|
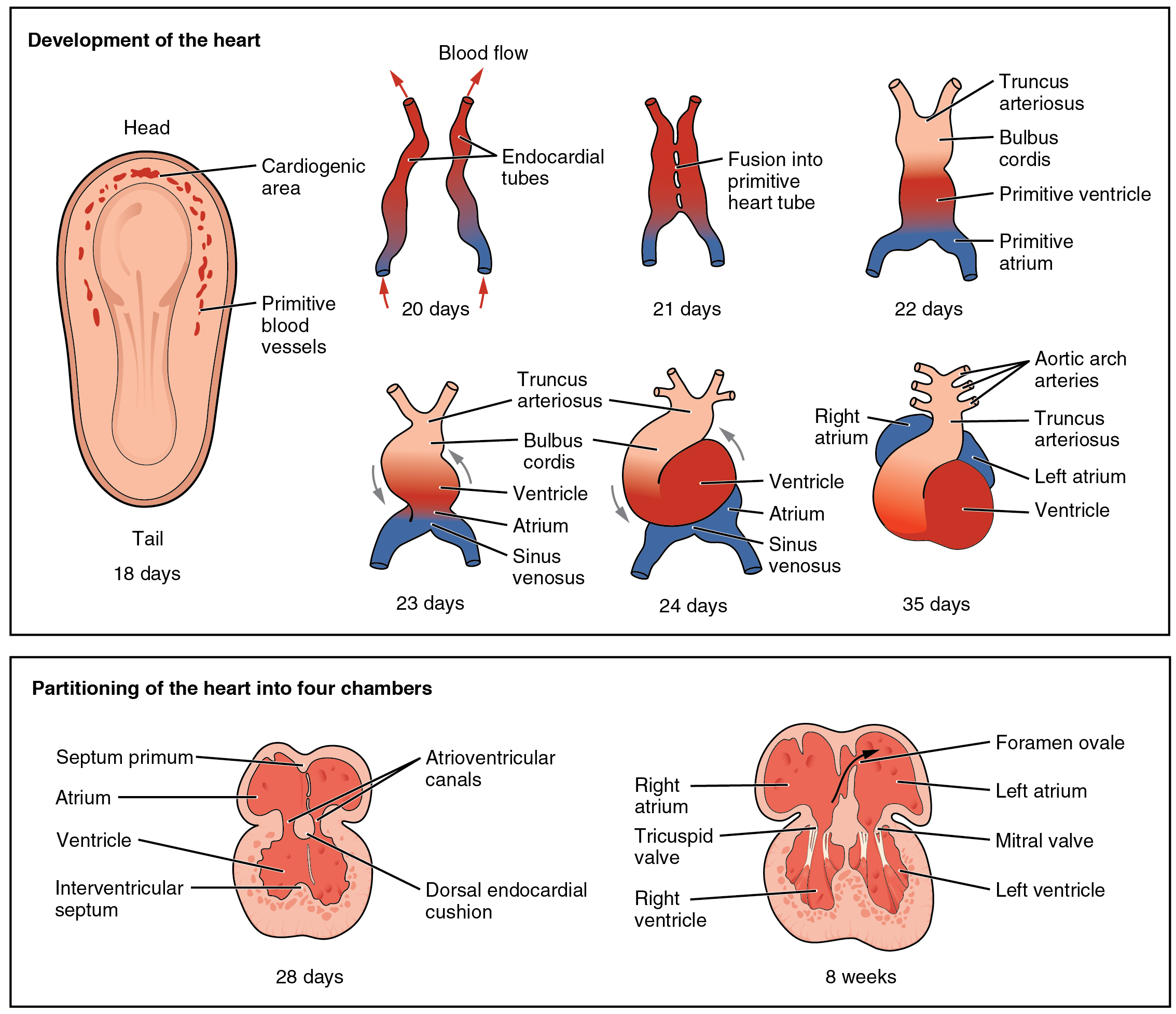
Primitive Ventricle
The primitive ventricle or embryonic ventricle of the developing heart, together with the bulbus cordis that lies in front of it, gives rise to the left and right ventricles. The primitive ventricle provides the trabeculated parts of the walls, and the bulbus cordis the smooth parts. The primitive ventricle becomes divided by the septum inferius which develops into the interventricular septum. The septum grows upward from the lower part of the ventricle, at a position marked on the heart's surface by a furrow. Its dorsal part increases more rapidly than its ventral portion, and fuses with the dorsal part of the septum intermedium Endocardial cushions project into the atrial canal, and, meeting in the middle line, unite to form the septum intermedium which divides the canal into two channels, the future right and left atrioventricular orifices. References External links .... For a time an interventricular foramen exists above its ventral portion, but this foramen is ultim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubular Heart
The tubular heart or primitive heart tube is the earliest stage of heart development. The heart is the first organ to develop during human embryonic development. From the inflow to the outflow, the tubular heart consists of sinus venosus, primitive atrium, the primitive ventricle, the bulbus cordis, and truncus arteriosus. The sinus venosus will become part of the right atrium and contain the primary cardiac pacemaker. The primitive atrium and primitive ventricle will develop into the upper and lower chambers of the heart. The bulbus cordis will form part of the right ventricle, while the truncus arteriosis split into pulmonary and aortic vessels that carry blood away from the heart. Blood flow is driven by contractions and is different compared to that of an adult heart. The tubular heart forms primarily from splanchnic mesoderm The lateral plate mesoderm is the mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo. It is to the side of the paraxial mesoderm, and further to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular System
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium (heart), atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulbus Cordis
The bulbus cordis (the bulb of the heart) is a part of the developing heart that lies ventral to the primitive ventricle after the heart assumes its S-shaped form. The superior end of the bulbus cordis is also called the conotruncus. Structure In the early tubular heart, the bulbus cordis is the major outflow pathway. It receives blood from the primitive ventricle, and passes it to the truncus arteriosus. After heart looping, it is located slightly to the left of the ventricle. Development The early bulbus cordis is formed by the fifth week of development. The truncus arteriosus is derived from it later. The adjacent walls of the bulbus cordis and ventricle approximate, fuse, and finally disappear, and the bulbus cordis now communicates freely with the right ventricle, while the junction of the bulbus with the truncus arteriosus is brought directly ventral to and applied to the atrial canal. By the upgrowth of the ventricular septum the bulbus cordis is separated from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum Inferius
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The interventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior interventricular sulci. The lower part of the septum, which is the major part, is thick and muscular, and its much smaller upper part is thin and membraneous. During each cardiac cycle the interventricular septum contracts by shortening longitudinally and becoming thicker. Structure The interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior interventricular sulci. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interventricular Septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricle (heart), ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The interventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior interventricular sulcus, anterior and Posterior interventricular sulcus, posterior interventricular sulci. The lower part of the septum, which is the major part, is thick and muscular, and its much smaller upper part is thin and membraneous. During each cardiac cycle the interventricular septum contracts by shortening longitudinally and becoming thicker. Structure The interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the Ventricle (heart), ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum Intermedium
Endocardial cushions project into the atrial canal, and, meeting in the middle line, unite to form the septum intermedium which divides the canal into two channels, the future right and left atrioventricular orifices. References External links Overview at edu.mt Embryology of cardiovascular system {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Interventricular Foramen
In human embryology, the primary interventricular foramen is a temporary opening between the developing ventricles of the heart. The ventricles arise as a single cavity that is divided by the developing interventricular septum The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricle (heart), ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The interventricular septum is di .... Before the septum closes completely, the remaining opening between the two ventricles is termed the interventricular foramen. In some individuals, the foramen fails to close, leading to an interventricular septal defect known as a patent interventricular foramen. References Embryology of cardiovascular system {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Septum
The aorticopulmonary septum is developmentally formed from neural crest, specifically the cardiac neural crest, and actively separates the aorta and pulmonary arteries and fuses with the interventricular septum within the heart during heart development. Structure In the developing heart, the truncus arteriosus and bulbus cordis are divided by the aortic septum. This makes its appearance in three portions. # Two distal ridge-like thickenings project into the lumen of the tube; these increase in size, and ultimately meet and fuse to form a septum, which takes a spiral course toward the proximal end of the truncus arteriosus. It divides the distal part of the truncus into two vessels, the aorta and pulmonary artery, which lie side by side above, but near the heart the pulmonary artery is in front of the aorta. # Four endocardial cushions appear in the proximal part of the truncus arteriosus in the region of the future semilunar valves; the manner in which these are related to the aort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |