|
Prabuty
Prabuty () is a town in Kwidzyn County within the Pomeranian Voivodeship of northern Poland. It is the seat of Gmina Prabuty. Geographical location Prabuty is located between the Liwieniec and Sowica lakes, approximately 18 kilometers east of Kwidzyn, 100 kilometers southeast of Gdańsk, 100 kilometers west of Olsztyn, and 133 kilometers southwest of Kaliningrad. Prabuty is a rail junction on the Warsaw–Gdynia railway. History In 1236, the Teutonic Knights under Henry III, Margrave of Meissen, destroyed an Old Prussian fortress between the lakes Dzierzgoń and Liwieniec. The settlement was first mentioned in 1250 as ''Riesenburg''. Albert, the Bishop of Pomesania, founded the castle and town in 1270 and moved his seat there. It would remain the primary seat of the Bishop of Pomesania until the diocese dissolved in 1587. The village grew around the castle and received Culm law city rights on 30 October 1330 from bishop Rudolf of Pomerania (1322–1332). The town suffered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Prabuty
__NOTOC__ Gmina Prabuty is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Kwidzyn County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. Its seat is the town of Prabuty, which lies approximately east of Kwidzyn and south-east of the regional capital Gdańsk. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 13,091 (out of which the population of Prabuty amounts to 8,488, and the population of the rural part of the gmina is 4,603). Villages Apart from the town of Prabuty, Gmina Prabuty contains the villages and settlements of Antonin, Bronowo Małe, Gdakowo, Gilwa, Gonty, Górowychy, Górowychy Małe, Grazymowo, Grodziec, Halinowo, Jakubowo, Julianowo, Kałdowo, Kamienna, Kleczewo, Kołodzieje, Kolonia Gąski, Kowale, Laskowice, Laskowicki Tartak, Młynisko, Obrzynowo, Orkusz, Pachutki, Pałatyki, Pilichowo, Pólko, Raniewo, Rodowo, Rodowo Małe, Rumunki, Stańkowo, Stary Kamień, Stary Młyn, Sypanica, Szramowo, Trumiejki a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwidzyn County
__NOTOC__ Kwidzyn County () is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Pomeranian Voivodeship, northern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Kwidzyn, which lies south of the regional capital Gdańsk. The only other town in the county is Prabuty, lying east of Kwidzyn. The county covers an area of . As of 2019 its total population is 83,231, out of which the population of Kwidzyn is 38,444, that of Prabuty is 8,695, and the rural population is 36,092. ''Kwidzyn County on a map of the counties of Pomeranian Voivodeship'' Kwidzyn County is bordered by Tczew County to the west, Sztum County to the north, Iława County to the east, Grudziądz County to the south and Świecie County to the south-west. Administrative division The county is subdivided into six gminas (one urban, one urban-rural and four rural). These are listed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeship Road
According to classes and categories of public roads in Poland, a voivodeship A voivodeship ( ) or voivodate is the area administered by a voivode (governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in ... road () is a category of roads one step below national roads in importance. The roads are numbered from 100 to 993. Total length of voivodeship roads in Poland is of which are unpaved (2008).Transport – activity results in 2008 , Główny Urząd Statystyczny List of voivodeship roads Current list of voivodeship road ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship ( ; ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk. The voivodeship was established on January 1, 1999, out of the former voivodeships of Gdańsk Voivodeship (1975–1998), Gdańsk, Elbląg Voivodeship, Elbląg and Słupsk Voivodeship, Słupsk, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1997. It is bordered by the West Pomeranian Voivodeship to the west, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Greater Poland and the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship to the south, the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship to the east, and the Baltic Sea to the north. It also shares a short land border with Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast), on the Vistula Spit. The bulk of the voivodeship is located in the historic region of Pomerania, with the territories on the eastern bank of the Vistula being part of Powiśle (region), Powiśle. The Pomeranian part of the region comprises most of Pomerelia (the easternmost part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culm Law
Kulm law, Culm law or Chełmno Law (; ; ) was a legal constitution for a municipal form of government used in several Central European cities in the Middle Ages and early modern period. It was initiated on 28 December 1233 in the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights by Grand Master Hermann von Salza and Hermann Balk when the towns of Toruń (''Thorn'') and Chełmno (''Kulm'') received German town law, in particular as a modification of Magdeburg rights. Named after the town it was signed in, the original document (''Kulmer Handfeste'') was lost in 1244 when the town hall burned due to an attack by Świętopełk II, Duke of Pomerania. The renewed charter of 1 October 1251 was based on a copy in Toruń, but the rights were reduced. The town hall in Chełmno was the seat of the higher court of Chełmno law until 1458. This type of law was mostly granted by the Teutonic Order to cities within their monastic state, and by the neighboring Duchy of Masovia, but also elsewhere in Pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Confederation
The Prussian Confederation (, ) was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Marienwerder (present-day Kwidzyn) by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia, to oppose the arbitrariness of the Teutonic Knights. It was based on an earlier similar organization, the Lizard Union established in 1397 by the nobles of Chełmno Land. In 1454, the leader of the Confederation, Johannes von Baysen (Jan Bażyński), formally asked King Casimir IV Jagiellon, to incorporate Prussia into the Kingdom of Poland. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War between the Order's State and Poland, with the cities co-financing the military costs of the latter. Background According to the 1411 First Peace of Thorn which followed the Teutonic Knights' defeat in the Battle of Grunwald, the Teutonic Order had to pay high reparations to the Kingdom of Poland. The monastic state imposed high taxes on the cities to raise the funds as well as to re-arm for another war again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Pomesania
The Bishopric of Pomesania (; ) was a Catholic diocese in the Prussia (region), Prussian regions of Pomesania and Pogesania, in modern northern Poland until the 16th century, then shortly a Lutheran diocese, and became a Latin titular see. The former Cathedral and Kwidzyn Castle, Castle of Pomesanian Cathedral Chapter complex in Kwidzyn is listed as a List of Historic Monuments (Poland), Historic Monument of Poland. Catholic diocese It was founded as one of four Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic dioceses in Prussia in 1243 by the papal legate William of Modena. The bishops, whose seat was Riesenburg (Prabuty), ruled one third of diocesan territory as his temporalities, temporality. The diocesan cathedral chapter met in the Fortified church, fortified cathedral of Marienwerder (Kwidzyn). In the 1280s the Teutonic Order succeeded to impose the simultaneous membership of all capitular canons in the Order thus winning influence in the diocese and in the capitular elections of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brama Kwidzyńska
Wout Brama (; born 21 August 1986) is a Dutch former professional footballer who played as a defensive midfielder. Club career Twente Born in Almelo, Brama began his youth team at PH Almelo before moving to FC Twente in 1999. After progressing through the Twente youth system, in which he was captain for both the youth team and the reserve team, he signed his first professional contract with the club in March 2005. Later that year, he was promoted to the first team. Brama made his debut in the Eredivisie in the 2005–06 season for FC Twente, which came on as a second–half substitute, in a 2–0 loss against Roda JC in the opening game of the season. Since making his FC Twente debut, Brama quickly established himself in the first team at a midfield position. Despite being sidelined for five matches, Brama finished his first season in the 2005–06 season, making 38 appearances in all competitions. The 2006–07 season saw Fred Rutten appointed as a new manager. Under Rutten, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem is in and in Latin . Thus the term "T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
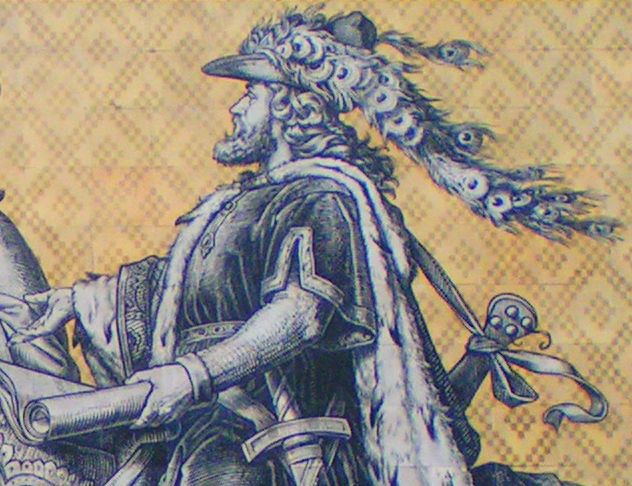
Henry III, Margrave Of Meissen
Henry III, called Henry the Illustrious (''Heinrich der Erlauchte'') (c. 1215 – 15 February 1288) from the House of Wettin was Margrave of Meissen and last Margrave of Lusatia (as Henry IV) from 1221 until his death; from 1242 also Landgrave of Thuringia. Life Born probably at the Albrechtsburg residence in Meissen, Henry was the youngest son of Margrave Theodoric I, Margrave of Meissen and his wife Jutta, daughter of Landgrave Hermann I of Thuringia. In 1221 he succeeded his father as Margrave of Meissen and Lusatia, at first under guardianship of his maternal uncle, Landgrave Louis IV of Thuringia, and after his death in 1227, under that of Duke Albert I of Saxony. In 1230 he was legally proclaimed an adult. Henry had his first combat experience in sometime around 1234, while on crusade in Prussia, fighting against the Pomesanians. His pilgrimage and company is well-documented by Peter of Dusburg, and it resulted in the construction of Balga castle, an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
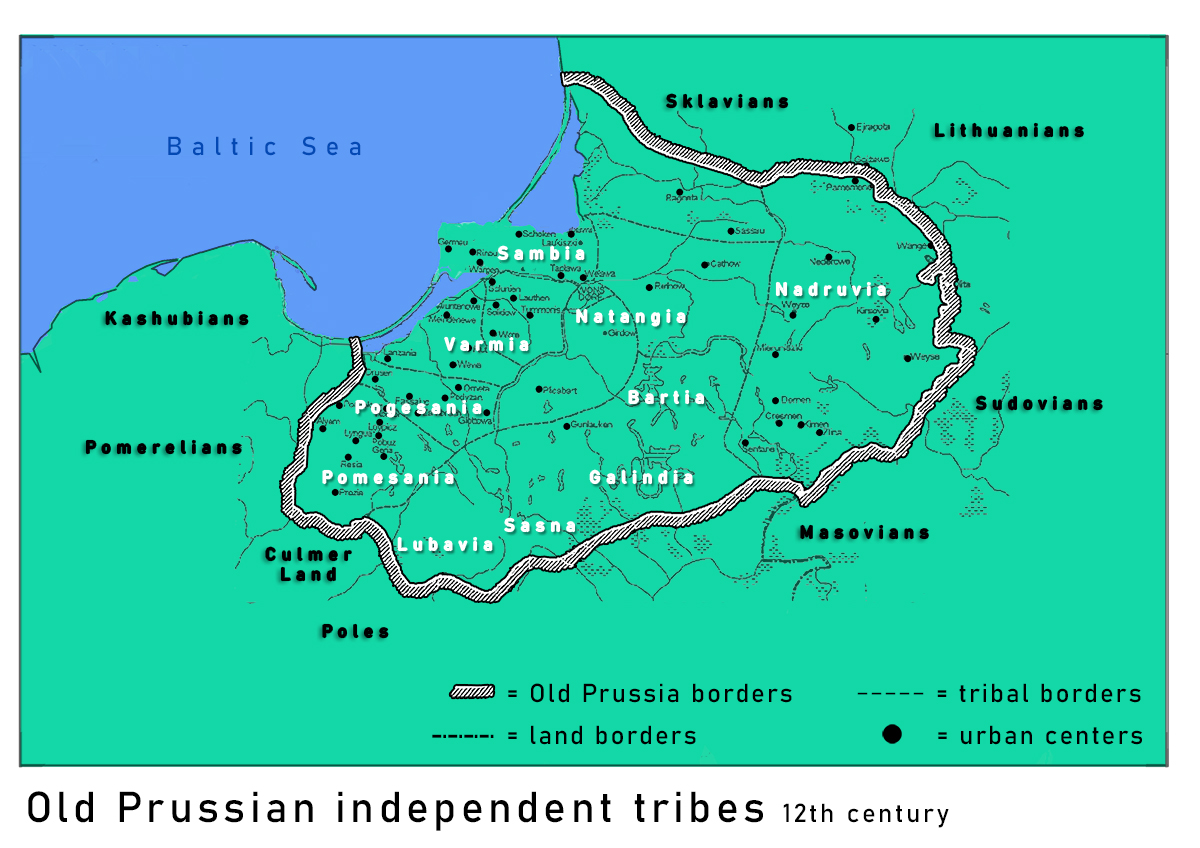
Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Balts, Baltic people that inhabited the Prussia (region), region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. As Balts, they spoke an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language of the Baltic languages, Baltic branch now known as Old Prussian language, Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian Prussian mythology, deities. Their ethnonym was later adopted by predominantly Low German language, Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the State of the Teuton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Germany and is part of the Central German Metropolitan Region. The name of the city is usually interpreted as a Slavic term meaning ''place of linden trees'', in line with many other Slavic placenames in the region. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (the Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster and its tributaries Pleiße and Parthe. The Leipzig Riverside Forest, Europe's largest intra-city riparian forest, has developed along these rivers. Leipzig is at the centre of Neuseenland (''new lake district''). This district has Bodies of water in Leipzig, several artificial lakes created from former lignite Open-pit_mining, open-pit mines. Leipzig has been a trade city s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |