|
Polyot 1
Polyot is a transliteration of the Russian term Полёт (meaning Flight) and can be transliterated as Polyot, Poljot or Polet. Polyot can refer to the following: *Polet Flight, a defunct Russian airline formerly based in Voronezh *Poljot, a brand of watches from the USSR, and now Russia *Polyot (rocket), an interim orbital carrier rocket from the USSR *Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Production Corporation "Polyot", a company based in Omsk, responsible for manufacture of the Antonov An-3 aircraft and Cosmos-3M space launch vehicle, amongst others *Polyot-Sirena, the major Russian Global Distribution System A global distribution system (GDS) is a computerised network system owned or operated by a company that enables transactions between travel industry service providers, mainly airlines, hotels, car rental companies, and Travel agency, travel agen ... *Polyot, Russian aerospace journal See also * :ru:Полёт (значения) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transliteration
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters (thus '' trans-'' + '' liter-'') in predictable ways, such as Greek → and → the digraph , Cyrillic → , Armenian → or Latin → . For instance, for the Greek term , which is usually translated as 'Hellenic Republic', the usual transliteration into the Latin script (romanization) is ; and the Russian term , which is usually translated as 'Russian Republic', can be transliterated either as or alternatively as . Transliteration is the process of representing or intending to represent a word, phrase, or text in a different script or writing system. Transliterations are designed to convey the pronunciation of the original word in a different script, allowing readers or speakers of that script to approximate the sounds and pronunciation of the original word. Transliterations do not change the pronunciation of the word. Thus, in the Greek above example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polet Flight
CJSC «Polet Flight» (, ''ZAO «Aviakompániya "Polyót"»'') was an airline based in Voronezh, Russia. It operated a worldwide cargo and domestic passenger charter services from Voronezh, as well as regional passenger and cargo services from Sokol. It was one of two airlines which flew the Antonov An-124 Ruslan, the world's highest gross weight cargo airplane which specialises in oversized freight. Its collapse, over lease payments for these massive aircraft, left only the Volga-Dnepr Airlines/Antonov Airlines joint partnership in this market. Its main base was Chertovitskoye Airport, Voronezh. Polet is the Russian word for flight. History The airline was established and started operations in 1988. In 2002 Polet began serving the agricultural, aeromedical and aerial photography markets. The airline was wholly owned by Anatoly S Karpov (Chief Executive and General Director) and had a 19.5% holding in Voronezhavia. In December 2013, the carrier announced that it was evaluat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronezh
Voronezh ( ; , ) is a city and the administrative centre of Voronezh Oblast in southwestern Russia straddling the Voronezh River, located from where it flows into the Don River. The city sits on the Southeastern Railway, which connects western Russia with the Urals and Siberia, the Caucasus and Ukraine, and the M4 highway (Moscow–Voronezh– Rostov-on-Don– Novorossiysk). In recent years the city has experienced rapid population growth, rising in 2021 to 1,057,681, up from 889,680 recorded in the 2010 Census, making it the 14th-most populous city in the country. History Foundation and name The first chronicle references to the word "Voronezh" are dated 1177, when the Ryazan prince Yaropolk, having lost the battle, fled "to Voronozh" and there was moving "from town to town". Modern data of archeology and history interpret Voronezh as a geographical region, which included the Voronezh river (tributary of the Don) and a number of settlements. In the lower rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poljot
Poljot (, literally meaning "flight"), is a brand of Soviet/Russian wristwatches, produced since 1964 by the First Moscow Watch Factory (, ''Perviy Moskovskiy Chasovoy Zavod''). The flagship brand of the USSR's watch industry, Poljot produced numerous historical watches used in many important space missions, including the world's first space watch worn by Yuri Gagarin. History Founded in 1930 under orders from Joseph Stalin, the First State Watch Factory () was the first large scale Soviet watch and mechanical movement manufacturer. Via its USA-based trading company Amtorg, the Soviet government bought the defunct Ansonia Clock Company of Brooklyn, New York in 1929, and the Dueber-Hampden Watch Company of Canton, Ohio. As part of the Soviet's first five-year plan, twenty-eight freight cars worth of machinery and parts were moved from the USA to Moscow in order to establish the factory; further, twenty-one former Dueber-Hampden technicians trained Russian workers in the art of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyot (rocket)
The Polyot (, ''flight'') (Also known as Sputnik, GRAU index 11A59) was an interim orbital carrier rocket, built to test ASAT spacecraft. It was required as a stopgap after the cancellation of the UR-200 programme, but before the Tsyklon could enter service. Only two were ever launched, the first on 1 November 1963, and the last on 12 April 1964. Both of these flights were successful. The rocket consisted of a core stage, and four boosters, which were taken from a Voskhod 11A57 rocket. It was capable of delivering a 1,400 kg payload into a 300 km by 59° Low Earth orbit. It is a member of the R-7 family. See also Comparable rockets * Tsyklon * UR-200 Related developments *R-7 Semyorka The R-7 Semyorka (, GRAU index: 8K71) was a Soviet Union, Soviet missile developed during the Cold War, and the world's first intercontinental ballistic missile. The R-7 made 28 launches between 1957 and 1961. A derivative, the R-7A Semyorka, R ... * Vostok rocket * Voskhod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC Polyot
Production Association Polyot () is a Russian aerospace engineering state corporation best known for being the manufacturer of GLONASS satellites and the Kosmos-3M space launch vehicle. The company is based in Omsk, in the Russian Federation. In 2007, the company was integrated into the Khrunichev enterprise. Its full name is ''"Polyot" Manufacturing Corporation – A Branch of The Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center".'' Overview The Kosmos-3M launch vehicle, produced at the company since 1969, has established a reputation as one of the most reliable rockets in its class with a reliability coefficient of 0.97. Polyot also develops navigation satellites, such as Nadezhda, Parus, GLONASS and GLONASS-M. In the aviation sector, the company's products include the AN-3T light multi-purpose aircraft, AN-70 transport aircraft and the AN-74 multi-purpose aircraft. PC Polyot is slated to produce the upcoming ''URM-1'' first stage of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonov An-3
The Antonov An-3 is a Soviet (later Ukrainian and Russian) civil multipurpose and agricultural aircraft. It is essentially a turboprop-powered development of the An-2, designed to upgrade or replace it. The basic transport version (An-3T) is supplemented by a cargo/passenger version (An-3TK), an agricultural version (An-3SH), a forest fire-fighting version (An-3P), as well as an ambulance version. It is designed to carry passengers and cargo, operating from paved or unpaved airfields, including snow covered surfaces up to deep (using a ski landing gear). Upgrading The upgrading consisted of replacement of the piston engine with a TVD-20 turboprop engine, featuring a three-blade reversible pitch (type AV-17) propeller and a R-17 speed governor. The flight compartment was rearranged; a heating and ventilation system was installed as well as advanced electric and flight and navigation equipment; centralized warning system; a new fire extinguishing system; and an improvement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos-3M
The Kosmos-3M ( meaning "''Cosmos''", GRAU index 11K65M) was a Russian space launch vehicle, member of the Kosmos rocket family. It was a liquid-fueled two-stage launch vehicle, first launched in 1967 and with over 420 successful launches to its name. The Kosmos-3M used UDMH fuel and AK27I oxidizer (red fuming nitric acid) to lift roughly of payload into orbit. It differed from the earlier Kosmos-3 in its finer control of the second-stage burn, allowing operators to tune the thrust and even channel it through nozzles that helped orient the rocket for the launching of multiple satellites at one time. PO Polyot manufactured these launch vehicles in the Russian city of Omsk for decades. It was originally scheduled to be retired from service in 2011; however, in April 2010 the Commander of the Russian Space Forces confirmed that it would be retired by the end of 2010. One further launch, with Kanopus-ST, was planned; however, this was cancelled in late 2012 as the launch vehic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
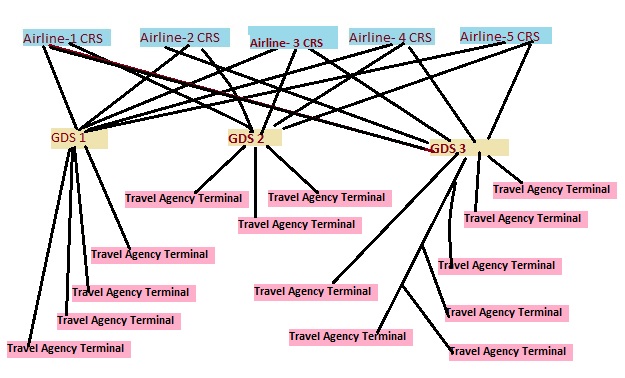
Global Distribution System
A global distribution system (GDS) is a computerised network system owned or operated by a company that enables transactions between travel industry service providers, mainly airlines, hotels, car rental companies, and Travel agency, travel agencies. The GDS mainly uses ''real-time inventory'' (e.g. number of hotel rooms available, number of flight seats available, or number of cars available) from the service providers. Travel agencies traditionally relied on GDS for services, products and rates in order to provide travel-related services to the end consumers. Thus, a GDS can link services, rates and bookings consolidating products and services across all three travel sectors: i.e., airline reservations, hotel reservations, car rentals. GDS is different from a computer reservation system, which is a reservation system used by the service providers (also known as vendors). Primary customers of GDS are travel agents (both online and office-based) who make reservations on various r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |