|
Positive Integer
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive integers Some authors acknowledge both definitions whenever convenient. Sometimes, the whole numbers are the natural numbers as well as zero. In other cases, the ''whole numbers'' refer to all of the integers, including negative integers. The counting numbers are another term for the natural numbers, particularly in primary education, and are ambiguous as well although typically start at 1. The natural numbers are used for counting things, like "there are ''six'' coins on the table", in which case they are called ''cardinal numbers''. They are also used to put things in order, like "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country", which are called ''ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are also used as labels, like jersey numbers on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Baskets With Apples
3 (three) is a number, numeral (linguistics), numeral and numerical digit, digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic numerals, Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a Product (mathematics), product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorization, factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow primality test, method of checking the primality of a given number , called trial division, tests whether is a multiple of any integer between 2 and . Faster algorithms include the Miller–Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as an Akkadian-populated but Amorites, Amorite-ruled state . During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was retrospectively called "the country of Akkad" ( in Akkadian), a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older ethno-linguistically related state of Assyria in the north of Mesopotamia and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi (floruit, fl. –1752 BC middle chronology, or –1654 BC, short chronology timeline, short chronology) created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arrondissement (district or ward) and home to some of the most Western canon, canonical works of Art of Europe, Western art, including the ''Mona Lisa,'' ''Venus de Milo,'' and ''Winged Victory''. The museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II of France, Philip II. Remnants of the Medieval Louvre fortress are visible in the basement of the museum. Due to urban expansion, the fortress eventually lost its defensive function, and in 1546 Francis I of France, Francis I converted it into the primary residence of the French kings. The building was redesigned and extended many times to form the present Louvre Palace. In 1682, Louis XIV chose the Palace of Versailles for his househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
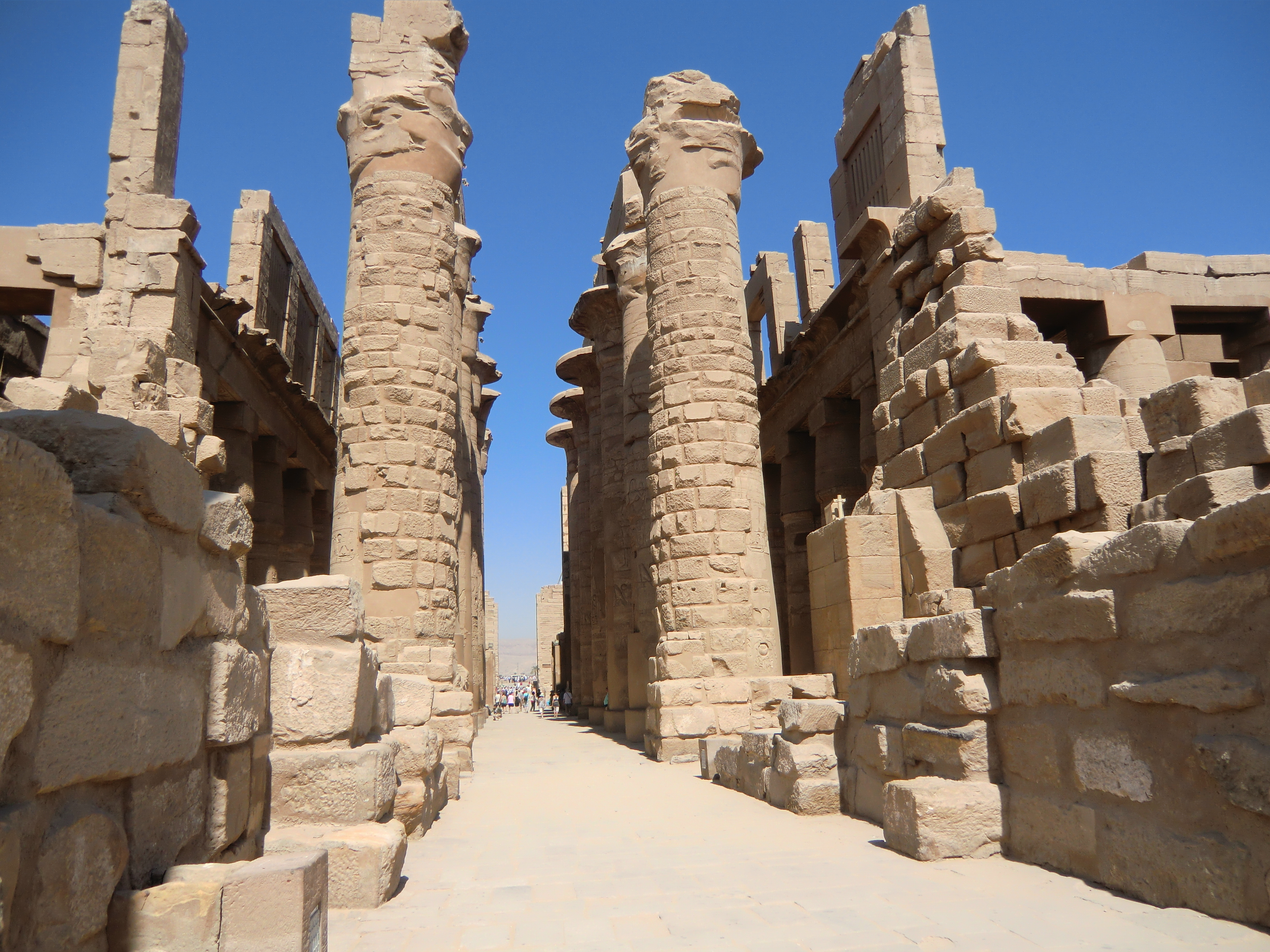
Karnak
The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak (), comprises a vast mix of temples, pylons, chapels, and other buildings near Luxor, Egypt. Construction at the complex began during the reign of Senusret I (reigned 1971–1926 BC) in the Middle Kingdom () and continued into the Ptolemaic Kingdom (305–30 BC), although most of the extant buildings date from the New Kingdom. The area around Karnak was the ancient Egyptian ''Ipet-isut'' ("The Most Selected of Places") and the main place of worship of the 18th Dynastic Theban Triad, with the god Amun as its head. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes, and in 1979 it was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List along with the rest of the city. Karnak gets its name from the nearby, and partly surrounded, modern village of El-Karnak, north of Luxor. Name The original name of the temple was ''Ipet-isut'', meaning "The Most Select of Places". The complex's modern name "Karnak" comes from the nearby village of el-Karnak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Hieroglyphs
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined Ideogram, ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters.In total, there were about 1,000 graphemes in use during the Old Kingdom period; this number decreased to 750–850 during the Middle Kingdom, but rose instead to around 5,000 signs during the Ptolemaic period. Antonio Loprieno, ''Ancient Egyptian: A Linguistic Introduction'' (Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1995), p. 12. Cursive hieroglyphs were used for Ancient Egyptian literature, religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic (Egyptian), demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet. Egyptian hieroglyphs are the ultimate ancestor of the Phoenician alphabet, the first widely adopted phonetic writing system. Moreov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt spans the period of Egyptian history from the early prehistoric Egypt, prehistoric settlements of the northern Nile valley to the Roman Egypt, Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC. The pharaonic period, the period in which Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh, is dated from the 32nd century BC, when Upper and Lower Egypt were unified, until the country fell under Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonian rule in 332 BC. Chronology ;Note: For alternative 'revisions' to the chronology of Egypt, see Egyptian chronology. Egypt's history is split into several different periods according to the ruling dynasty of each pharaoh. The dating of events is still a subject of research. The conservative dates are not supported by any reliable absolute date for a span of about three millennia. The following is the list according to conventional Egyptian chronology. * Prehistoric Egypt (prior to 3100 BC) * Naqada III ("the protodynastic period", approximately 3100–3000 BC; somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numeral System
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers; that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using digits or other symbols in a consistent manner. The same sequence of symbols may represent different numbers in different numeral systems. For example, "11" represents the number ''eleven'' in the decimal or base-10 numeral system (today, the most common system globally), the number ''three'' in the binary or base-2 numeral system (used in modern computers), and the number ''two'' in the unary numeral system (used in tallying scores). The number the numeral represents is called its ''value''. Additionally, not all number systems can represent the same set of numbers; for example, Roman, Greek, and Egyptian numerals don't have a representation of the number zero. Ideally, a numeral system will: *Represent a useful set of numbers (e.g. all integers, or rational numbers) *Give every number represented a unique representation (or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
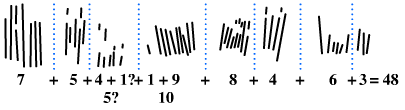
Tally Mark
Tally marks, also called hash marks, are a form of numeral used for counting. They can be thought of as a unary numeral system. They are most useful in counting or tallying ongoing results, such as the score in a game or sport, as no intermediate results need to be erased or discarded. However, because of the length of large numbers, tallies are not commonly used for static text. Notched sticks, known as tally sticks, were also historically used for this purpose. Early history Counting aids other than body parts appear in the Upper Paleolithic. The oldest tally sticks date to between 35,000 and 25,000 years ago, in the form of notched bones found in the context of the European Aurignacian to Gravettian and in Africa's Late Stone Age. The so-called '' Wolf bone'' is a prehistoric artifact discovered in 1937 in Czechoslovakia during excavations at Dolní Věstonice, Moravia, led by Karl Absolon. Dated to the Aurignacian, approximately 30,000 years ago, the bone is mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger Counting
Finger-counting, also known as dactylonomy, is the act of counting using one's fingers. There are multiple different systems used across time and between cultures, though many of these have seen a decline in use because of the spread of Arabic numerals. Finger-counting can serve as a form of manual communication, particularly in marketplace trading – including hand signaling (open outcry), hand signaling during open outcry in floor trading – and also in hand games, such as Morra (game), morra. Finger-counting is known to go back to ancient Egypt at least, and probably even further back. notes that as early as the 3rd millennium BCE, in Egypt's Old Kingdom, in the Pyramid texts' "Spell for obtaining a ferry-boat", the ferryman might object "Did you bring me a man who cannot number his fingers?". This spell was needed to cross a canal of the nether-world, as detailed in the Book of the Dead. Historical counting Complex systems of dactylonomy were used in the ancient world. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishango Bone (cropped)
The Ishango bone, discovered at the "Fisherman Settlement" of Ishango in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, is a bone tool and possible mathematical device that dates to the Upper Paleolithic era. The curved bone is dark brown in color, about 10 centimeters in length, and features a sharp piece of quartz affixed to one end, perhaps for engraving. Because the bone has been narrowed, scraped, polished, and engraved to a certain extent, it is no longer possible to determine what animal the bone belonged to, although it is assumed to have been a mammal.Association pour la diffusion de l'information archéologique/Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, Brussels (n.d.). "Have You Heard of Ishango?" (PDF). ''Natural Sciences''. The ordered engravings have led many to speculate the meaning behind these marks, including interpretations like mathematical significance or astrological relevance. It is thought by some to be a tally stick, as it features a series of what has been in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numeral System
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers; that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using digits or other symbols in a consistent manner. The same sequence of symbols may represent different numbers in different numeral systems. For example, "11" represents the number ''eleven'' in the decimal or base-10 numeral system (today, the most common system globally), the number ''three'' in the binary or base-2 numeral system (used in modern computers), and the number ''two'' in the unary numeral system (used in tallying scores). The number the numeral represents is called its ''value''. Additionally, not all number systems can represent the same set of numbers; for example, Roman, Greek, and Egyptian numerals don't have a representation of the number zero. Ideally, a numeral system will: *Represent a useful set of numbers (e.g. all integers, or rational numbers) *Give every number represented a unique representation (or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |