|
Prasna Marga
''Prasna Marga'' is a unique work on Hindu astrology, natal and horary ('Prashna' means 'Horary'), that appears to be a major classical text covering every aspect of human existence. It was written in Sanskrit Sloka – format in the year 1649 A.D. in a place called Edakad near Tellasseri in the present Indian State of Kerala, by Narayanan Nambutiri of Panakkattu house (a Namboodari Brahmin) of Kerala. The author himself wrote a brief commentary to his book with the name 'Durgamartha prakasini'. This work is known in English through the commentary written by Punnasseri Nambi Neelakantha Sarma, a disciple of Kerala Varma. All Parashari principles are briefly available in this classic, and about which principles it is claimed that one conversant with the six branches of Jyotisa will never err in predictions. ''Prasna Marga'' is the most comprehensive and elaborate exposition of Horary astrology. This classic occupies a high position of pride without entering into which like mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangalore Venkata Raman
Bangalore Venkata Raman (8 August 1912 – 20 December 1998) was an Indian astrologer in modern India and an author of numerous books and articles. He was instrumental in making Vedic Astrpology (Saint Parashar System) or Hindu astrology known and respected throughout India and across the world. With the help of his sons Niranjan Babu and Sachidananda Babu, he also started the Raman & Rajeswari Research Foundation to promote the knowledge of Astrology and Vastu Shastra. Career Raman restarted "The Astrological Magazine" in 1936, which was earlier run by his grandfather, and remained its editor for over 62 years. After his death, the magazine was run until December 2007 by his son, Niranjan Babu Bangalore, and his daughter, Gayatri Devi Vasudev, when it was shut down citing no reason. It is now relaunched as The Astrological eMagazine by his son Niranjan Babu. He represented India at the Astrological Congress held at Cambridge, England, and the International Astrology Conference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
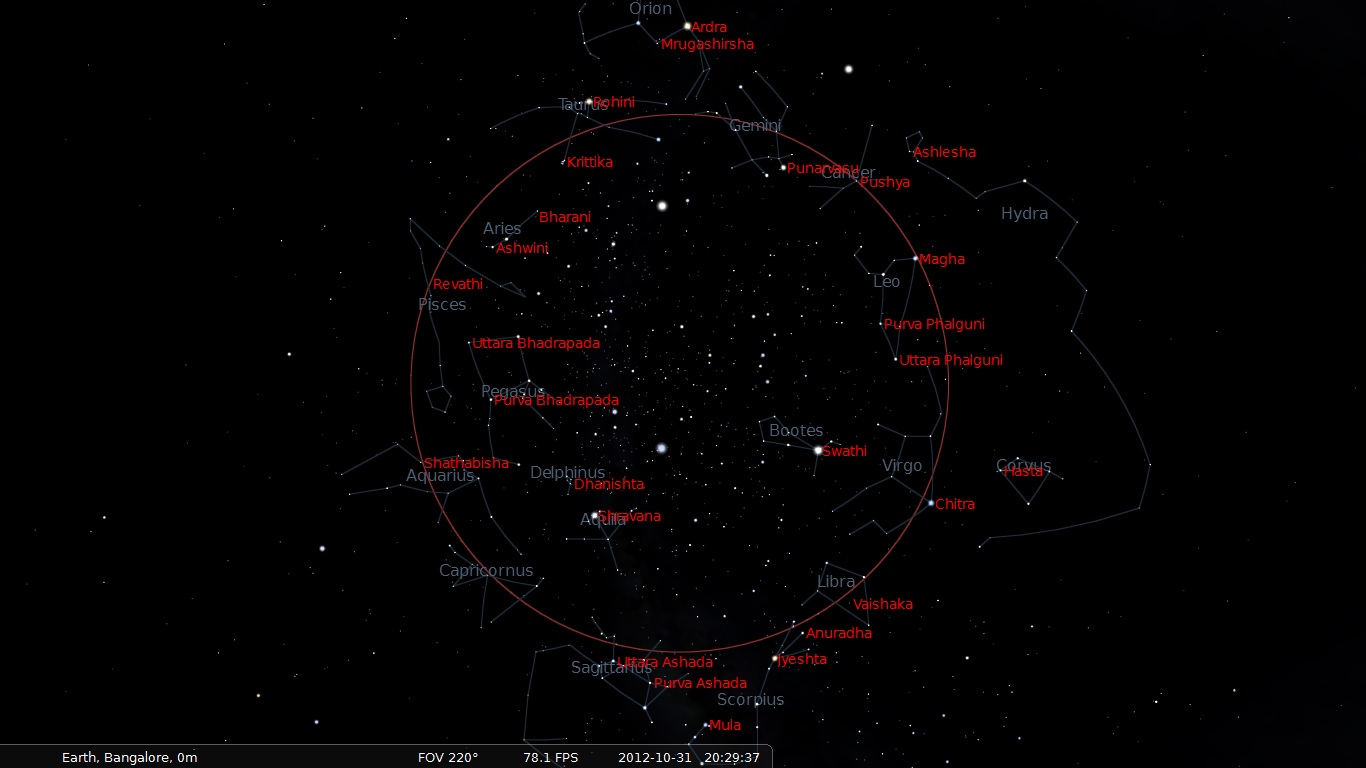
Hindu Astrology
Jyotisha or Jyotishya (from Sanskrit ', from ' “light, heavenly body" and ''ish'' - from Isvara or God) is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism, that is connected with the study of the Vedas. The '' Vedanga Jyotisha'' is one of the earliest texts about astronomy within the Vedas. Some scholars believe that the horoscopic astrology practiced in the Indian subcontinent came from Hellenistic influences, however, this is a point of intense debate and other scholars believe that Jyotisha developed independently although it may have interacted with Greek astrology. Following a judgement of the Andhra Pradesh High Court in 2001 which favoured astrology, some Indian universities now offer advanced degrees in Hindu astrology. The scientific consensus is that astrology is a pseudoscience. Etymology Jyotisha, states Monier-Williams, is ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominalization, nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloka Meter
Sanskrit prosody or Chandas refers to one of the six Vedangas, or limbs of Vedic studies.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Chandas" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A-M, Rosen Publishing, , page 140 It is the study of poetic metres and verse in Sanskrit. This field of study was central to the composition of the Vedas, the scriptural canons of Hinduism, so central that some later Hindu and Buddhist texts refer to the Vedas as ''Chandas''. The Chandas, as developed by the Vedic schools, were organized around seven major metres, and each had its own rhythm, movements and aesthetics. Sanskrit metres include those based on a fixed number of syllables per verse, and those based on fixed number of morae per verse. Extant ancient manuals on Chandas include Pingala's ''Chandah Sutra'', while an example of a medieval Sanskrit prosody manual is Kedara Bhatta's ''Vrittaratnakara''. The most exhaustive compilations of Sanskrit prosody describe over 600 metres. This is a subst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Canara, and Thiruvithamkoor. Spread over , Kerala is the 21st largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33 million inhabitants as per the 2011 census, Kerala is the 13th-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state. The Chera dynasty was the first prominent kingdom based in Kerala. The Ay kingdom in the deep south and the Ezhimala kingdom in the north formed the other kingdoms in the early years of the Common Era (CE). The region had been a prominent spice exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyotisa
Jyotisha or Jyotishya (from Sanskrit ', from ' “light, heavenly body" and ''ish'' - from Isvara or God) is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. It is one of the six auxiliary disciplines in Hinduism, that is connected with the study of the Vedas. The ''Vedanga Jyotisha'' is one of the earliest texts about astronomy within the Vedas. Some scholars believe that the horoscopic astrology practiced in the Indian subcontinent came from Hellenistic influences, however, this is a point of intense debate and other scholars believe that Jyotisha developed independently although it may have interacted with Greek astrology. Following a judgement of the Andhra Pradesh High Court in 2001 which favoured astrology, some Indian universities now offer advanced degrees in Hindu astrology. The scientific consensus is that astrology is a pseudoscience. Etymology Jyotisha, states Monier-Williams, is rooted i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashtamangala Prasnam
Ashtamangala prasnam is a certain type of practice of the ''prasna'' branch of Hindu astrology. The terminology indicates the use of eight (''ashta'') auspicious (''mangala'') objects in its practice. These objects are ghee lamps (brass lamps with a wick in clarified butter), mirror, gold, milk, yogurt, fruits, book, and white cloth. The practice of ''ashtamangala prasnam'' is highly popular and held in high esteem in the Indian state of Kerala and Tulu Nadu. In fact, the author of Prasna Marga, an authoritative book on its practice was written by Narayanan Nambutiri, an astrologer from Edakad, Thalasseri in Kerala. Prasna Marga was written in 1649 CE. ''Prasna'' is one of the six important branches of Hindu astrology. It deals with horary astrology in which an astrologer attempts to answer a question by constructing a horoscope for the exact time at which the question was received and understood by the astrologer. The other branches are ''jataka'' (natal astrology) which attemp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit Texts
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Astrological Texts
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (सिन्धु ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-identity within the local In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
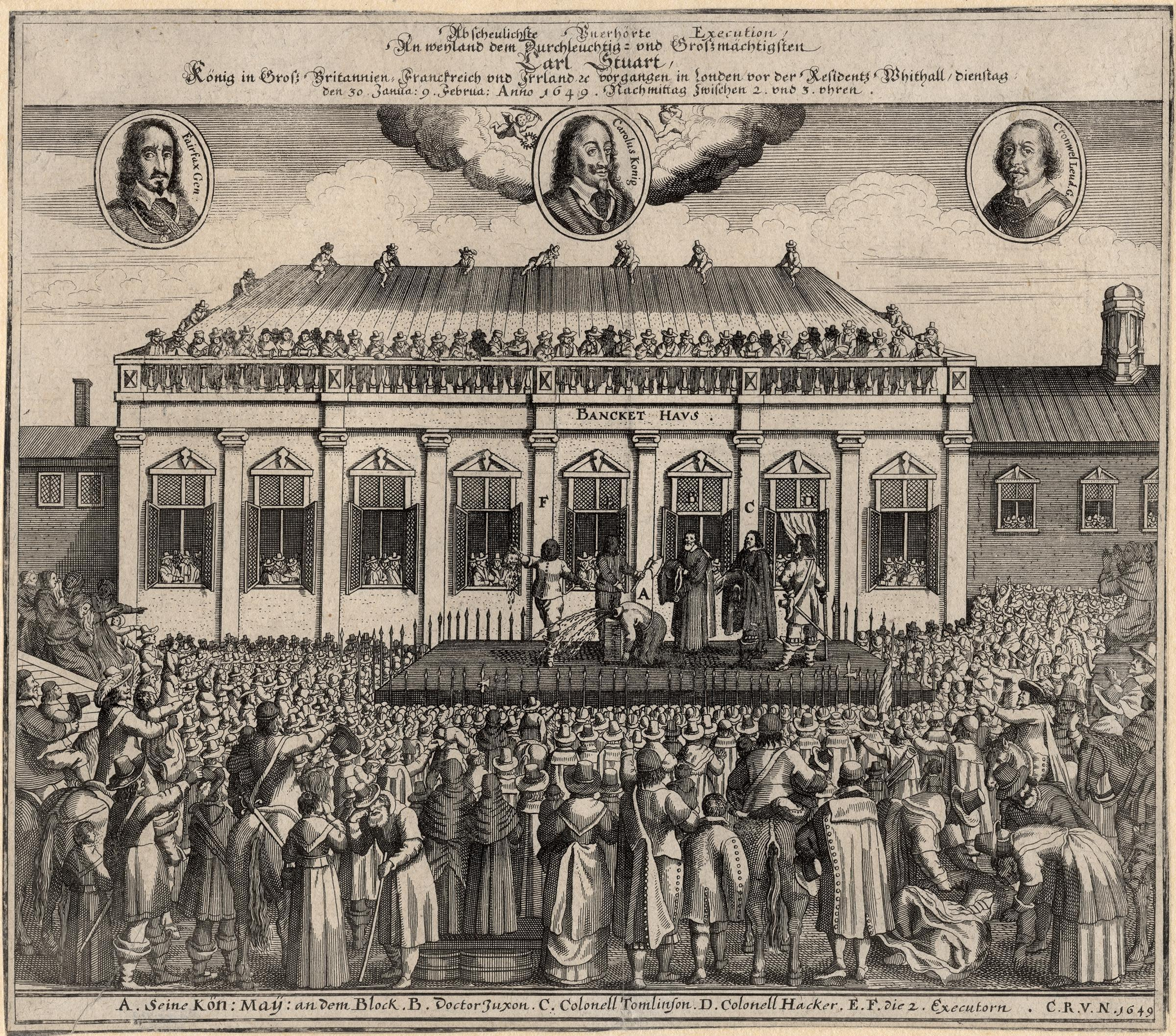
1649 Books
Events January–March * January 4 – In England, the Rump Parliament passes an ordinance to set up a High Court of Justice, to try Charles I for high treason. * January 17 – The Second Ormonde Peace concludes an alliance between the Irish Royalists and the Irish Confederates during the War of the Three Kingdoms. Later in the year the alliance is decisively defeated during the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. * January 20 – Charles I of England goes on trial, for treason and other " high crimes". * January 27 – King Charles I of England, Scotland and Ireland is found guilty of high treason in a public session. He is beheaded three days later, outside the Banquet Hall in the Palace of Whitehall, London. * January 29 – Serfdom in Russia begins legally as the Sobornoye Ulozheniye (, "Code of Law") is signed by members of the Zemsky Sobor, the parliament of the estates of the realm in the Tsardom of Russia. Slaves and free pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
