|
Price Terrace
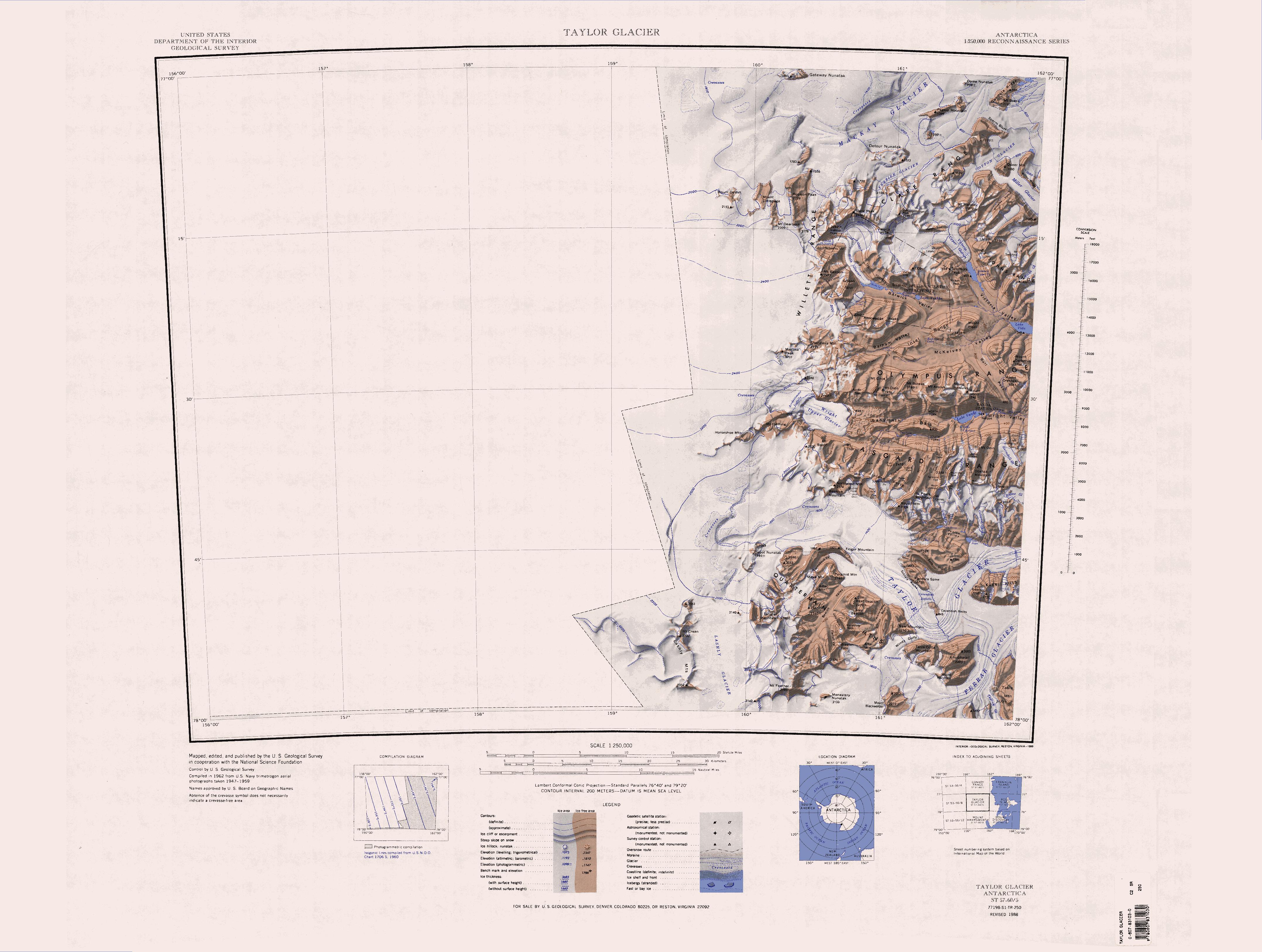
The Cruzen Range () is a mountain range that rises to in Vashka Crag and extends west to east for between Salyer Ledge and Nickell Peak in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Victoria Land, Antarctica. The range is bounded to north, east, south and west by the Clare Range, Victoria Valley, Barwick Valley, and the Webb Glacier. Name The Cruzen Range was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAP) in 2005 after Rear Admiral Richard H. Cruzen, commander of Task Force 68 during the U.S. Navy Antarctic Developments Project, 1946-47 (Operation Highjump). Location The Cruzen Range was formerly the southern part of the Clare Range, to the north. It is separated from the Clare Range by Webb Cirque which holds the névé at the head of the Webb Glacier to the northwest, and Victoria Upper Névé that feeds Victoria Upper Glacier to the northeast. The two are separated by a ridge leading south from Parker Mesa to The Fortress. To the south the range is bounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beacon Sandstone
The Beacon Supergroup is a geological formation exposed in Antarctica and deposited from the Devonian to the Triassic (). The unit was originally described as either a formation or sandstone, and upgraded to group and supergroup as time passed. It contains a sandy member known as the Beacon Heights Orthoquartzite. Overview The base of the Beacon Supergroup is marked by an unconformity and is composed of the Devonian Taylor Group, a quartzose sandstone sequence; and the Late Carboniferous to Early Jurassic Victoria Group, consisting of glacial beds, sandstone, shale, conglomerate, and coal. The Beacon Sandstone was named by Hartley T. Ferrar during Scott's Discovery Expedition (1901–1904), using the Beacon Heights survey points as reference. ''Glossopteris'' fossils dated the sandstone to the Permian and linked the lithology to similar sequences on neighboring continents. Generally flat lying, the supergroup is up to 3.2 km thick and is fairly continuous from south Victor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkey Valley
Barwick Valley () is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. A large part of the valley has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area because of its pristine condition. Naming Barwick Valley was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for Richard Essex Barwick (1929-2012), summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Location The Barwick Valley is one of the McMurdo Dry Valleys. It runs southeast from the Webb Icefall to the Insel Range, where it is joined from the southwest by Balham Valley. The combined valley continues east to Victoria Valley. To the north the valley is bounded by The Fortress and other features of the Cruzen Range (formerly part of the Clare Range). To the west and southwest it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Delaware
The University of Delaware (colloquially known as UD, UDel, or Delaware) is a Statutory college#Delaware, privately governed, state-assisted Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Newark, Delaware, United States. UD offers four associate's programs, 163 bachelor's programs, 136 master's programs, and 64 doctoral programs across its ten colleges and schools. The main campus is in Newark, with satellite campuses in Dover, Delaware, Dover, Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington, Lewes, Delaware, Lewes, and Georgetown, Delaware. With 24,221 students , UD is the List of colleges and universities in Delaware, largest university in Delaware by enrollment. UD is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". According to the National Science Foundation, UD spent $186 million on research and development in 2018, ranking it 119th in the nation. It is recognized with the Community Enga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartol Research Institute
The Bartol Research Institute (formerly the ''Bartol Research Foundation'') is a scientific research institution at the Department of Physics and Astronomy of the University of Delaware. Its members belong to the faculty of the University of Delaware and perform research in areas such as astroparticle physics, astrophysics, cosmology, particle physics, and space science. Research Having a strong research mission, the Bartol Research Institute has counted several renowned physicists among its members, mostly focusing on fundamental science. Starting with its first director, W.F.G. Swann, cosmic rays were and still are one of the main research topics. With its second director, Martin A. Pomerantz, an Antarctic research program was developed along these lines and is maintained until today: Bartol scientists contribute to several Antarctic cosmic-ray projects, including ballon-borne cosmic-ray detectors such as ANITA, and ground-based experiments such as neutron monitors and the Ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas K
Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the Apostle * Thomas (bishop of the East Angles) (fl. 640s–650s), medieval Bishop of the East Angles * Thomas (Archdeacon of Barnstaple) (fl. 1203), Archdeacon of Barnstaple * Thomas, Count of Perche (1195–1217), Count of Perche * Thomas (bishop of Finland) (1248), first known Bishop of Finland * Thomas, Earl of Mar (1330–1377), 14th-century Earl, Aberdeen, Scotland Geography Places in the United States * Thomas, Idaho * Thomas, Illinois * Thomas, Oklahoma * Thomas, Oregon * Thomas, South Dakota * Thomas, Virginia * Thomas, Washington * Thomas, West Virginia * Thomas County (other) * Thomas Township (other) Elsewhere * Thomas Glacier (Greenland) Arts and entertainment * ''Thomas'' (Burton novel), a 1969 nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Vashka
Barwick Valley () is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. A large part of the valley has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area because of its pristine condition. Naming Barwick Valley was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for Richard Essex Barwick (1929-2012), summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Location The Barwick Valley is one of the McMurdo Dry Valleys. It runs southeast from the Webb Icefall to the Insel Range, where it is joined from the southwest by Balham Valley. The combined valley continues east to Victoria Valley. To the north the valley is bounded by The Fortress and other features of the Cruzen Range (formerly part of the Clare Range). To the west and southwest it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the lithospheric mantle (or mantle lithosphere), the uppermost part of the mantle that is not convecting. The layer below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere, which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle that is able to convect. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church (Manhattan), Trinity Church in Manhattan, it is the oldest institution of higher education in New York (state), New York and the fifth-First university in the United States, oldest in the United States. Columbia was established as a Colonial colleges, colonial college by royal charter under George II of Great Britain. It was renamed Columbia College (New York), Columbia College in 1784 following the American Revolution, and in 1787 was placed under Trustees of Columbia University in the City of New York, a private board of trustees headed by former students Alexander Hamilton and John Jay. In 1896, the campus was moved to its current location in Morningside Heights and renamed Columbia University. Columbia is organized into twenty schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robin E
Robin most commonly refers to several species of passerine birds. Robin may also refer to: Animals * Australasian robins, red-breasted songbirds of the family Petroicidae * Many members of the subfamily Saxicolinae (Old World chats), including: **European robin (''Erithacus rubecula'') ** Bush-robin **Forest robin ** Magpie-robin ** Scrub robin ** Robin-chat ** Bagobo robin ** White-starred robin **White-throated robin ** Blue-fronted robin **Larvivora (6 species) **Myiomela (3 species) * Some red-breasted New-World true thrushes (''Turdus'') of the family Turdidae, including: ** American robin (''T. migratorius'') (so named by 1703) ** Rufous-backed thrush (''T. rufopalliatus'') ** Rufous-collared thrush (''T. rufitorques'') ** Formerly other American thrushes, such as the clay-colored thrush (''T. grayi'') * Pekin robin or Japanese (hill) robin, archaic names for the red-billed leiothrix (''Leiothrix lutea''), red-breasted songbirds * Sea robin, a fish with small "leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |