|
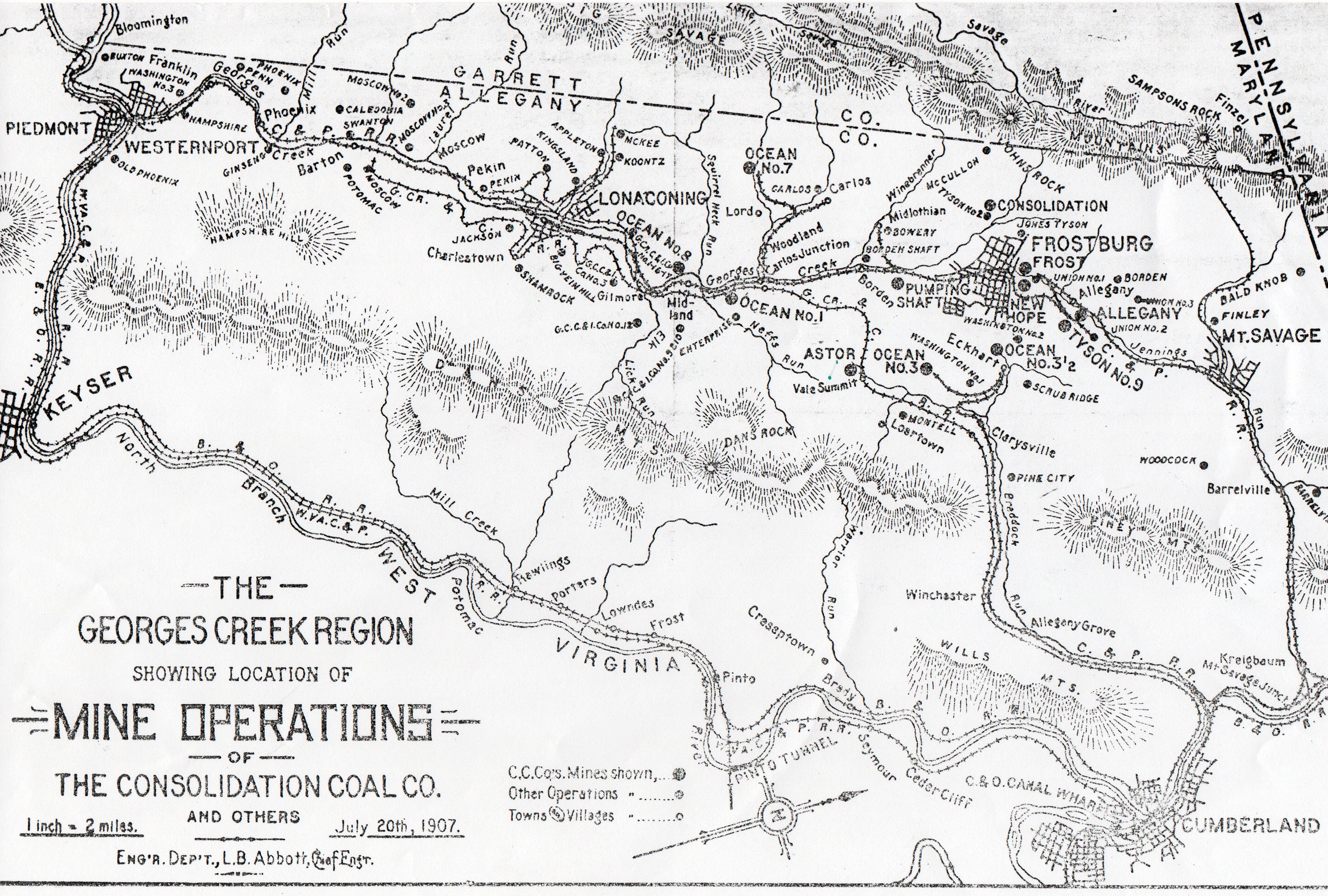
Potomac Wharf Branch
The Potomac Wharf Branch was a historic railroad located in Maryland. It was built by the Maryland Mining Company between 1846 and 1850, as an extension to the Eckhart Branch Railroad. The Potomac Wharf Branch crossed Wills Creek on a bridge (no longer present) just east of the present Route 40 road bridge near Cumberland. Rail tracks from this line may still be seen near some billboards, and a gas station in that area. The area near the creek end of present-day Wills Creek Avenue is known as City Junction, and had a water tank and a tower. The Potomac Wharf Branch was crossed by the Georges Creek & Cumberland Railroad (GC&C). Rail was removed from the section west of the Valley Street crossing as late as 1990. In 1994, rail was removed from this area to maintain the Western Maryland Scenic Railroad, the former GC&C line to Frostburg. The Potomac Wharf Branch Railroad was an early intermodal experiment to provide easy access for western Maryland coal to the markets of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight (see CargoSprinter). Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, push-pull operation has become common, where the train may have a locomotive (or locomotives) at the front, at the rear, or at each end. Most recently railroads have begun adopting DPU or distributed power. The front may have one or two locomotives followed by a mid-train locomotive that is controlled remotely from the lead unit. __TOC__ Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin 'from a place', ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing motion', and is a shortened form of the term ''locomotive engine'', which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate 68
Interstate 68 (I-68) is a Interstate Highway in the US states of West Virginia and Maryland, connecting I-79 in Morgantown, West Virginia, to I-70 in Hancock, Maryland. I-68 is also Corridor E of the Appalachian Development Highway System. From 1965 until the freeway's construction was completed in 1991, it was designated as U.S. Route 48 (US 48). In Maryland, the highway is known as the National Freeway, an homage to the historic National Road, which I-68 parallels between Keysers Ridge and Hancock. The freeway mainly spans rural areas and crosses numerous mountain ridges along its route. A road cut at Sideling Hill exposed geological features of the mountain and has become a tourist attraction. US 219 and US 220 overlap I-68 in Garrett County and Cumberland, respectively, and US 40 overlaps with the freeway from Keysers Ridge to the eastern end of the freeway at Hancock. The construction of I-68 began in 1965 and continued for over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Corps Of Engineers
, colors = , anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day) , battles = , battles_label = Wars , website = , commander1 = Lieutenant general (United States), LTG Scott A. Spellmon , commander1_label = List of United States Army Corps of Engineers Chiefs of Engineers, Chief of Engineers and Commanding General of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers , commander2 = Major general (United States), MG]Richard J. Heitkamp, commander2_label = Deputy Chief of Engineers and Deputy Commanding General , commander3 = Major general (United States), MGKimberly M. Colloton, commander3_label = Deputy Commanding General for Military and International Operations , commander4 = Major general (United States), MG]William H. Graham, commander4_label = Deputy Command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood Control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water levels. Flooding can be caused by a mix of both natural processes, such as extreme weather upstream, and human changes to waterbodies and runoff. Though building hard infrastructure to prevent flooding, such as flood walls, can be effective at managing flooding, increased best practice within landscape engineering is to rely more on soft infrastructure and natural systems, such as marshes and flood plains, for handling the increase in water. For flooding on coasts, coastal management practices have to not only handle changes water flow, but also natural processes like tides. Flood control and relief is a particularly important part of climate change adaptation and climate resilience, both sea level rise and changes in the weather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guard Lock
A control lock, guard lock or stop lock differs from a normal canal lock in that its primary purpose is controlling variances in water level rather than raising or lowering vessels. A control lock may also be known as a tide lock where it is used to control seawater entering into a body of fresh water. Examples The T. J. O’Brien Lock and Dam at Chicago, Illinois is a guard lock that controls the outflow of water from Lake Michigan into the Illinois Waterway while locking vessels through between the waterway and Lake Michigan. Lock 8 near the south end of the Welland Canal at Port Colborne, Ontario, Canada is a guard lock. Due to the large expanse of shallow water in Lake Erie Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ..., changes in wind direction and force create water level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Maryland Railway Station (Cumberland, Maryland)
Cumberland station is a historic railway station in Cumberland, Allegany County, Maryland. It was built in 1913 as a stop for the Western Maryland Railway (WM). The building was operated as a passenger station until the WM ended service in 1959, and it continued to be used by the railway until 1976. It was subsequently restored and currently serves as a museum and offices, as well as the operating base for a heritage railway. Description The station was designed by Baltimore architect C. M. Anderson, and sited on a filled-in basin at the terminus of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal. The building is a large commercial-style building that expresses the architectural functionalism of the turn of the 20th century. The brick structure is nine bays long and three bays wide, with two monumental stories on the west facade and three stories on the east. A one-story platform shelter runs along the west facade and extends out toward the tracks. History The WM began daily through-train passen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore And Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of the National Road early in the century, wanted to do business with settlers crossing the Appalachian Mountains. The railroad faced competition from several existing and proposed enterprises, including the Albany-Schenectady Turnpike, built in 1797, the Erie Canal, which opened in 1825, and the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal. At first, the B&O was located entirely in the state of Maryland; its original line extending from the port of Baltimore west to Sandy Hook, Maryland, opened in 1834. There it connected with Harper's Ferry, first by boat, then by the Wager Bridge, across the Potomac River into Virginia, and also with the navigable Shenandoah River. Because of competition with the C&O Canal for trade with coal fields in western Marylan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate Commerce Commission
The Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) was a regulatory agency in the United States created by the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887. The agency's original purpose was to regulate railroads (and later trucking) to ensure fair rates, to eliminate rate discrimination, and to regulate other aspects of common carriers, including interstate bus lines and telephone companies. Congress expanded ICC authority to regulate other modes of commerce beginning in 1906. Throughout the 20th century, several of ICC's authorities were transferred to other federal agencies. The ICC was abolished in 1995, and its remaining functions were transferred to the Surface Transportation Board. The Commission's five members were appointed by the President with the consent of the United States Senate. This was the first independent agency (or so-called '' Fourth Branch''). Creation The ICC was established by the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887, which was signed into law by President Grover Cleveland. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Savage Railroad
The Mount Savage Railroad was a railroad operated by the Maryland and New York Coal and Iron Company of Mount Savage, Maryland between 1845 and 1854. The 14.9 miles (24 km) rail line ran from Frostburg, Maryland, Frostburg to Cumberland, Maryland. History The railroad was opened for use on Monday, September 24, 1845. The railroad was the first in America to use iron rail that was produced within the country, having to rely on British rail beforehand. Linking Mount Savage to the regional infrastructure Before the railroad linked Mount Savage to Cumberland, Mount Savage had no way of transporting manufactured goods to the rest of the region. When the railroad reached Cumberland, Mount Savage now had a link to the National Road, the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, and the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. The interchange in the Cumberland Narrows area also linked Mount Savage to the Potomac Wharf Branch. The Potomac Wharf Branch The Potomac Wharf Branch was built by the Maryland Mining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wharf
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more Berth (moorings), berths (Mooring (watercraft), mooring locations), and may also include piers, warehouses, or other facilities necessary for handling the ships. Wharves are often considered to be a series of docks at which boats are stationed. Overview A wharf commonly comprises a fixed platform, often on deep foundation, pilings. Commercial ports may have warehouses that serve as interim storage: where it is sufficient a single wharf with a single berth constructed along the land adjacent to the water is normally used; where there is a need for more capacity multiple wharves, or perhaps a single large wharf with multiple berths, will instead be constructed, sometimes projecting over the water. A pier, raised over the water rather than within it, is commonly use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesapeake And Ohio Canal
The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, abbreviated as the C&O Canal and occasionally called the "Grand Old Ditch," operated from 1831 until 1924 along the Potomac River between Washington, D.C. and Cumberland, Maryland. It replaced the Potomac Canal, which shut down completely in 1828, and could operate during months in which the water level was too low for the former canal. The canal's principal cargo was coal from the Allegheny Mountains. Construction on the canal began in 1828 and ended in 1850 with the completion of a stretch to Cumberland, although the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad had already reached Cumberland in 1842. Rising and falling over an elevation change of , it required the construction of 74 Lock (water transport), canal locks, 11 Navigable aqueduct, aqueducts to cross major streams, more than 240 culverts to cross smaller streams, and the Paw Paw Tunnel. A planned section to the Ohio River at Pittsburgh was never built. The canalway is now maintained as the Chesapeake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_train.jpg)