|
PowerBook 165
The PowerBook 160 is a portable computer that was released by Apple Computer along with the PowerBook 180 on October 19, 1992 and the PowerBook 165 variants were released the following year. At the time, it constituted the mid-range model replacing the previous PowerBook 140 in processing power. The PowerBook 160 was sold until August 16, 1993. Basic features Its case design is the same as that of the PowerBook 180, but it shipped with the less powerful 25 MHz Motorola 68030 CPU and no FPU, identically to the low-end 145. However, the PowerBook 160 came with a (diagonal) passive matrix LCD screen, which for the first time was capable of displaying 4-bit grayscale. The 160 and the 180 were the first PowerBooks to add an external color video port like the Macintosh Portable before it, as well as increasing the maximum RAM to 14 MB. Both PowerBooks introduced a new power saving feature which allowed their processors to run at a slower 16 MHz rate, the same speed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerBook 100 Series
The PowerBook 100 series is a line of laptop PCs produced by Apple Computer. In October 1991, Apple released the first three PowerBooks: the low-end PowerBook 100, the more powerful PowerBook 140, and the high-end PowerBook 170, the only one with an active matrix display. These machines caused a stir in the industry with their compact dark grey cases, use of a trackball, and the clever positioning of the keyboard which left room for palmrests on either side of the pointing device. Portable PC computers at the time tended to have the keyboard forward towards the user, with empty space behind it, so this was a surprising innovation and set the standard layout all future notebook computers would follow. The PowerBook 140 and 170 were designed first. The 100 benefited from their development and by components miniaturized by Sony after Apple sent them schematics of the Mac Portable. The 100, however, did not sell well until Apple dropped the price substantially. The 100 and 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerBook 190
The PowerBook 190 and its companion PowerBook 190cs are laptop computers manufactured by Apple Computer as part of their PowerBook brand, introduced to the market in August 1995. The two models differ only in their screen: the 190 had a 9.5" greyscale display, while the 190cs featured a 10.4" color display. Apple's target sales audience for this model was the college student in need of a no-frills portable computer. In terms of hardware, along with the PowerBook 150, the 190 has much in common with Apple's "professional" laptop of the same period, the PowerBook 5300 series. In exchange for the cheaper price point (approximately US$2,200 compared to over US$6,000 for the cutting-edge PowerBook 5300ce), the 190 was equipped with a passive matrix LCD rather than a crisper active matrix screen. More significantly, while the 5300s ran PowerPC 603e processors at 100 or 117 MHz, the 190 had only a Motorola 68LC040 clocked at 33 MHz - in fact, the 190/cs were the last Macintoshes to us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerBook
The PowerBook (known as Macintosh PowerBook before 1997) is a family of Macintosh-type laptop computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer from 1991 to 2006. It was targeted at the professional market; in 1999, the line was supplemented by the home and education-focused iBook family. During its lifetime, the PowerBook went through several major revisions and redesigns, often being the first to incorporate features that would later become standard in competing laptops. The PowerBook was replaced by the MacBook Pro in 2006 as part of the Mac transition to Intel processors. 680x0-based models PowerBook 100 series In October 1991, Apple released the first three PowerBooks: the low-end PowerBook 100, the more powerful PowerBook 140, and the high end PowerBook 170, the only one with an active matrix display. These machines caused a stir in the industry with their compact dark grey cases, built-in trackball, and the innovative positioning of the keyboard tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac OS 7
System 7 (later named Mac OS 7) is the seventh major release of the classic Mac OS operating system for Macintosh computers, made by Apple Computer. It was launched on May 13, 1991, to succeed System 6 with virtual memory, personal file sharing, QuickTime, TrueType fonts, the Force Quit dialog, and an improved user interface. It was code-named "Big Bang" in development and the initial release was named "The System" or "System" like all earlier versions. With version 7.5.1, the name "Mac OS" debuted on the boot screen, and the operating system was officially renamed to Mac OS in 1997 with version 7.6. The Mac OS 7 line was the longest-lasting major version of the Classic Mac OSes due to the troubled development of Copland, an operating system intended to be the successor to OS 7 before its cancellation and replacement with Mac OS 8. Development By 1988, the Macintosh had been on the market for four years. Some aspects of the operating system were beginning to fall behind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
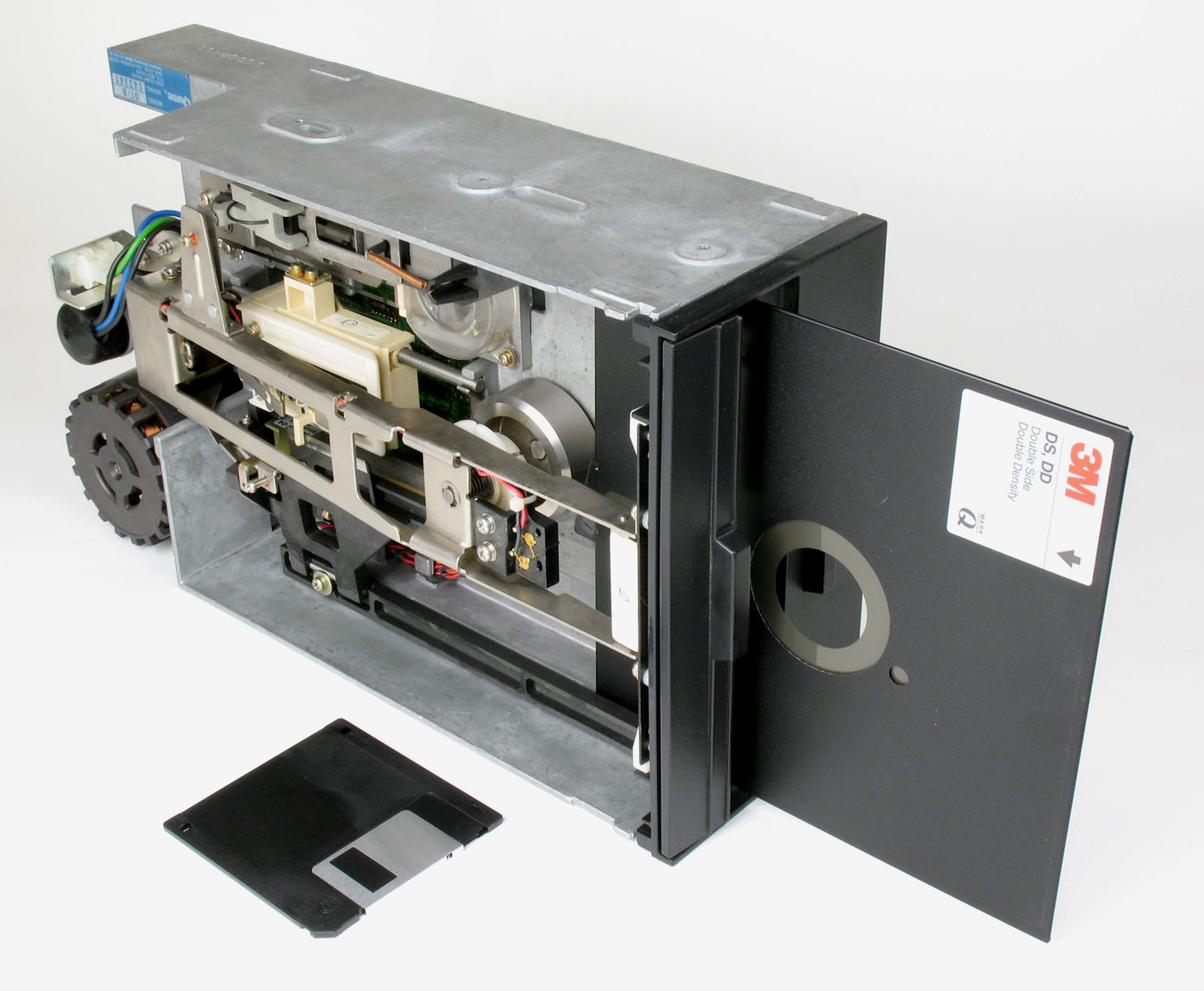
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. The three most popular (and commercially available) floppy disks are the 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch floppy disks. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM in 1971, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch (133.35 mm) and then the 3½-inch (88.9 mm) became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with disk read-and-write head, magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual Block (data storage), blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small disk enclosure, rectangular box. Hard disk drives were introduced by IBM in 1956, and were the dominant secondary storage device for History of general-purpose CPUs, general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Its recommended unit symbol is MB. The unit prefix ''mega'' is a multiplier of (106) in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one megabyte is one million bytes of information. This definition has been incorporated into the International System of Quantities. In the computer and information technology fields, other definitions have been used that arose for historical reasons of convenience. A common usage has been to designate one megabyte as (220 B), a quantity that conveniently expresses the binary architecture of digital computer memory. Standards bodies have deprecated this binary usage of the mega- prefix in favor of a new set of binary prefixes, by means of which the quantity 220 B is named mebibyte (symbol MiB). Definitions The unit megabyte is commonly used for 10002 (one million) bytes or 10242 bytes. The interpretation of using base 1024 originated as technical jargon for the byte m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola 68882
The Motorola 68881 and Motorola 68882 are floating-point units (FPUs) used in some computer systems in conjunction with Motorola's 32-bit 68020 or 68030 microprocessors. These coprocessors are external chips, designed before floating point math became standard on CPUs. The Motorola 68881 was introduced in 1984. The 68882 is a higher performance version produced later. Overview The 68020 and 68030 CPUs were designed with the separate 68881 chip in mind. Their instruction sets reserved the "F-line" instructions – that is, all opcodes beginning with the hexadecimal digit "F" could either be forwarded to an external coprocessor or be used as "traps" which would throw an exception, handing control to the computer's operating system. If an FPU is not present in the system, the OS would then either call an FPU emulator to execute the instruction's equivalent using 68020 integer-based software code, return an error to the program, terminate the program, or crash and require a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
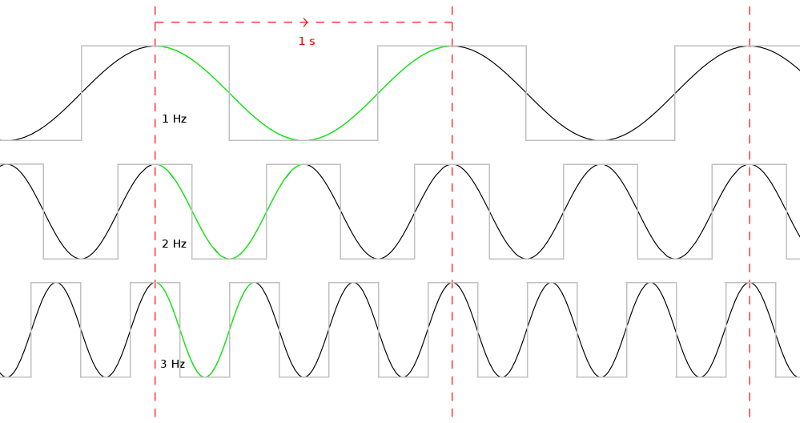
Clock Speed
Clock rate or clock speed in computing typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses used to synchronize the operations of its components. It is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. Clock rate is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers from the 1970s through the 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz). In the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Inc
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Company by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne, the company was incorporated by Jobs and Wozniak as Apple Computer, Inc. the following year. It was renamed Apple Inc. in 2007 as the company had expanded its focus from computers to consumer electronics. Apple is the largest technology company by revenue, with billion in the 2024 fiscal year. The company was founded to produce and market Wozniak's Apple I personal computer. Its second computer, the Apple II, became a best seller as one of the first mass-produced microcomputers. Apple introduced the Lisa in 1983 and the Macintosh in 1984, as some of the first computers to use a graphical user interface and a mouse. By 1985, internal company problems led to Jobs leavin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerBook 180c
The PowerBook 180 is a portable computer released by Apple Computer along with the PowerBook 160 in October 1992. At the time, it constituted the new top-of-the-range model, replacing the previous PowerBook 170. Its case design and features are the same as that of the 170, but it shipped with the more powerful 33 MHz Motorola 68030 CPU and Motorola 68882 FPU. Along with the 160, it introduced a new power-saving feature which allowed the processor to run at a slower 16 MHz rate, the same speed as the original 140. PowerBook 180 The PowerBook 180 came with a (diagonal) active matrix LCD screen capable of displaying 4-bit grayscale at a resolution of 640×400, and a trackball was mounted beneath the keyboard. A 1.44 MB floppy disk drive and 80 MB 2.5-inch hard drive were also standard. The Apple Powerbook also gave an option of possible expansion to a 120 MB hard drive. They are equipped with keyboard stands to slant the keyboard. Like the Macintosh P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating Point Unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root. Modern designs generally include a fused multiply-add instruction, which was found to be very common in real-world code. Some FPUs can also perform various transcendental functions such as exponential or trigonometric calculations, but the accuracy can be low, so some systems prefer to compute these functions in software. Floating-point operations were originally handled in software in early computers. Over time, manufacturers began to provide standardized floating-point libraries as part of their software collections. Some machines, those dedicated to scientific processing, would include specialized hardware to perform some of these tasks with much greater speed. The introduction of microcode in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |