|
Popeye Deformity
A biceps tendon rupture or bicep tear is a complete or partial tendon rupture, rupture of a tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. It can affect any of the three biceps brachii tendons - the proximal tendon of the short head of the muscle belly, the proximal tendon of the long head of the muscle belly, or the distal tendon. The characteristic finding of a biceps tendon rupture is the Popeye sign. Patients often report an audible pop at the time of injury as well as pain, bruising, and swelling. Provocative physical exam maneuvers to assess for a rupture include Ludington's test, Hook test, and the Ruland biceps squeeze test. Treatment and prognosis are highly dependent on the site of the injury described in further detail below. __TOC__ Signs and symptoms When a tendon of the biceps brachii ruptures, the muscle belly retracts, meaning that it goes from a lengthened position under tension at two attachments to a shortened position with a single attachment. This shortened position f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceps Brachii Muscle06
The biceps or biceps brachii (, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper forearm. While the long head of the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it flexes and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps screws in the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (flexion). Structure The biceps is one of three muscles in the anterior compartment of the upper arm, along with the brachialis muscle and the coracobrachialis muscle, with which the biceps shares a nerve supply. The biceps muscle has two heads, the short head and the long head, distinguished according to their origin at the coracoid process and supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, respectively. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
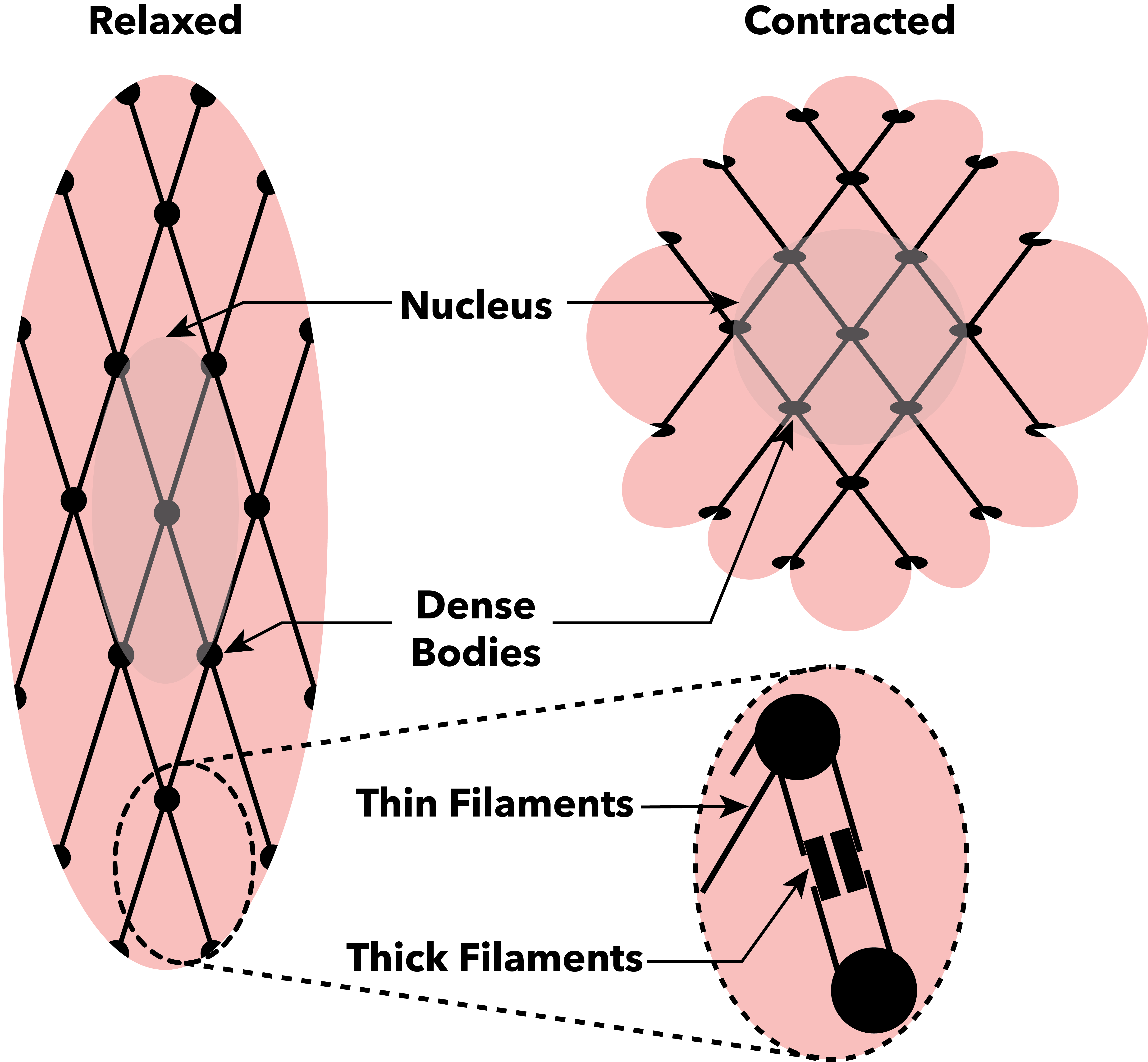
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the change in action of two types of Myofilament, filaments: thin and thick filaments. The major constituent of thin filaments is a chain formed by helical coiling of two strands of actin, and thick filaments dominantly consist of chains of the Motor protein, motor-protein myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils - the basic functional organelles in the skeletal muscle system. In vertebrates, Muscle cell#Muscle contraction in striated muscle, skele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supinated
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomy, Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadlift
The deadlift is a strength training exercise in which a weight-loaded barbell is lifted off the ground to the level of the hips, with the torso perpendicular to the floor, before being placed back on the ground. It is one of the three powerlifting movements along with the Squat (exercise), squat and bench press, as well as a quintessential lift in strongman. The all-time world record deadlift stands at , achieved by Iceland's Hafþór Júlíus Björnsson. Two styles of deadlift are commonly used in competition settings: the conventional deadlift and the sumo deadlift. While both of these styles are permitted under the rules of powerlifting, only the conventional stance is permitted in strongman. Execution Form The conventional deadlift can be broken down into three phases: the setup, the initial pull or drive, and the lockout. Setup: When performing a deadlift, a lifter sets in a position that eccentrically loads the gluteus maximus, gluteus minimus, trapezius, biceps femoris, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccentric Training
Eccentric training is a type of strength training that involves using the target muscles to control weight as it moves in a downward motion. This type of training can help build muscle, improve athletic performance, and reduce the risk of injury. An eccentric contraction is the motion of an active muscle while it is lengthening under load. Eccentric training is repetitively doing eccentric muscle contractions. For example, in a biceps curl the action of lowering the dumbbell back down from the lift is the eccentric phase of that exercise – as long as the dumbbell is lowered slowly rather than letting it drop (i.e., the biceps are in a state of contraction to control the rate of descent of the dumbbell). An eccentric contraction is one of the distinct phases in the movement of muscles and tendons; they include isometric contraction (no movement), isotonic contraction, and concentric contraction (shortening). Eccentric training focuses on slowing down the process of muscle el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a syndrome involving tendonitis (inflammation of tendons) of the rotator cuff muscles as they pass through the subacromial space, the passage beneath the acromion. It is particularly associated with tendonitis of the supraspinatus muscle. This can result in pain, weakness, and loss of movement at the shoulder. Signs and symptoms The most common symptoms in impingement syndrome are pain, weakness and a loss of movement at the affected shoulder. The pain is often worsened by shoulder overhead movement and may occur at night, especially when lying on the affected shoulder. The onset of the pain may be acute if due to an injury or insidious if due to a gradual process such as an Osteoarthritis, osteoarthritic Bone spur, spur. The pain has been described as dull rather than sharp, and lingers for long periods of time, making it hard to fall asleep. Other symptoms can include a grinding or popping sensation during movement of the shoulder. The range of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound Computer Tomography
Ultrasound computer tomography (USCT), sometimes also ''Ultrasound computed tomography'', ''Ultrasound computerized tomography'' or just ''Ultrasound tomography'', is a form of medical ultrasound tomography utilizing ultrasound waves as physical phenomenon for imaging. It is mostly in use for soft tissue medical imaging, especially breast imaging. Description ''Ultrasound computer tomographs'' use ultrasound waves to create images. In the first measurement step, a defined ultrasound wave is generated with typically Piezoelectric ultrasound transducers, transmitted in direction of the measurement object and received with other or the same ultrasound transducers. While traversing and interacting with the object the ultrasound wave is changed by the object and carries now information about the object. After being recorded the information from the modulated waves can be extracted and used to create an image of the object in a second step. Unlike X-ray or other physical properties wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Nanometre, nanometers to 10 Picometre, picometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range of 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 electronvolt, eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 in science, 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity And Specificity
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives: * Sensitivity (true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result, conditioned on the individual truly being positive. * Specificity (true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative. If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a " gold standard test" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both diagnoses and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |