|
Prepuce (other)
Prepuce , or as an adjective, preputial , refers to two homologous Homology may refer to: Sciences Biology *Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor *Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences * Homologous chrom ... structures of male and female genitals: * Foreskin, skin surrounding and protecting the head of the penis in humans * Penile sheath, skin surrounding and protecting the head of the penis in other mammals * Clitoral hood, skin surrounding and protecting the head of the clitoris in humans * Clitoral sheath, skin surrounding and protecting the head of the clitoris in other mammals {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreskin
In male human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce, is the double-layered fold of skin, mucosal and muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans and the urinary meatus. The foreskin is attached to the glans by an elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum. The outer skin of the foreskin meets with the inner preputial mucosa at the area of the mucocutaneous junction. The foreskin is mobile, fairly stretchable and sustains the glans in a moist environment. Except for humans, a similar structure, known as penile sheath, appears in the male sexual organs of all primates and the vast majority of mammals. In humans, foreskin length varies widely and coverage of the glans in a flaccid and erect state can also vary. The foreskin is fused to the glans at birth and is generally not retractable in infancy and early childhood. Inability to retract the foreskin in childhood should not be considered a problem unless there are other symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
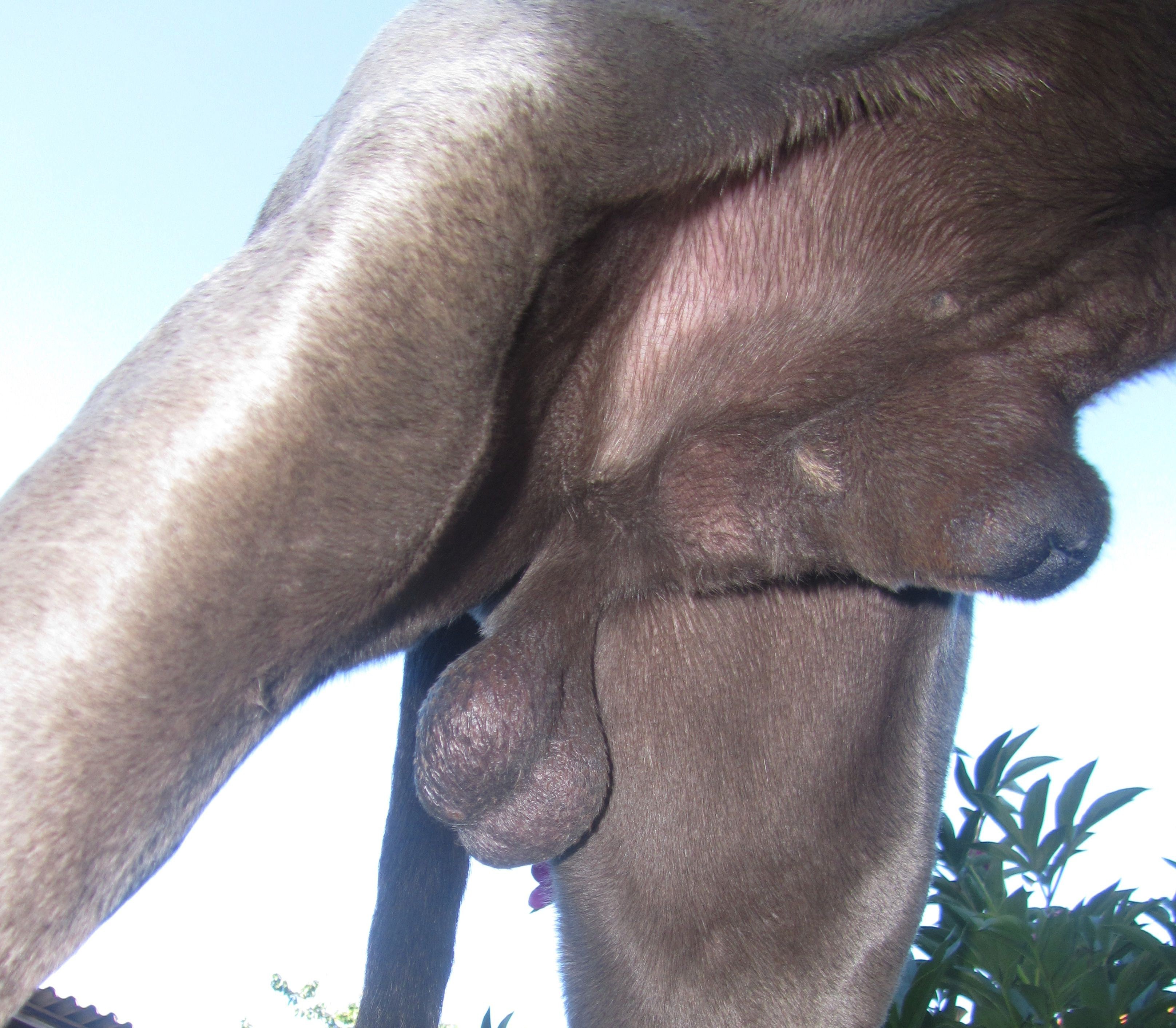
Penile Sheath
Almost all mammal penises have foreskins or prepuce, although in non-human cases the foreskin is usually a sheath (sometimes called the ''preputial sheath'', ''praeputium'' or ''penile sheath'') into which the whole penis is retracted. In koalas, the foreskin contains naturally occurring bacteria that play an important role in fertilization. In some bat species, the prepuce contains an erectile tissue structure called the ''accessory corpus cavernosus''. During musth, a male elephant may urinate with the penis still in the sheath, which causes the urine to spray on the hind legs.Sukumar, pp. 100–08. Male dogs have a conspicuous penis sheath. In stallions, the retractor penis muscle contracts to retract the stallion's penis into the sheath and relaxes to allow the penis to extend from the sheath. The penis sheath of a male axis deer is elongated and urine-stained. When rubbing trees with their horns, these stags sometimes move the penis back and forth rapidly inside its s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
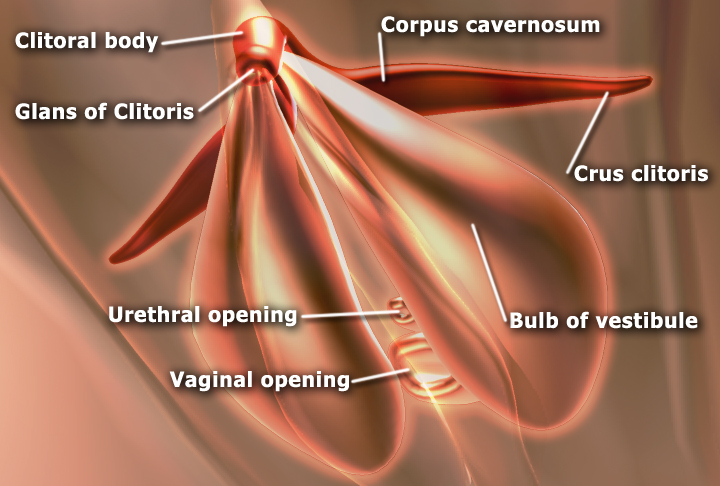
Clitoral Hood
In the female human body, the clitoral hood (also called preputium clitoridis and clitoral prepuce) is a fold of skin that surrounds and protects the glans of the clitoris; it also covers the external shaft of the clitoris, develops as part of the labia minora and is homologous with the foreskin (also called the ''prepuce'') in the male reproductive system. The clitoral hood is composed of muccocutaneous tissues; these tissues are between the mucous membrane and the skin, and they may have immunological importance because they may be a point of entry of mucosal vaccines. The clitoral hood is also important not only in the protection of the clitoral glans, but also in pleasure, as its tissue forms part of the erogenous zones of the vulva. Development and variation The clitoral hood is formed during the fetal stage by the cellular lamella. The cellular lamella grows down on the dorsal side of the clitoris and is eventually fused with the clitoris. The clitoral hood is formed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |