|
Prasinovirus
''Prasinovirus'' is a genus of large double-stranded DNA viruses, in the family ''Phycodnaviridae'' that infect phytoplankton in the '' Prasinophyceae''. The genus contains two species, including Micromonas pusilla virus SP1, which infects the cosmopolitan photosynthetic flagellate '' Micromonas pusilla''. There is a large group of genetically diverse but related viruses that show considerable evidence of lateral gene transfer Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e .... Taxonomy The genus contains the following species, listed by scientific name and followed by the exemplar virus of the species: * ''Prasinovirus micromonas'', Micromonas pusilla virus SP1 * ''Prasinovirus ostreotauri'', Ostreococcus tauri virus OtV5 Structure Viruses in ''Prasinovirus'' are envelo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycodnaviridae Virion
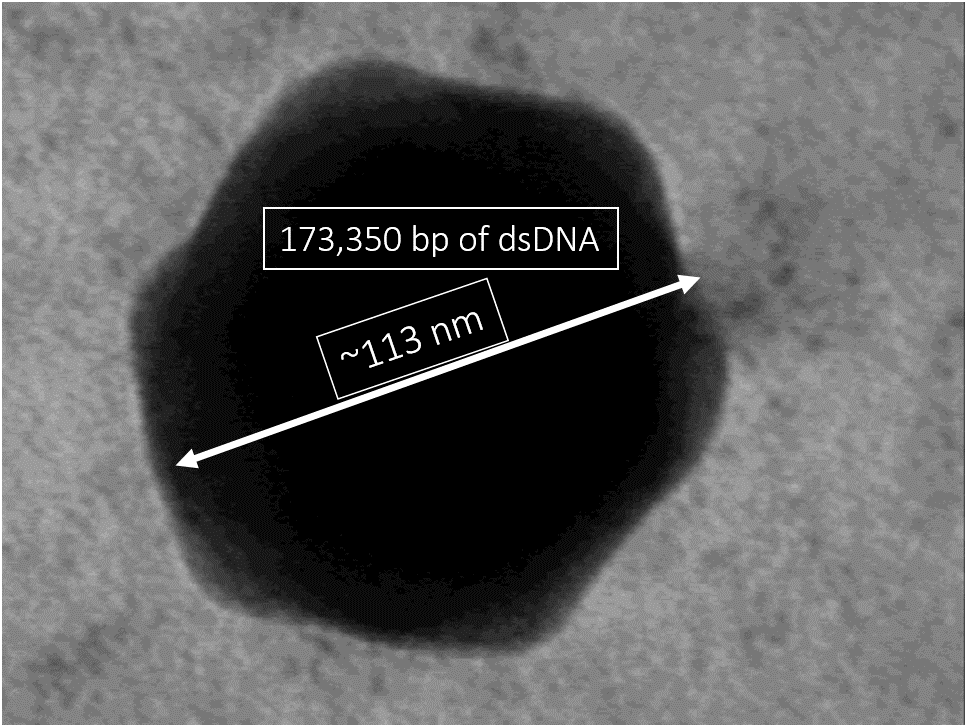
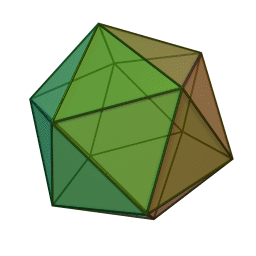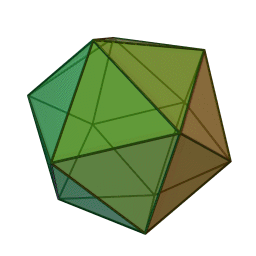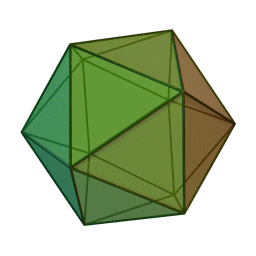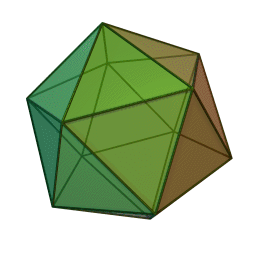
''Phycodnaviridae'' is a family of large (100–560 kb) double-stranded DNA viruses that infect marine or freshwater eukaryotic algae. Viruses within this family have a similar morphology, with an icosahedral capsid (polyhedron with 20 faces). As of 2014, there were 33 species in this family, divided among 6 genera. This family belongs to a super-group of large viruses known as nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Evidence was published in 2014 suggesting that specific strains of ''Phycodnaviridae'' might infect humans rather than just algal species, as was previously believed. Most genera under this family enter the host cell by cell receptor endocytosis and replicate in the nucleus. ''Phycodnaviridae'' play important ecological roles by regulating the growth and productivity of their algal hosts. Algal species such '' Heterosigma akashiwo'' and the genus '' Chrysochromulina'' can form dense blooms which can be damaging to fisheries, resulting in losses in the aquaculture i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycodnaviridae
''Phycodnaviridae'' is a family of large (100–560 kb) double-stranded DNA viruses that infect marine or freshwater eukaryotic algae. Viruses within this family have a similar morphology, with an icosahedral capsid (polyhedron with 20 faces). As of 2014, there were 33 species in this family, divided among 6 genera. This family belongs to a super-group of large viruses known as nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Evidence was published in 2014 suggesting that specific strains of ''Phycodnaviridae'' might infect humans rather than just algal species, as was previously believed. Most genera under this family enter the host cell by cell receptor endocytosis and replicate in the nucleus. ''Phycodnaviridae'' play important ecological roles by regulating the growth and productivity of their algal hosts. Algal species such '' Heterosigma akashiwo'' and the genus '' Chrysochromulina'' can form dense blooms which can be damaging to fisheries, resulting in losses in the aquacultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prasinophyceae
The prasinophytes are a group of unicellular green algae. Prasinophytes mainly include marine planktonic species, as well as some freshwater representatives.Sym, S. D. and Pienaar, R. N. 1993. The class Prasinophyceae. In Round, F. E. and Chapman, D. J. (eds) ''Progress in Phycological Research'', Vol. 9. Biopress Ltd., Bristol, pp. 281-376. The prasinophytes are morphologically diverse, including flagellates with one to eight flagella and non-motile (coccoid) unicells, as well as dormant or cyst stage phycoma. The cells of many species are covered with organic body scales; others are naked. Well studied genera include '' Ostreococcus'', considered to be the smallest (ca. 0.95 μm) free-living eukaryote, and '' Micromonas'', both of which are found in marine waters worldwide. Prasinophytes have simple cellular structures, containing a single chloroplast and a single mitochondrion. The genomes are relatively small compared to other eukaryotes (about 12 Mbp for '' Ostreococcus'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long molecules of DNA or RNA that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as trees and other plants do on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micromonas
''Micromonas'' is a genus of green algae in the family '' Mamiellaceae''. ''Micromonas'' is a widespread prasinophyte alga that is very small in size, motile, and phototactic. Before characterization and naming of a second species, ''Micromonas commoda'' through genome analysis, ''Micromonas pusilla'' was considered to be the only species in the genus. This led to a disproportionate amount of research discussing a single species and the suggestion that it was the dominant photosynthetic picoeukaryote in some marine ecosystems. Unlike many marine algae, this single species was thought to be distributed widely in both warm and cold waters, but genome sequencing confirmed indications from single-gene studies that its global distribution really reflected presence of multiple species occupying different niches in the ocean. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher-order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various mechanisms of HGT such as transformation, transduction and conjugation, subsequently armin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Coding Sequences Of Micromonas Pusilla Viruses And Micromonas Pusilla
Shared may refer to: * Sharing * Shared ancestry or Common descent * Shared care * Shared-cost service * Shared decision-making in medicine * Shared delusion, various meanings * Shared government * Shared intelligence or collective intelligence * Shared library * Shared morality * Shared ownership * Shared parenting or shared custody * Shared property * Shared reading * Shared secret * Shared services * Shared universe, in fiction * Shared vision planning, in irrigation * Shared workspace Science and technology * Shared medium, in telecommunication * Shared neutral, in electric circuitry * Shared pair, in chemistry *Shared vertex (or shared corner or common corner), point of contact between polygons, polyhedra, etc. *Shared edge, line of contact between polygons, polyhedra, etc. Computing * Shared agenda, in groupware * Shared computing * Shared desktop * Shared data structure * Shared IP address * Shared-memory architecture * Shared memory (interprocess communication) * Shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micromonas Pusilla Virus SP1
''Micromonas'' is a genus of green algae in the family '' Mamiellaceae''. ''Micromonas'' is a widespread prasinophyte alga that is very small in size, motile, and phototactic. Before characterization and naming of a second species, ''Micromonas commoda'' through genome analysis, ''Micromonas pusilla'' was considered to be the only species in the genus. This led to a disproportionate amount of research discussing a single species and the suggestion that it was the dominant photosynthetic picoeukaryote in some marine ecosystems. Unlike many marine algae, this single species was thought to be distributed widely in both warm and cold waters, but genome sequencing confirmed indications from single-gene studies that its global distribution really reflected presence of multiple species occupying different niches in the ocean. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostreococcus Tauri Virus OtV5
''Ostreococcus'' is a genus of unicellular coccoid or spherically shaped green algae belonging to the class Mamiellophyceae. It includes prominent members of the global picoplankton community, which plays a central role in the oceanic carbon cycle. History The first member of the genus, '' O. tauri'', was discovered in 1994 in an investigation of the picoplankton in the Thau lagoon by Courties and Chretiennot-Dinet using flow cytometry. Unicellular photosynthetic organisms are generally amenable to study using flow cytometry because of the autofluorescence provided by chlorophyll and other fluorophores used by the cells for the harvesting and control of sunlight, which allows such pigments to be studied without any staining of the cells. The different pigments present can be distinguished and identified on a cell-by-cell basis using flow cytometry, allowing researchers to deduce the different species present in the sample and help classify any new species found. ''O. tauri'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |