|
Polyglecaprone
Monocryl is a synthetic, absorbable suture manufactured in Cornelia, Georgia, USA, and trademarked by Ethicon. It is composed of poliglecaprone 25, which is a copolymer of glycolide and ε-caprolactone. It comes both dyed (violet) and undyed (clear) and is an absorbable monofilament suture. It is generally used for soft-tissue approximation and ligation. It is used frequently for subcuticular dermis closures of the face. It has less of a tendency to exit through the skin after it breaks down, such as Vicryl. It is contraindicated for use in cardiovascular and neurologic tissues and for usage in ophthalmic and microsurgery. The use of poliglecaprone suture may be inappropriate in patients who are older, malnourished, or debilitated, as well as in patients with conditions that may delay wound healing. Monocryl has a low tissue reactivity, maintains high tensile strength, and has a half-life of 7 to 14 days. At 1 week, its in vivo tensile strength is at 50–60% undyed (60–70% dye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ε-caprolactone
ε-Caprolactone or simply caprolactone is a lactone (a cyclic ester) possessing a seven-membered ring. Its name is derived from caproic acid. This colorless liquid is miscible with most organic solvents and water. It was once produced on a large scale as a precursor to caprolactam. Production and uses Caprolactone is prepared industrially by Baeyer-Villiger oxidation of cyclohexanone with peracetic acid. Caprolactone is a monomer used in the production of highly specialised polymers. Ring-opening polymerization, for example, gives polycaprolactone. Another polymer is polyglecaprone, used as suture material in surgery. Reactions Although no longer economical, caprolactone was once produced as a precursor to caprolactam. Caprolactone is treated with ammonia at elevated temperatures to give the lactam: :(CH2)5CO2 + NH3 → (CH2)5C(O)NH + H2O Carbonylation of caprolactone gives, after hydrolysis, pimelic acid. The lactone ring is easily opened with nucleophiles including alcohols a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
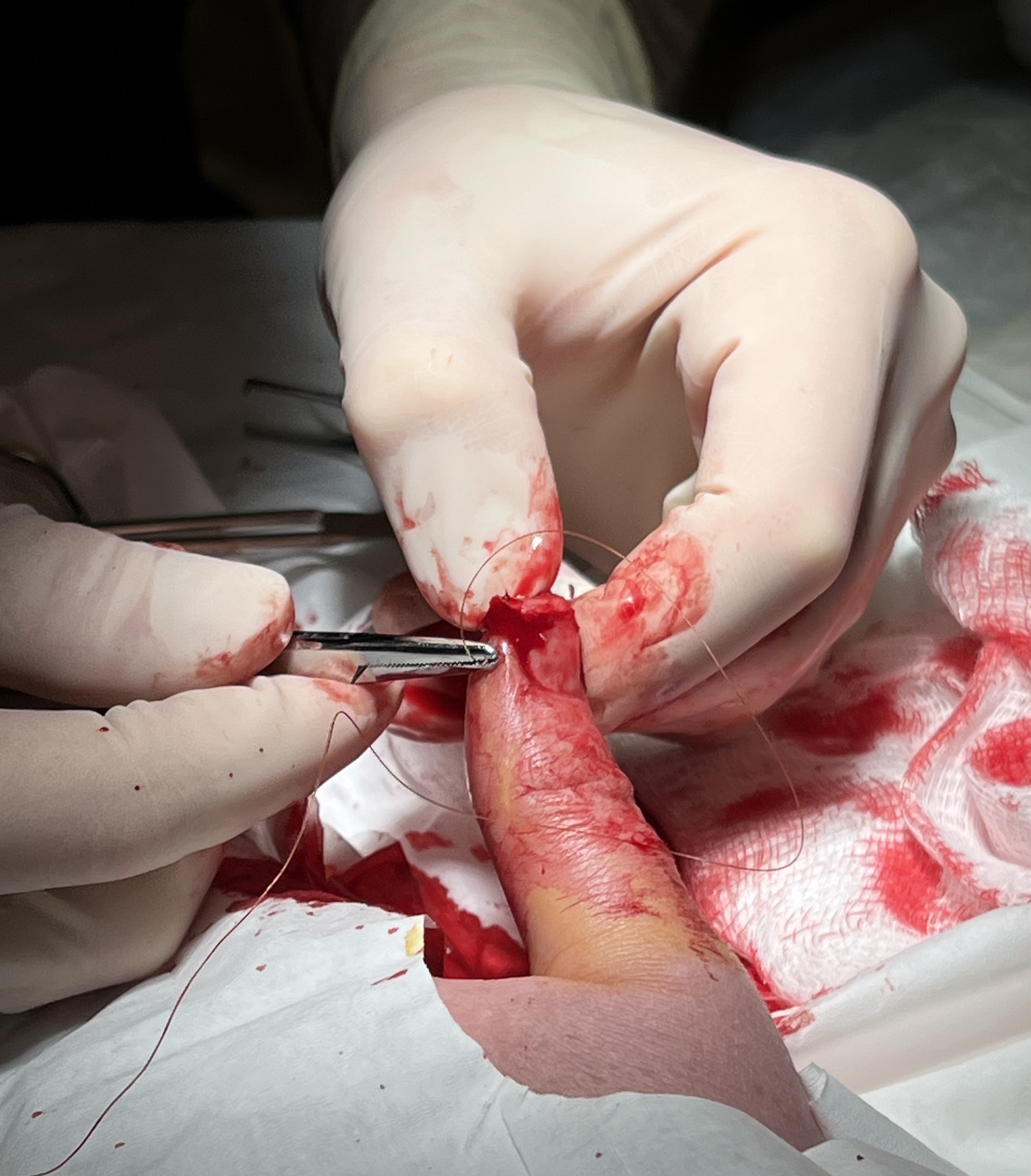
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold Tissue (biology), body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a Sewing needle, needle with an attached length of thread (yarn), thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethicon Inc
Ethicon, Inc., is a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson. The company is part of the Johnson & Johnson MedTech business segment. It was incorporated as a separate company under the Johnson & Johnson umbrella in 1949 to expand and diversify the Johnson & Johnson product line. Ethicon has manufactured surgical sutures and wound closure devices since 1887. After World War II, Ethicon's market share in surgical sutures rose from 15% to 70% worldwide. In the United States, the market share is approximately 80%. Ethicon conducts business in 52 countries. Corporate history In 1915, George F. Merson opened a facility in Edinburgh for the manufacturing, packaging and sterilising of catgut, silk and nylon sutures. Johnson & Johnson acquired Mr. Merson's company in 1947, and this was renamed Ethicon Suture Laboratories. In 1953 this became Ethicon Inc. In 1992, Ethicon was restructured, and Ethicon Endo-Surgery became a separate corporate entity. In 2008, Ethicon sold its wound management b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolide
Glycolide (1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione) is a dimer of glycolic acid. Its structure is six-membered ring containing two lactones, an oxidized variant of ''p''-dioxane. The compound can be synthesized from glycolic acid, via a high-temperature oligomerization to form polyglycolide followed by a depolymerization process. A more direct method is by self-condensation of the sodium salt of chloroacetic acid Chloroacetic acid, industrially known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is the organochlorine compound with the formula . This carboxylic acid is a useful building block in organic synthesis. It is a colorless solid. Related compounds are dichlo .... It is useful as a starting material for the production of polyglycolide. References Dimers (chemistry) Lactones Dioxanes {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicryl
Vicryl (polyglactin 910) is an absorbable, synthetic, usually braided surgical suture, suture, manufactured by Ethicon Inc., a subsidiary of Johnson and Johnson. A monofilament version is also made for use in Ophthalmology, ophthalmic practice. It is indicated for soft tissue approximation and Ligature (medicine), ligation. The suture holds its tensile strength for approximately two to three weeks in tissue and is completely absorbed by acid hydrolysis within 8-10 weeks. Vicryl and other Polyglycolide, polyglycolic-acid sutures may also be treated for more rapid breakdown ("Vicryl Rapide") in rapidly healing tissues such as mucous membrane or impregnated with triclosan ("Vicryl Plus Antibacterial") to provide antimicrobial protection of the suture line. Because Vicryl is slow-absorbing and often braided, its use is contraindicated in the closure of any cutaneous wound exposed to the air, as it draws moisture from the healing tissue to the skin and allows bacteria and irritants t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In drug discovery, for example, verification of efficacy ''in vivo'' is crucial, because ''in vitro'' assays can sometimes yield misleading results with drug c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location. The knowledge of fascial structures is essential in surgery, as they create borders for infectious processes (for example Psoas abscess) and haematoma. An increase in pressure may result in a compartment syndrome, where a prompt fasciotomy may be necessary. For this reason, profound descriptions of fascial structures are available in anatomical literature from the 19th century. Function Fasciae were traditionally thought of as passive structures that transmit mechanical tension generated by muscular activities or external forces throughout the body. An important function of muscle fasciae is to reduce friction of muscular force. In doing so, fasciae provide a supportive and movable wrapping for nerves and blood vessels as they pass thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |