|
Pope Gregory VI
Pope Gregory VI (; died 1048), born Giovanni Graziano (John Gratian) in Rome (), was bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 1 May 1045 until his resignation at the Council of Sutri on 20 December 1046. Accession Gratian, the archpriest of St. John by the Latin Gate,Cowdrey, H. E. J., ''Pope Gregory VII, 1073-1085'', Clarendon Press, 1998, p. 29 was a man of great reputation for uprightness of character. He was also the godfather of , who, at the age of twenty, was foisted on the papacy by his powerful family, the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Popes
This chronological list of the popes of the Catholic Church corresponds to that given in the under the heading "" (The Roman Supreme Pontiffs), excluding those that are explicitly indicated as antipopes. Published every year by the Roman Curia, the no longer #Numbering of popes, identifies popes by regnal number, stating that it is impossible to decide which pope represented the legitimate succession at various times. The 2001 edition of the introduced "almost 200 corrections to its existing biographies of the popes, from St Peter to John Paul II". The corrections concerned dates, especially in the first two centuries, birthplaces and the family name of one pope. The term ''Pope (word), pope'' () is used in several churches to denote their high spiritual leaders (for example Coptic pope). This title is usually used in English to refer to the head of the Catholic Church. The Catholic pope uses various titles by tradition, including , , and . Each title has been added by unique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
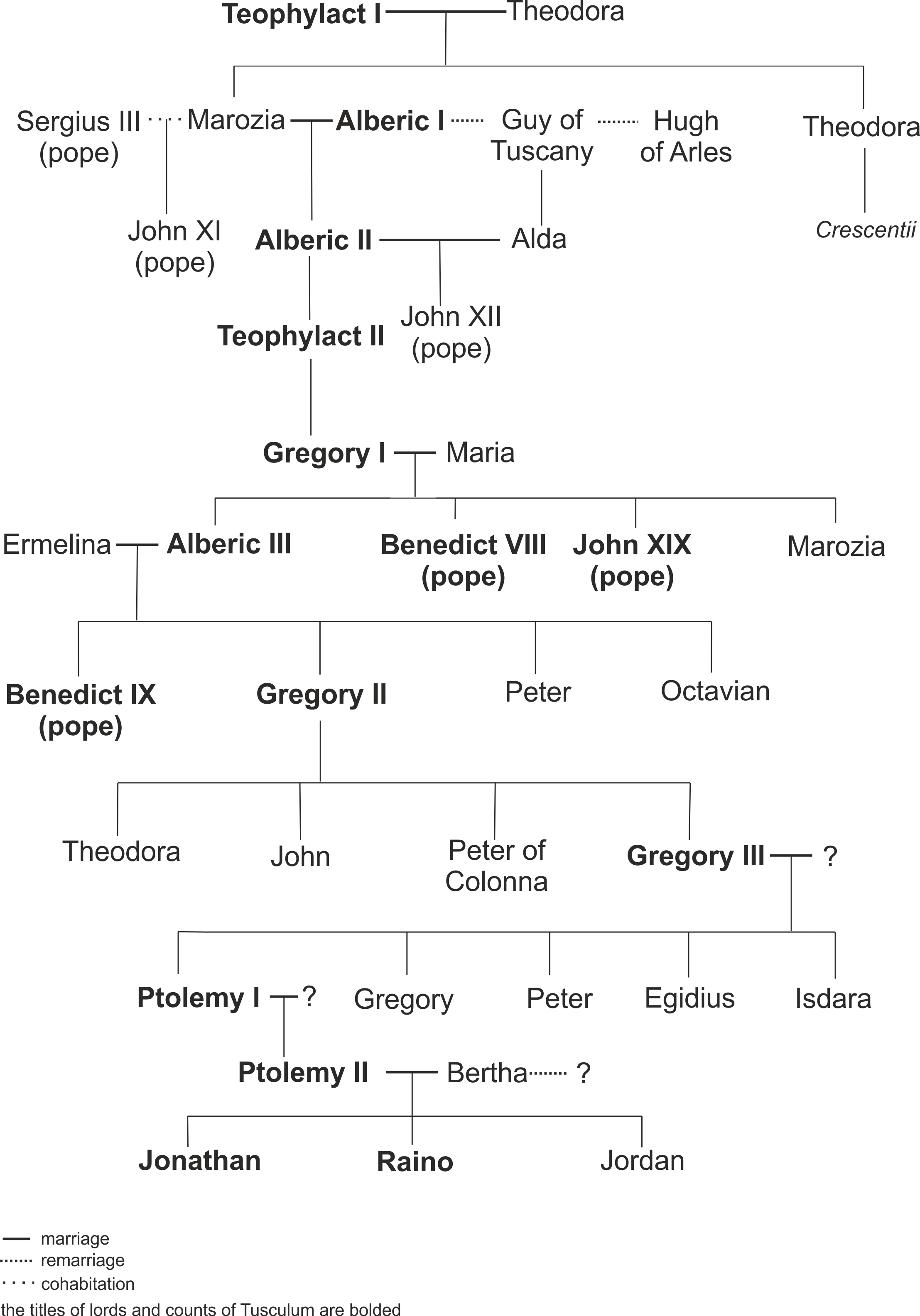
Theophylacti
The counts of Tusculum or Tuscolo, also known as the Theophylacti, were a family of secular noblemen from Latium that maintained a powerful position in Rome between the 10th and 12th centuries. Several popes and antipopes during the 11th century came from their ranks. They created and perfected the political formula of noble-papacy, wherein the pope was arranged to be elected only from the ranks of the Roman nobles. The Pornocracy, the period of influence by powerful female courtesans of the family, also influenced papal history. The counts of Tusculum remained arbiters of Roman politics and religion for more than a century. In addition to the papal influence, they held lay power through consulships and senatorial membership. Traditionally they were pro-Byzantine and anti-Germanic in their political affiliation. After 1049, the Tusculan Papacy came to an end with the election of Pope Leo IX. In fact, the Tusculan papacy was largely responsible for the reaction known as the Greg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Bamberg
This is a list of bishops and archbishops of the Prince-Bishopric of Bamberg and the modern Archdiocese of Bamberg in Germany. __TOC__ Bishops, 1007–1245 * Eberhard I 1007-1040 * Pope Clement II, Suidger von Morsleben 1040-1046 (Later Pope Clement II) * Hartwig von Bogen 1047-1053 * Adalbert of Carinthia 1053-1057 * Gunther of Bamberg, Günther 1057-1065 * Herman I of Bamberg, Herman I 1065-1075 * Rupprecht 1075-1102 * Otto of Bamberg, Otto I of Mistelbach 1102-1139 * Egilbert 1139-1146 *Eberhard II von Otelingen 1146-1170 * Hermann II von Aurach 1170-1177 * Berthold II, Count of Andechs, Otto II of Andechs 1177-1196 * Thimo von Lyskirch 1196-1201 * Konrad von Ergersheim 1202-1203 * Ekbert of Bamberg, Ekbert of Andechs 1203-1231 * Siegfried von Öttingen 1231-1238 * Berthold I of Istria, Poppo of Andechs 1238-1242 * Heinrich I von Bilversheim 1242-1245, continued as Prince-Bishop Prince-Bishops, 1245–1802 * Heinrich I von Bilversheim 1245-1257, bishop since 1242 * Ladislaus of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simony
Simony () is the act of selling church offices and roles or sacred things. It is named after Simon Magus, who is described in the Acts of the Apostles as having offered two disciples of Jesus payment in exchange for their empowering him to impart the power of the Holy Spirit in Christianity, Holy Spirit to anyone on whom he would Laying on of hands, place his hands. The term extends to other forms of trafficking for money in "spiritual things". Origin The earliest church legislation against simony may be that of the forty-eighth canon of the Synod of Elvira (), against the practice of making a donation following a baptism. Following the Edict of Milan (313), the increased power and wealth of the church hierarchy attracted simony. There are several accusations of simony (not by that name) against Arianism, Arians, from Athanasius of Alexandria, Hilary of Poitiers, Pope Liberius and Gregory of Nazianzus. Many Church Fathers, such as Ambrose, spoke out against the selling of mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synod Of Sutri
The Council of Sutri (or Synod of Sutri) was called by the Holy Roman Emperor Henry III and opened on December 20, 1046, in the hilltown of Sutri, at the edge of the Duchy of Rome. The Catholic Church does not list this as an ecumenical council. Record in the ''Annales Romani'' The ''Annales Romani'' record the events thus: Reasons for calling the council The council was called to resolve disorder over the papacy. A faction in the church encouraged Henry III to intervene, both to resolve the conflict and to receive his crown from the pope in an official ceremony. In the autumn of 1046 Henry III, already King of the Germans, crossed the Alps at the head of a large army and accompanied by a retinue of the secular and ecclesiastical princes of the empire, all of whom were his sworn vassals. Henry had two intentions, to be crowned Holy Roman emperor by the pope at Rome and, in order that the pontiff concerned have an unassailable title—one that would not cast doubts upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutri
Sutri (Latin ''Sutrium'') is an Ancient town, modern ''comune'' and former bishopric (now a Latin titular see) in the province of Viterbo, about from Rome and about south of Viterbo. It is picturesquely situated on a narrow tuff hill, surrounded by ravines, a narrow neck on the west alone connecting it with the surrounding country. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia ("The most beautiful villages of Italy"). The modern ''comune'' of Sutri has a few more than 5,000 inhabitants. Its ancient remains are a major draw for tourism: a Roman amphitheatre excavated in the tuff rock, an Etruscan necropolis with dozens of rock-cut tombs, a Mithraeum incorporated in the crypt of its church of the Madonna del Parto, a Romanesque Duomo. History Ancient Sutrium occupied an important position, commanding as it did the road into Etruria, the later Via Cassia: Livy describes it as one of the keys of Etruria, nearby Nepi being the other. It came into the hands of Rome after the fall of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia. The Alpine arch extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrust fault, thrusting and Fold (geology), folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 82 peaks higher than List of Alpine four-thousanders, . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry III Of Germany
Henry III (, 28 October 1016 – 5 October 1056), called the Black () or the Pious, was Holy Roman Emperor from 1046 until his death in 1056. A member of the Salian dynasty, he was the eldest son of Conrad II and Gisela of Swabia. Henry was raised by his father, who made him Duke of Bavaria in 1026, appointed him co-ruler in 1028 and bestowed him with the duchy of Swabia and the Kingdom of Burgundy ten years later in 1038. The emperor's death the following year ended a remarkably smooth and harmonious transition process towards Henry's sovereign rule, that was rather uncharacteristic for the Ottonian and Salian monarchs. Henry succeeded Conrad II as Duke of Carinthia and King of Italy and continued to pursue his father's political course on the basis of ''virtus et probitas'' (courage and honesty), which led to an unprecedented sacral exaltation of the kingship. In 1046 Henry ended the papal schism, was crowned Emperor by Pope Clement II, freed the Vatican from dependence on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII (; 1015 – 25 May 1085), born Hildebrand of Sovana (), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 April 1073 to his death in 1085. He is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church. One of the great reforming popes, he initiated the Gregorian Reform, and is perhaps best known for the part he played in the Investiture Controversy, his dispute with Emperor Henry IV to establish the primacy of papal authority and the new canon law governing the election of the pope by the College of Cardinals. He was also at the forefront of developments in the relationship between the emperor and the papacy during the years before he became pope. He was the first pope to introduce a policy of obligatory celibacy for the clergy, which had until then commonly married, and also attacked the practice of simony. During the power struggles between the papacy and the Holy Roman Empire, Empire, Gregory excommunicated Henry IV three times, and Henry appointed An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory VI-face-coats
Gregory may refer to: People and fictional characters * Gregory (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Gregory (surname), a surname *Gregory (The Walking Dead), fictional character from the walking dead * Gregory (Five Nights at Freddy's), main protagonist of '' Five Nights at Freddy's: Security Breach'' ** Places Australia *Gregory, a town in the Northern Territory *Gregory, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Burke **Electoral district of Gregory, Queensland, Australia * Gregory, Western Australia. United States *Gregory, South Dakota * Gregory, Tennessee * Gregory, Texas Outer space *Gregory (lunar crater) *Gregory (Venusian crater) Other uses * "Gregory" (''The Americans''), the third episode of the first season of the television series ''The Americans'' See also * Greg (other) * Greggory * Gregoire (other) * Gregor (other) * Gregores (other) * Gregorian (other) * Gregory C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Sylvester III
Pope Sylvester III (c. 1000 – October 1063), born John () in Rome, was bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 20 January to 10 March 1045. Background Christened John, he was born into the powerful Roman patrician family Crescentii. Upon the death of Pope John XIX in October 1032, the papal throne became the subject of dispute between rival factions of nobles. Theophylactus, a youth of about twenty, the son of Alberic III, Count of Tusculum, was supported by the nobles of Tusculum. The nephew and namesake of Pope Benedict VIII, he took the name Benedict IX. The young man was not only unqualified, but led a reportedly dissolute life, and factional strife continued. A revolt in Rome led to Benedict IX being driven from the city in 1044. Papacy John, bishop of Sabina, was elected after fierce and protracted infighting, c. 21 January 1045. He took the name Sylvester III. Benedict IX excommunicated him, and in March returned to Rome and expelled Sylvester, who himself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Sabina
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of dioceses. The role or office of the bishop is called episcopacy or the episcopate. Organisationally, several Christian denominations utilise ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority within their dioceses. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full Priest#Christianity, priesthood given by Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |