|
Popliteal Artery
The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries. The deepest (most anterior) structure in the fossa, the popliteal artery runs close to the joint capsule of the knee as it spans the intercondylar fossa. Five genicular branches of the popliteal artery supply the capsule and ligaments of the knee joint. The genicular arteries are the superior lateral, superior medial, middle, inferior lateral, and inferior medial genicular arteries. They participate in the formation of the periarticular genicular anastomosis, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation capable of maintaining blood supply to the leg during full knee flexion, which may kink the popliteal artery. Structure The popliteal artery is the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh. The femoral artery proximal to the origin of the deep femoral artery is referred to as the ''common femoral artery'', whereas the femoral artery distal to this origin is referred to as the ''superficial femoral artery''. Structure The femoral artery represents the continuation of the external iliac artery beyond the inguinal ligament underneath which the vessel passes to enter the thigh. The vessel passes under the inguinal ligament just medial of the midpoint of this ligament, midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercondylar Fossa Of Femur
The intercondylar fossa of femur (intercondyloid fossa of femur, intercondylar notch of femur) is a deep notch between the rear surfaces of the medial and lateral epicondyle of the femur, two protrusions on the distal end of the femur (thigh bone) that joins the knee. On the front of the femur, the condyles are but much less prominent and are separated from one another by a smooth shallow articular depression called the patellar surface because it articulates with the posterior surface of the patella The patella (: patellae or patellas), also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in m ... (kneecap). The intercondylar fossa of femur and/or the patellar surface may also be referred to as the patellar groove, patellar sulcus, patellofemoral groove, femoropatellar groove, femoral groove, femoral sulcus, trochlear groove of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
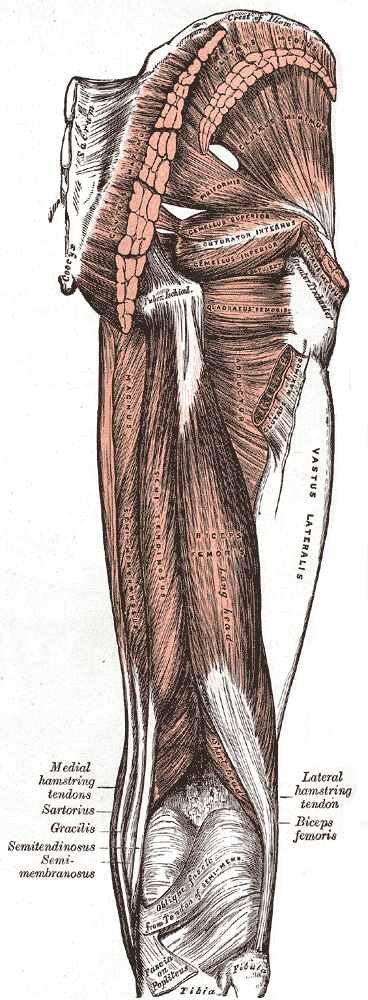
Hamstring
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris. Etymology The word " ham" is derived from the Old English “ham” or “hom” meaning the hollow or bend of the knee, from a Germanic base where it meant "crooked". It gained the meaning of the leg of an animal around the 15th century. ''String'' refers to tendons, and thus the hamstrings' string-like tendons felt on either side of the back of the knee. Criteria The common criteria of any hamstring muscles are: # Muscles should originate from ischial tuberosity. # Muscles should be inserted over the knee joint, in the tibia or in the fibula. # Muscles will be innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve. # Muscle will participate in flexion of the knee joint and extension of the hip joint. Those muscles which fulfill all of the four criteria are called true hamstrings. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Inferior Genicular Artery
The medial inferior genicular is an artery of the leg. Course It first descends along the upper margin of the popliteus, to which it gives branches; it then passes below the medial condyle of the tibia, beneath the tibial collateral ligament, at the anterior border of which it ascends to the front and medial side of the joint, to supply the upper end of the tibia The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ... and the knee-joint, anastomosing with the lateral inferior genicular artery, lateral inferior and medial superior genicular arteries. References See also * Patellar anastomosis Arteries of the lower limb {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Inferior Genicular Artery
The lateral inferior genicular is an artery of the leg. Course It runs lateralward above the head of the fibula to the front of the knee-joint, passing in its course beneath the lateral head of the gastrocnemius, the fibular collateral ligament, and the tendon of the biceps femoris. Branching It ends by dividing into branches, which anastomose with the Inferior medial genicular and superior lateral genicular arteries, and with the anterior recurrent tibial artery. See also * Patellar anastomosis The patellar network (circulatory anastomosis around the knee-joint, patellar anastomosis, genicular anastomosis, articular vascular network of knee or rete articulare genus) is an intricate network of blood vessels around and above the patella, ... References Arteries of the lower limb {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Superior Genicular Artery
The lateral superior genicular artery is a branch of the popliteal artery that supplies a portion of the knee joint. Anatomy Course and relations It passes above the lateral condyle of the femur. It runs deep to the tendon of the biceps femoris. Branches It divides into a superficial and a deep branch; the superficial branch supplies the vastus lateralis, and anastomoses with the descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex and the lateral inferior genicular arteries; the deep branch supplies the lower part of the femur and knee-joint In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ..., and forms an anastomotic arch across the front of the bone with the highest genicular and the medial inferior genicular arteries. Additional images File:Thigh arteries schema.s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Superior Genicular Artery
The medial superior genicular artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It runs deep to the semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and tendon of the adductor magnus, and superior to the medial head of the gastrocnemius. It divides into two branches, one of which supplies the vastus medialis The vastus medialis (vastus internus or teardrop muscle) is an extensor muscle located medially in the thigh that extends the knee. The vastus medialis is part of the quadriceps muscle group. Structure The vastus medialis is a muscle presen ..., anastomosing with the highest genicular and medial inferior genicular arteries; the other ramifies close to the surface of the femur, supplying it and the knee-joint, and anastomosing with the lateral superior genicular artery. The medial superior genicular artery is frequently of small size, a condition which is associated with an increase in the size of the highest genicular. See also * Patellar anastomosis References Arteries of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sural Artery
Sural (, also Romanized as Sūrāl; also known as Surhāl) is a village in Sis Rural District (Dehgolan County), Sis Rural District, Bolbanabad District, Dehgolan County, Kurdistan province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 241, in 56 families. The village is populated by Kurds. References Towns and villages in Dehgolan County Kurdish settlements in Kurdistan province {{Dehgolan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semimembranosus
The semimembranosus muscle () is the most medial of the three hamstring muscles in the thigh. It is so named because it has a flat tendon of origin. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, deep to the semitendinosus muscle. It extends the hip joint and flexes the knee joint. Structure The semimembranosus muscle, so called from its membranous tendon of origin, is situated at the back and medial side of the thigh. It is wider, flatter, and deeper than the semitendinosus (with which it shares very close insertion and attachment points). The muscle overlaps the upper part of the popliteal vessels. Origin The semimembranosus muscle originates by a thick tendon from the superolateral aspect of the ischial tuberosity. It arises above and medial to the biceps femoris muscle and semitendinosus muscle. The tendon of origin expands into an aponeurosis, which covers the upper part of the anterior surface of the muscle; from this aponeurosis, muscular fibers arise, and converge to another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantaris
The plantaris is one of the superficial muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, one of the fascial compartments of the leg. It is composed of a thin muscle belly and a long thin tendon. While not as thick as the achilles tendon, the plantaris tendon (which tends to be between in length) is the longest tendon in the human body. Not including the tendon, the plantaris muscle is approximately long and is absent in 8-12% of the population. It is one of the plantar flexors in the posterior compartment of the leg, along with the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. The plantaris is considered to have become an unimportant muscle when human ancestors switched from climbing trees to bipedalism and in anatomically modern humans it mainly acts with the gastrocnemius. Structure The plantaris muscle arises from the inferior part of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the femur at a position slightly superior to the origin of the lateral head of gastrocnemius. It passes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceps Femoris
The biceps femoris () is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion (but not hip extension) and is activated by a separate nerve (the peroneal, as opposed to the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve). Structure It has two heads of origin: *the ''long head'' arises from the lower and inner impression on the posterior part of the tuberosity of the ischium. This is a common tendon origin with the semitendinosus muscle, and from the lower part of the sacrotuberous ligament. *the ''short head'', arises from the lateral lip of the linea aspera, between the adductor magnus and vastus lateralis extending up almost as high as the insertion of the gluteus maximus, from the lateral prolongation of the linea aspera to within 5 cm. of the lateral condyle; and from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibial Nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus. Structure Popliteal fossa The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root values of L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3. It lies superficial (or posterior) to the popliteal vessels, extending from the superior angle to the inferior angle of the popliteal fossa, crossing the popliteal vessels from lateral to medial side. It gives off branches as shown below: * Muscular branches - Muscular branches arise from the distal part of the popliteal fossa. It supplies the medial and lateral heads of gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and popliteus muscles. Nerve to popliteus crosses the popliteus muscle, runs downwards and laterally, winds around the lower border of the popliteus to supply the deep (or anterior) surface of the popliteus. This nerve also supplies the tibialis posterior muscle, superior tibiofibular joint, tibia bone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |