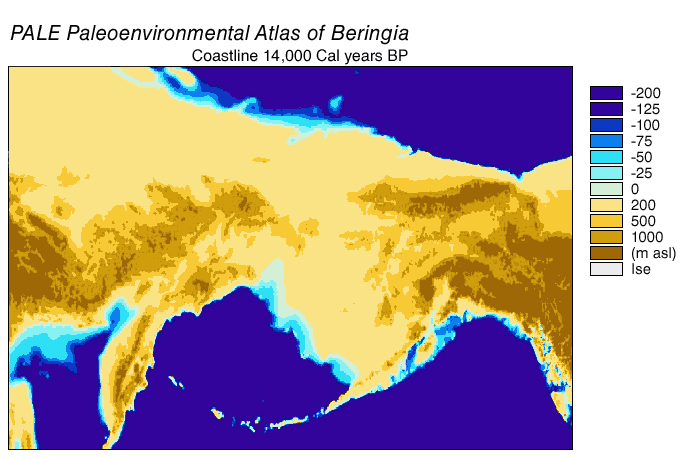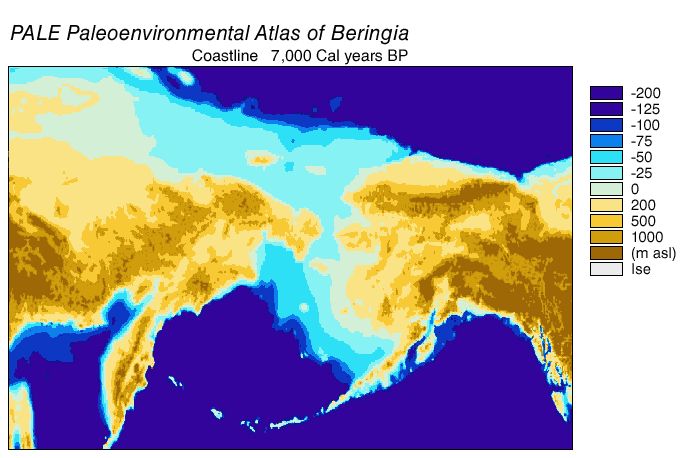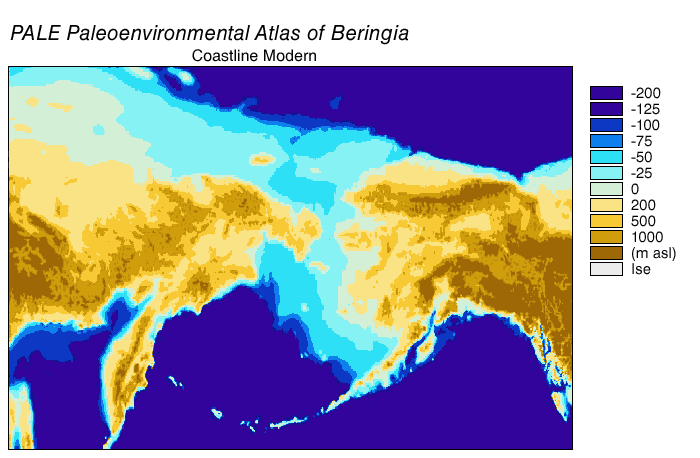
Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Peninsula, Chukchi and Kamchatka peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and Yukon in Canada. The area includes land lying on the North American Plate and Siberian land east of the Chersky Range. At various times, it formed a land bridge referred to as the Bering land bridge, that was up to wide at its greatest extent and which covered an area as large as British Columbia and Alberta together, totaling about , allowing biological dispersal to occur between Asia and North America. Today, the only land that is visible from the central part of the Bering land bridge are the Diomede Islands, the Pribilof Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of the first quarter of 2025 is 45,074. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and the only city in the territory; its population was 20,340 as of the 2021 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. At first, it was named the North-West Territories. The name was changed to the present Northwest Territories in 1906. Since 1870, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primula
''Primula'' () is a genus of herbaceous plant, herbaceous flowering plants in the family (biology), family Primulaceae. They include the primrose (''Primula vulgaris, P. vulgaris''), a familiar wildflower of banks and verges. Other common species are ''Primula auricula, P. auricula'' (auricula), ''Primula veris, P. veris'' (cowslip), and ''Primula elatior, P. elatior'' (oxlip). These species and many others are valued for their ornamental flowers. They have been extensively cultivated and Hybrid (biology)#Hybrid plants, hybridised (in the case of the primrose, for many hundreds of years). ''Primula'' are native plant, native to the temperate climate, temperate Northern Hemisphere, south into tropical mountains in Ethiopia, Indonesia, and New Guinea, and in temperate southern South America. Almost half of the known species are from the Himalayas. ''Primula'' has over 500 species in traditional treatments, and more if certain related genera are included within its circumscription ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma (botany), stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example bees, beetles or butterflies; birds, and bats; water; wind; and even plants themselves. Pollinating animals travel from plant to plant carrying pollen on their bodies in a vital interaction that allows the transfer of genetic material critical to the reproductive system of most flowering plants. Self-pollination occurs within a closed flower. Pollination often occurs within a species. When pollination occurs between species, it can produce hybrid (biology), hybrid offspring in nature and in plant breeding work. In angiosperms, after the pollen grain (gametophyte) has landed on the stigma (botany), stigma, it germinates and develops a pollen tube which grows down the style (botany), style until it reaches an ovary (botany), ovary. Its two gametes travel down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |