|
Primary Flight Control System
Primary or primaries may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels * Primary (band), from Australia * Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea * Primary Music, Israeli record label Works * ''Primary'' (album) by Rubicon (2002) * "Primary" (song) by The Cure * "Primary", song by Spoon from the album '' Telephono'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Primaries or primary beams, in E. E. Smith's science-fiction series '' Lensman'' * ''Primary'' (film), American political documentary (1960) Computing * PRIMARY, an X Window selection * Primary data storage, computer technology used to retain digital data * Primary server, main server on the server farm Education * Primary education, the first stage of compulsory education * Primary FRCA, academic examination for anaesthetists in the U.K. * Primary school, school providing primary education Mathematics * ''p''-group of prime power order * Primary decom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Source
In the study of history as an academic discipline, a primary source (also called an original source) is an Artifact (archaeology), artifact, document, diary, manuscript, autobiography, recording, or any other source of information that was created at the time under study. It serves as an original source of information about the topic. Similar definitions can be used in library science and other areas of scholarship, although different fields have somewhat different definitions. In journalism, a primary source can be a person with direct knowledge of a situation, or a document written by such a person. Primary sources are distinguished from ''secondary sources'', which cite, comment on, or build upon primary sources. Generally, accounts written after the fact with the benefit of hindsight are secondary. A secondary source may also be a primary source depending on how it is used. For example, a memoir would be considered a primary source in research concerning its author or about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Ideal
In mathematics, specifically commutative algebra, a proper ideal ''Q'' of a commutative ring ''A'' is said to be primary if whenever ''xy'' is an element of ''Q'' then ''x'' or ''y''''n'' is also an element of ''Q'', for some ''n'' > 0. For example, in the ring of integers Z, (''p''''n'') is a primary ideal if ''p'' is a prime number. The notion of primary ideals is important in commutative ring theory because every ideal of a Noetherian ring has a primary decomposition, that is, can be written as an intersection of finitely many primary ideals. This result is known as the Lasker–Noether theorem. Consequently, an irreducible ideal of a Noetherian ring is primary. Various methods of generalizing primary ideals to noncommutative rings exist, but the topic is most often studied for commutative rings. Therefore, the rings in this article are assumed to be commutative rings with identity. Examples and properties * The definition can be rephrased in a more symmetric m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Line
An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and Electric power distribution, distribution to transmit electrical energy along large distances. It consists of one or more electrical conductor, conductors (commonly multiples of three) suspended by Transmission tower, towers or Utility pole, poles. Since the surrounding air provides good cooling, electrical insulation, insulation along long passages, and allows optical inspection, overhead power lines are generally the lowest-cost method of power transmission for large quantities of electric energy. Construction Towers for support of the lines are made of wood (as-grown or laminated), steel or aluminum (either lattice structures or tubular poles), concrete, and occasionally reinforced plastics. The bare wire conductors on the line are generally made of aluminum (either plain or ACSR, reinforced with steel, or composite materials such as carbon and glass fiber), though some copper wires are used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Mirror
A primary mirror (or primary) is the principal light-gathering surface (the objective) of a reflecting telescope. Description The primary mirror of a reflecting telescope is a spherical, parabolic, or hyperbolic shaped disks of polished reflective metal ( speculum metal up to the mid 19th century), or in later telescopes, glass or other material coated with a reflective layer. One of the first known reflecting telescopes, Newton's reflector of 1668, used a 3.3 cm polished metal primary mirror. The next major change was to use silver on glass rather than metal, in the 19th century such was with the Crossley reflector. This was changed to vacuum deposited aluminum on glass, used on the 200-inch Hale telescope. Solid primary mirrors have to sustain their own weight and not deform under gravity, which limits the maximum size for a single piece primary mirror. Segmented mirror configurations are used to get around the size limitation on single primary mirrors. For exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Field
In theoretical physics Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain, and predict List of natural phenomena, natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental p ..., a primary field, also called a primary operator, or simply a primary, is a local operator in a conformal field theory which is annihilated by the part of the conformal algebra consisting of the lowering generators. From the representation theory point of view, a primary is the lowest dimension operator in a given representation of the conformal algebra. All other operators in a representation are called ''descendants''; they can be obtained by acting on the primary with the raising generators. History of the concept Primary fields in a ''D''-dimensional conformal field theory were introduced in 1969 by Mack and Salam where they were called ''interpolating fields''. They were then studied by Ferrara, Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Circuit
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force, electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change Alternating current, AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon Design
Nuclear weapons design are physical, chemical, and engineering arrangements that cause the physics package of a nuclear weapon to detonate. There are three existing basic design types: # Pure fission weapons are the simplest, least technically demanding, were the first nuclear weapons built, and so far the only type ever used in warfare, by the United States on Empire of Japan, Japan in World War II. # Boosted fission weapons are fission weapons that use nuclear fusion reactions to generate high-energy neutrons that accelerate the fission chain reaction and increase its efficiency. Boosting can more than double the weapon's fission energy yield. # Staged thermonuclear weapons are arrangements of two or more "stages", most usually two, where the weapon derives a significant fraction of its energy from nuclear fusion (as well as, usually, nuclear fission), . The first stage is typically a boosted fission weapon (except for the earliest thermonuclear weapons, which used a pure fission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six period (geology), geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (geologist), John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''palaiós'' (π� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is named after Cambria, the Latinized name for Wales, where rocks from this age were first studied. The Precambrian accounts for 88% of the Earth's geologic time. The Precambrian is an informal unit of geologic time, subdivided into three eons ( Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic) of the geologic time scale. It spans from the formation of Earth about 4.6 billion years ago ( Ga) to the beginning of the Cambrian Period, about million years ago ( Ma), when hard-shelled creatures first appeared in abundance. Overview Relatively little is known about the Precambrian, despite it making up roughly seven-eighths of the Earth's history, and what is known has largely been discovered from the 1960s onwards. The Precambrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Time Scale
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (a scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardised international units of geological time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to preci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
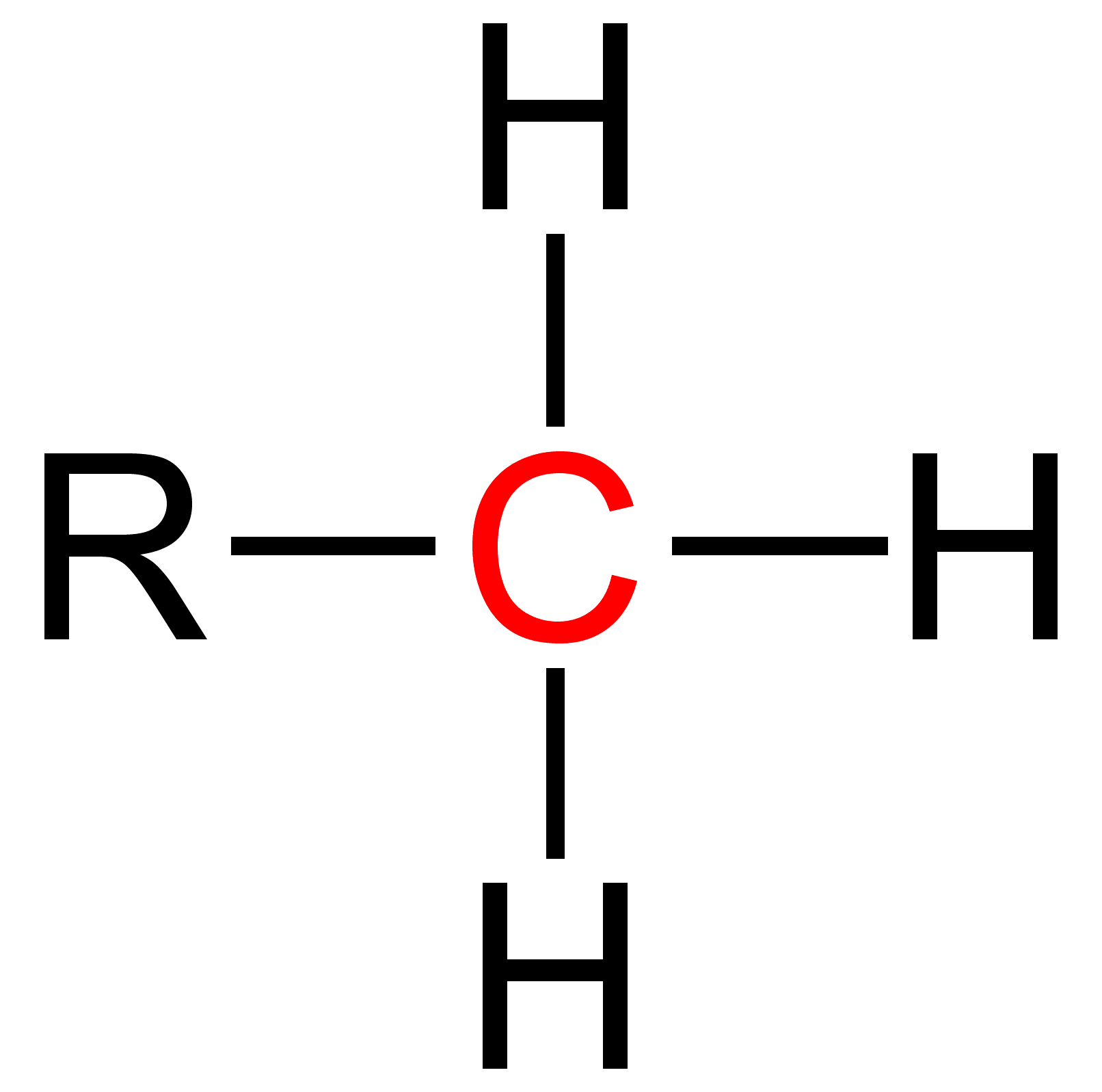
Primary (chemistry)
Primary is a term used in organic chemistry to classify various types of compounds (e.g. alcohols, alkyl halides, amines) or reactive intermediates (e.g. alkyl radicals, carbocations). {{clear See also * Secondary (chemistry) * Tertiary (chemistry) * Quaternary (chemistry) References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary (astronomy)
A primary bodyalso called a central body, host body, gravitational primary, or simply primaryis the main physical body of a gravitationally bound, multi-object system. This object constitutes most of that system's mass and will generally be located near the system's barycenter. In the Solar System, the Sun is the primary for all objects that orbit the star. In the same way, the primary of all satellites (be they natural satellites (moons) or artificial ones) is the planet they orbit. The term ''primary'' is often used to avoid specifying whether the object near the barycenter is a planet, a star, or any other astronomical object. In this sense, the word ''primary'' is always used as a noun. The center of mass is the average position of all the objects weighed by mass. The Sun is so massive that the Solar System's barycenter frequently lies very near the Sun's center but owing to the mass and distance of the gas giant planets, the Solar System's barycenter occasionally lies ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |