|
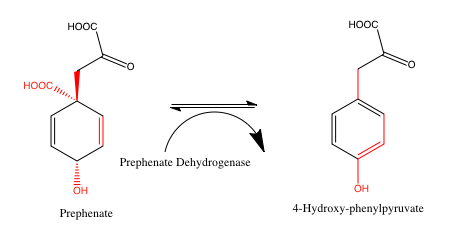
Prephenate Dehydrogenase
Prephenate dehydrogenase is an enzyme found in the shikimate pathway, and helps catalyze the reaction from prephenate to tyrosine. Nomenclature Gene: (Saccharomyces Cerevisiae) TYR1 Shikimate pathway: Arogenate/Prephenate (ADH/PDH). Although in the shikimate pathway arogenate and prephenate dehydrogenase catalyze different reactions, they can at times be used interchangeably. * TyrA (tyrosine A: within the tyrosine pathway) * Prephenate dehydrogenase * Prephenate (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) dehydrogenase * Prephenate dehydrogenase (NADP) * NADP+ oxidoreductase Homology This enzyme so far has been found in sixteen different organisms; twelve different kinds of bacteria (mostly cyanobacteria) and four different kinds of plants (mostly different kinds of beans). Bacteria organisms (examples): Acenitobacter calcoaceticus, Fischerella sp., Flavobacterium so., Comamonas testosteroni, and nostoc sp. Plant organisms: phaseolus coccineus, phaseolus vulgaris, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies against ''S. cerevis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. Functions Aside from being a proteinogenic amino acid, tyrosine has a special role by virtue of the phenol functionality. It occurs in proteins that are part of signal transduction processes and functions as a receiver of phosphate groups that are transferred by way of protein kinases. Phosphorylation of the hydroxyl group can change the activity of the targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (4-HPPA) is an intermediate in the metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. The aromatic side chain of phenylalanine is hydroxylated by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase to form tyrosine. The conversion from tyrosine to 4-HPPA is in turn catalyzed by tyrosine aminotransferase. Additionally, 4-HPPA can be converted to homogentisic acid which is one of the precursors to ochronotic pigment. It is an intermediary compound in the biosynthesis of scytonemin. See also * 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD), also known as α-ketoisocaproate dioxygenase (KIC dioxygenase), is an Fe(II)-containing non-heme oxygenase that catalyzes the second reaction in the catabolism of tyrosine - the conversion of 4-hydroxy ... References Natural phenols Phenols Alpha-keto acids Propionic acids Hydroxy acids {{biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (chemistry)
Products are the species formed from chemical reactions. During a chemical reaction, reactants are transformed into products after passing through a high energy transition state. This process results in the consumption of the reactants. It can be a spontaneous reaction or mediated by catalysts which lower the energy of the transition state, and by solvents which provide the chemical environment necessary for the reaction to take place. When represented in chemical equations, products are by convention drawn on the right-hand side, even in the case of reversible reactions. The properties of products such as their energies help determine several characteristics of a chemical reaction, such as whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic. Additionally, the properties of a product can make it easier to extract and purify following a chemical reaction, especially if the product has a different state of matter than the reactants. Spontaneous reaction : R \rightarrow P *Where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively. In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The cofactor is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction, also with H+, forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prephenate
Prephenic acid, commonly also known by its anionic form prephenate, is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine, as well as of a large number of secondary metabolites of the shikimate pathway. It is biosynthesized by a ,3 sigmatropic Claisen rearrangement of chorismate. : Stereochemistry Prephenic acid is an example of achiral (optically inactive) molecule which has two pseudoasymmetric atoms (''i.e.'' stereogenic but not chirotopic centers), the C1 and the C4 cyclohexadiene ring atoms. It has been shown that of the two possible diastereoisomers In stereochemistry, diastereomers (sometimes called diastereoisomers) are a type of stereoisomer. Diastereomers are defined as non-mirror image, non-identical stereoisomers. Hence, they occur when two or more stereoisomers of a compound have dif ..., the natural prephenic acid is one that has both substituents at higher priority (according to CIP rules) on the two pseudoas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biochemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and microsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |