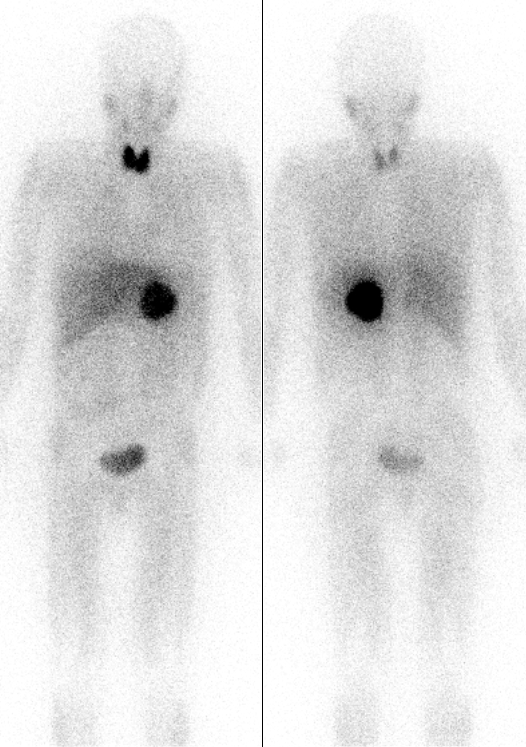
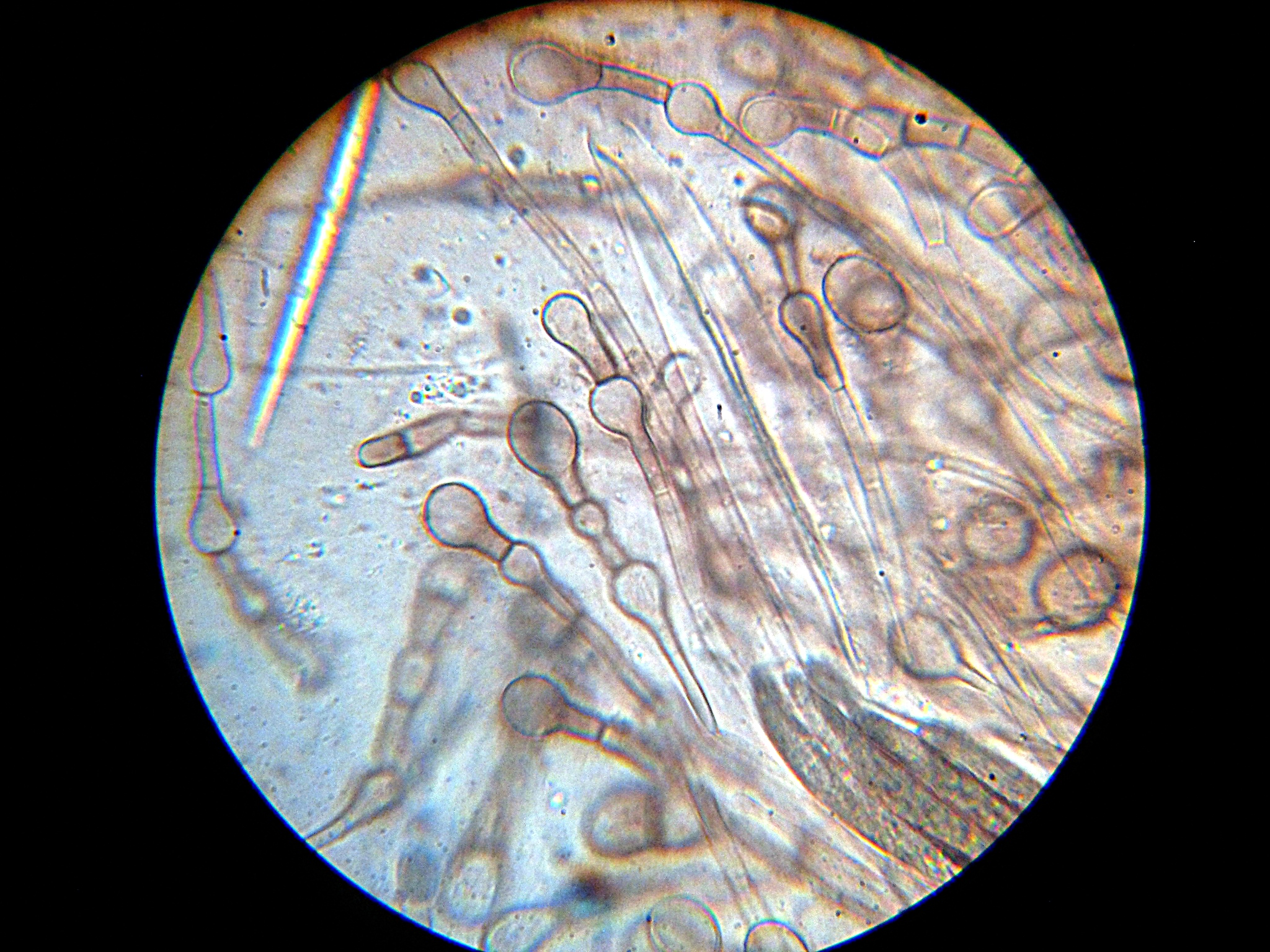
|
Porina Leptalea
''Porina'' is a genus of crustose lichens in the family Porinaceae. , Species Fungorum (in the Catalogue of Life) accepts 161 species of ''Porina''. Taxonomy The genus was circumscribed in 1809 by the Swedish lichenologist Erik Acharius. His of the genus was as follows (translated from Latin): "Apothecium wart-like, formed from the thallus, including several thalamia covered by a very delicate, transparent perithecium, marked above by impressed ostioles; nuclei somewhat globose, containing cellular vesicles. Thallus cartilaginous-membranous, uniform". Acharius included a single species in the genus, ''Porina pertusa'' (originally named by Carl Linnaeus in 1767 as ''Lichen pertusus''); this species is now known as ''Pertusaria pertusa''. Description The genus ''Porina'' comprises crustose lichens, characterised by their crust-like appearance that can range from being completely immersed in their to sitting on the surface. The thallus, or body of the lichen, may or may not hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary Colony (biology), colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a lophophore, a "crown" of tentacles used for filter feeder, filter feeding. Most Marine (ocean), marine bryozoans live in tropical waters, but a few are found in oceanic trenches and polar waters. The bryozoans are classified as the Stenolaemata, marine bryozoans (Stenolaemata), Phylactolaemata, freshwater bryozoans (Phylactolaemata), and Gymnolaemata, mostly-marine bryozoans (Gymnolaemata), a few members of which prefer brackish water. 5,869living species are known. Originally all of the crown group Bryozoa were colonial, but as an adaptation to a mesopsammal (interstitial spaces in marine sand) life or to deep-sea habitats, secondarily solitary forms have since evolved. Solitary species have been described i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is a form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specialized reproductive structures, which are sometimes called vegetative propagules. Many plants naturally reproduce this way, but it can also be induced artificially. Horticulturists have developed asexual propagation techniques that use vegetative propagules to replicate plants. Success rates and difficulty of propagation vary greatly. Monocotyledons typically lack a vascular cambium, making them more challenging to propagate. Plant propagation Plant propagation is the process of plant reproduction of a species or cultivar, and it can be sexual or asexual. It can happen through the use of vegetative parts of the plants, such as leaves, stems, and roots to produce new plants or through growth from specialized vegetative plant parts. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascospore
In fungi, an ascospore is the sexual spore formed inside an ascus—the sac-like cell that defines the division Ascomycota, the largest and most diverse Division (botany), division of fungi. After two parental cell nucleus, nuclei fuse, the ascus undergoes meiosis (halving of genetic material) followed by a mitosis (cell division), ordinarily producing eight genetically distinct haploid spores; most yeasts stop at four ascospores, whereas some moulds carry out extra post-meiotic divisions to yield dozens. Many asci build turgor, internal pressure and shoot their spores clear of the calm boundary layer, thin layer of still air enveloping the fruit body, whereas subterranean truffles depend on animals for biological dispersal, dispersal. Ontogeny, Development shapes both form and endurance of ascospores. A hook-shaped crozier aligns the paired nuclei; a double-biological membrane, membrane system then parcels each daughter nucleus, and successive wall layers of β-glucan, chitosan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascus
An ascus (; : asci) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. '' Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. '' Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some '' Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Iodide
Potassium iodide is a chemical compound, medication, and dietary supplement. It is a medication used for treating hyperthyroidism, in radiation emergencies, and for protecting the thyroid gland when certain types of radiopharmaceuticals are used. It is also used for treating skin sporotrichosis and phycomycosis. It is a supplement used by people with low dietary intake of iodine. It is administered orally. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash, and swelling of the salivary glands. Other side effects include allergic reactions, headache, goitre, and depression. While use during pregnancy may harm the baby, its use is still recommended in radiation emergencies. Potassium iodide has the chemical formula K I. Commercially it is made by mixing potassium hydroxide with iodine. Potassium iodide has been used medically since at least 1820. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Potassium iodide is available as a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
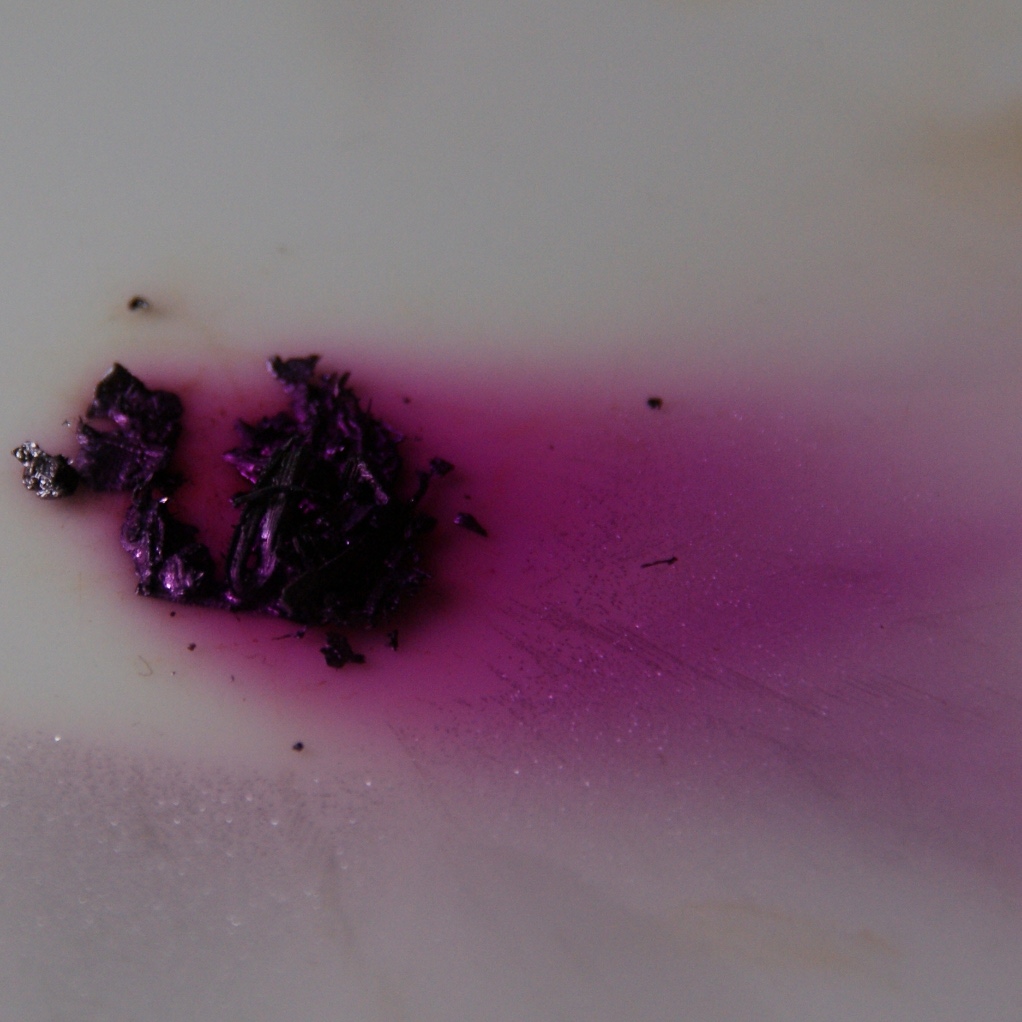
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek , meaning 'violet'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compounds, it has also found favour as a non-toxic radiocontrast material. Because of the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia ( basidiomycetes) or paraphyses ( ascomycetes). Cystidia are often important for microscopic identification. The subhymenium consists of the supportive hyphae from which the cells of the hymenium grow, beneath which is the hymenophoral trama, the hyphae that make up the mass of the hymenophore. The position of the hymenium is traditionally the first characteristic used in the classification and identification of mushrooms. Below are some examples of the diverse types which exist among the macroscopic Basidiomycota and Ascomycota. * In agarics, the hymenium is on the vertical faces of the gills. * In boletes and polypores, it is in a spongy mass of downward-pointing tubes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (: cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are o ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycopeltis
''Phycopeltis'' is a genus of green algae in the family Trentepohliaceae.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Phycopeltis Data extracted from the It is widespread in humid, tropical or subtropical regions. It typically occurs as an epiphyte on the surface of leaves, but may sometimes be found on rock, metal, or plastic surfaces. It can also be a phycobiont in lichens. Description ''Phycopeltis'' consists of a single layer of coalescing, prostrate filaments that irregularly or regularly branch to form a small rounded or irregular disk. Some species have erect filaments growing out from the thallus, and/or "glandular" papillate cells. The thalli grow up to 7 mm in diameter. In shade, the thalli are green; with exposure to light or less humid conditions, they become pale yellow, orange or reddish brown due to the accumulation of carotenoid pigments and oil. Asexual reproduction occurs by quadriflagellate zoospores, which are produced in sporangia that arise on curved, one- to many-celled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foliicolous Lichen
A foliicolous lichen is a lichen which grows on the surfaces of living leaves of vascular plants, usually inhabiting the upper surface (''epiphyllous'') but sometimes also the lower surface (''hypophyllous''). Foliicolous lichens largely occur in tropical environments and of the over 800 foliicolous lichens accepted (as of 2008) over 600 of these are known from the tropics. Unlike most lichens which are common in humid but cool and temperate climates, these tropical lichens are more suited to the higher temperatures and lower light levels present beneath the rainforest Canopy (biology), canopy, where they are involved in the nutrient cycle and water cycle, water retention. Chlorophyta are common photosynthetic partner phycobionts of epiphyllous lichens.Lichen Photobionts, University of Nebraska Oma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trentepohlia (alga)
''Trentepohlia'' is a genus of filamentous chlorophyte green algae in the family Trentepohliaceae, living free on terrestrial supports such as tree trunks and wet rocks or symbiotically in lichens. The filaments of ''Trentepohlia'' often have a strong orange colour (photograph at right) caused by the presence of large quantities of carotenoid pigments which mask the green of the chlorophyll. Nomenclature Organisms belonging to the genus ''Trentepohlia'' were first described by Linnaeus in 1759; he named his species ''Byssus aureus'' (currently known as ''Trentepohlia aurea''). The genus was circumscribed by Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius in Fl. Crypt. Erlang. on page 351 in 1817. The genus name of ''Trentepohlia'' is in honour of Johann Friedrich Trentepohl (1748–1806), who was a German clergyman and botanist. He worked as a lecturer and Pastor in various places in Wesermarsch. Martius' name was conserved in favor of the moss genus ''Trentepohlia'' and the Brassicaceae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |