|
Poplar Railway Station
Poplar was a railway station in Poplar, London, that was opened in 1840 by the Commercial Railway (later the London and Blackwall Railway (LBR)) and was situated between Millwall Junction and Blackwall, down-line from . It was closed in 1926, at which time it was owned by the London and North Eastern Railway. History The station was opened on 6 July 1840 on the west side of Brunswick Street, to the north of the Blackwall Yard shipyard, but was re-sited five years later across the road to the east side.http://www.disused-stations.org.uk/p/poplar/index.shtml It remained open until 4 May 1926, when all passenger services on the line east of Stepney ceased. The station buildings were demolished in the 1930s but the platforms remained as the railway fell into disuse in the 1960s before finally being demolished in the early 1980s to make way for the Docklands Light Railway. During its life there was another station named Poplar on the North London Railway (NLR), which was situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And Blackwall Railway
Originally called the Commercial Railway, the London and Blackwall Railway (L&BR) in east London, England, ran from Minories to Blackwall via Stepney, with a branch line to the Isle of Dogs, connecting central London to many of London's docks. It was operational from 1840 until 1926 (for passengers) and 1968 (for goods), closing after the decline of inner London's docks. Much of its infrastructure was reused as part of the Docklands Light Railway. The L&BR was leased by the Great Eastern Railway in 1866, but remained independent until absorbed into the London and North Eastern Railway at the 1923 Grouping. Another branch was opened in 1871, the Millwall Extension Railway. History It was authorised by an Act of Parliament entitled ''An Act for making a Railway from the Minories to Blackwall, with Branches, to be called "The Commercial Railway"'' dated 28 July 1836 in the reign of William IV. The length of the railway was to be . The engineer of the line was intended to be Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Dock Road
East India Dock Road is a major arterial route from Limehouse to Canning Town in London. The road takes its name from the former East India Docks in the Port of London, and partly serves as the high street of Poplar. To the west it becomes Commercial Road and to the east Newham Way. It forms part of the A13, a major road connecting the historic City of London to Tilbury and Southend. History The road begins in the west at Burdett Road and continues to the River Lea bridge in the east at Bow Creek. It was built in order to connect the newly built Commercial Road at Limehouse with the East India Docks, which opened in 1806, bypassing Poplar High Street. It passed over undeveloped land and was assumed to be cheap to construct, but the costs of buying garden land proved higher than anticipated. The original plan called for the road to be built as far as the River Lea, and it is shown ending there on Richard Horwood's 1807 map of London. In June 1809, an Act of Parliament was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Closed In 1926
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1840
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Eastern Railway
The Great Eastern Railway (GER) was a pre-grouping British railway company, whose main line linked London Liverpool Street to Norwich and which had other lines through East Anglia. The company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway in 1923. Formed in 1862 after the amalgamation of the Eastern Counties Railway and several other smaller railway companies the GER served Cambridge, Chelmsford, Colchester, Great Yarmouth, Ipswich, King's Lynn, Lowestoft, Norwich, Southend-on-Sea (opened by the GER in 1889), and East Anglian seaside resorts such as Hunstanton (whose prosperity was largely a result of the GER's line being built) and Cromer. It also served a suburban area, including Enfield, Chingford, Loughton and Ilford. This suburban network was, in the early 20th century, the busiest steam-hauled commuter system in the world. The majority of the Great Eastern's locomotives and rolling stock were built at Stratford Works, part of which was on the site of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poplar DLR Station
Poplar is a Docklands Light Railway (DLR) station in Poplar in London, England. Poplar is a cross-platform interchange station for three of the six lines on the DLR (-, Bank- and Tower Gateway-) making it one of the busiest stations on the network in terms of services. It is also nearby the Canary Wharf Station on Crossrail's Elizabeth Line. History Long before the opening of the DLR in 1987, there had been three stations with the name Poplar. However, none was on the site of the current station. * Poplar railway station was on the London and Blackwall Railway between 8 July 1840 to 4 May 1926. This is near the site of Blackwall DLR station. * Poplar (East India Dock Road) railway station on the North London Railway was in use from 1866 until 1944. This is now the site of All Saints DLR station. * A third station named Poplar was constructed in 1851 but never opened. This was sited due south of the North London Railway station (now All Saints DLR), and due east of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackwall DLR Station
Blackwall is a Docklands Light Railway (DLR) station in Blackwall area of Poplar in London, England. It is located very close to the northern entrance to the Blackwall road tunnel under the River Thames. The station is on the Beckton branch of the DLR between Poplar and East India stations. The DLR station opened, with the Beckton Branch, on 28 March 1994. There was a previous station very close to this site, called Poplar station, which was served by the London and Blackwall Railway from 6 July 1840 to 3 May 1926. Poplar station was along the route of Aspen Way just to the south and east of the DLR station. Blackwall station on the London and Blackwall Railway was actually farther east, on what is today Jamestown Way. A crossover west of the station allows trains from Beckton and Poplar to reverse here. Connections London Buses London Buses is the subsidiary of Transport for London (TfL) that manages most bus services in London, England. It was formed foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Saints DLR Station
All Saints is a Docklands Light Railway (DLR) station in Poplar in East London. The station is named after nearby All Saints, a Church of England parish church dating from 1821 to 1823. The station entrance is on the East India Dock Road, the high street of Poplar and is opposite Chrisp Street Market while adjacent to the Poplar Baths, it also has two rail sidings directly west of the station forming part of Poplar DLR depot. On-train announcements for trains approaching the station describe it as "All Saints for Chrisp Street Market". History There was a previous station on the same site, called Poplar station, which was served by the North London Railway. The location of this station can be seen in the bottom-right hand corner of thMap of Poplar, 1885 Serco announced that from 24 August 2009, the frequency on the Stratford to Lewisham branch would be reduced at peak times to one train every seven minutes, from the current five-minute frequency. This was to accommodat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North London Railway
The North London Railway (NLR) company had lines connecting the northern suburbs of London with the East and West India Docks further east. The main east to west route is now part of London Overground's North London Line. Other NLR lines fell into disuse but were later revived as part of the Docklands Light Railway, and London Overground's East London Line. The company was originally called the East & West India Docks & Birmingham Junction Railway (E&WID&BJR) from its start in 1850, until 1853. in 1909 it entered into an agreement with the London and North Western Railway which introduced common management, and the NLR was taken over completely by the LNWR in 1922. The LNWR itself became part of the LMS from the start of 1923. The railways were nationalised in 1948 and most LMS lines, including the North London route, then came under the control of the London Midland Region of British Railways. History The East & West India Docks & Birmingham Junction Railway was incorporated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
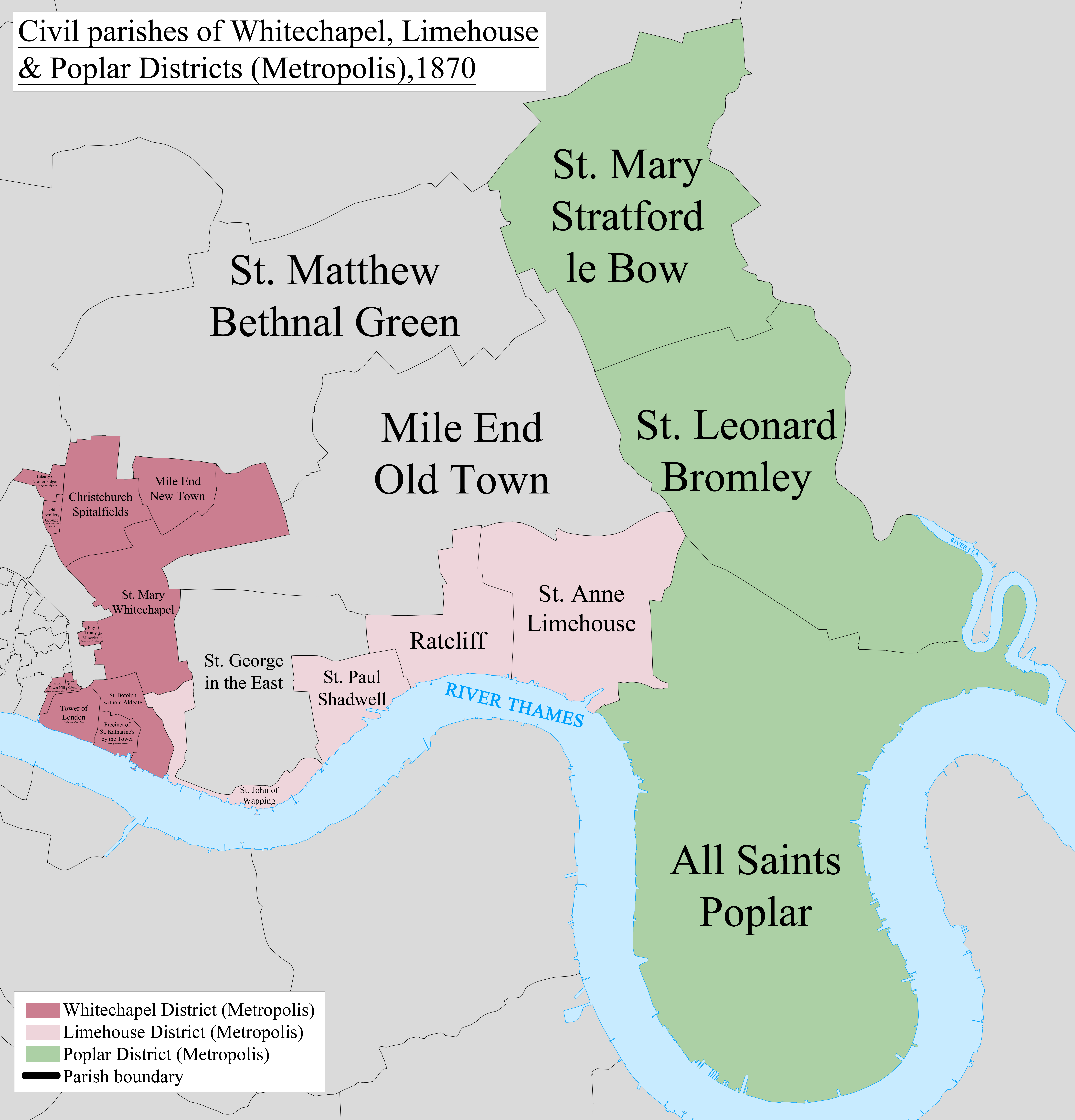
Poplar, London
Poplar is a district in East London, England, the administrative centre of the borough of Tower Hamlets. Five miles (8 km) east of Charing Cross, it is part of the East End. It is identified as a major district centre in the London Plan, with its district centre being Chrisp Street Market, a significant commercial and retail centre surrounded by extensive residential development. Poplar includes Poplar Baths, Blackwall Yard and Trinity Buoy Wharf and the locality of Blackwall. Originally part of the Manor and Ancient Parish of Stepney, the ''Hamlet of Poplar'' had become an autonomous area of Stepney by the 17th century, and an independent parish in 1817. The Hamlet and Parish of Poplar included Blackwall and the Isle of Dogs. After a series of mergers, Poplar became part of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in 1965. History Origin and administrative history Poplar was formerly part of the Manor and Ancient Parish of Stepney, and was first recorded in eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poplar (East India Road) Railway Station
Poplar (East India Road) was a railway station located on the East India Dock Road in Poplar, London. It was opened in 1866 by the North London Railway. It was the southern passenger terminus of the NLR, although goods trains ran on to connect to the London and Blackwall Railway (LBR) for the East India Docks or to the LBR's Millwall Extension Railway for the West India Docks. The station site is now (2021) occupied by All Saints DLR station whilst Poplar DLR station is to the south and west. Description The station building was located on the south side of the East India Dock Road bridge over the railway and was a substantial brick building with some Portland Stone features designed by architect Thomas Matthews. There were four arched windows arranged either side of three arched doors. It had a flat roof. Within the building was a parcels office and ticket office and after passing the ticket inspector the passenger had the choice of the going left for the terminating platfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_&_Poplar_RJD_56.jpg)