|
Polydiscia Deuterosminthurus
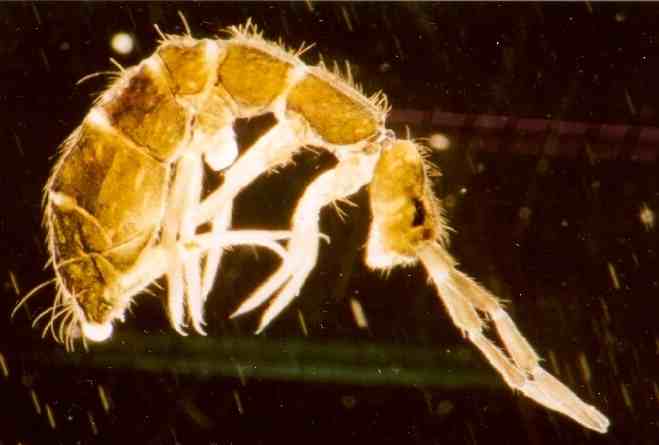
''Polydiscia deuterosminthurus'' is a species of mite recently discovered in the autonomous community of Navarre in Spain. Only the six-legged larval stage is so far known. This lives as a parasite on the springtail '' Deuterosminthurus bisetosus'', which was discovered at the same time as the parasite. The association between the two species only seems to last for a few weeks in May and June. Both creatures appear to be entirely restricted to a single host plant at this stage of their life cycle: the broom '' Genista hispanica''. These red mites are tiny, less than 0.3 mm in length but are huge in comparison to their hosts, averaging a third of the length of ''Deuterosminthurus bisetosus'', to which they attach piggyback-fashion, the jaws embedded in the joint between head and prothorax The prothorax is the foremost of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the first pair of legs. Its principal sclerites (exoskeletal plates) are the pronotum (dorsal), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group invalid as a clade. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are Predation, predators or Parasitism, parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive ''Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy Mites are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Communities In Spain
The autonomous communities () are the first-level administrative divisions of Spain, created in accordance with the Spanish Constitution of 1978, with the aim of guaranteeing limited autonomy to the nationalities and regions that make up Spain. There are 17 autonomous communities and two autonomous cities (Ceuta and Melilla) that are collectively known as "autonomies". The two autonomous cities have the right to become autonomous communities. The autonomous communities exercise their right to self-government within the limits set forth in the constitution and organic laws known as Statutes of Autonomy, which broadly define the powers that they assume. Each statute sets out the devolved powers () for each community; typically those communities with stronger local nationalism have more powers, and this type of devolution has been called ''asymmetrical'' which is on the whole seen as advantageous, able to respond to diversity. Despite the Constitution not setting a mandato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navarre
Navarre ( ; ; ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre, is a landlocked foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Autonomous Community, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and New Aquitaine in France. The capital city is Pamplona (). The present-day province makes up the majority of the territory of the medieval Kingdom of Navarre, a long-standing Pyrenean kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost part, Lower Navarre, located in the southwest corner of France. Navarre is in the transition zone between the green Cantabrian Coast and semi-arid interior areas and thus its landscapes vary widely across the region. Being in a transition zone also produces a highly variable climate, with summers that are a mix of cooler spells and heat waves, and winters that are mild for the latitude. Navarre is one of the historic Basque provinces: its Basque features are conspicuous in the north, but vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. A larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. In the case of smaller primitive arachnids, the larval stage differs by having three instead of four pairs of legs. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springtail
Springtails (class Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern Hexapoda, hexapods that are no longer considered insects. Although the three lineages are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal Arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to insects, which have external mouthparts. Springtails are omnivorous, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from Ancient Greek 'glue' and 'peg'; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature. Early DNA sequence studies suggested that Collembola represent a separate Lineage (evolution), evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterosminthurus Bisetosus
''Deuterosminthurus bisetosus'' is a species of springtail discovered living on the broom '' Genista hispanica'' in the autonomous community of Navarre in Spain. This small globular springtail (up to 1.4 mm in length) is yellow, usually, though not always, with variable reddish-brown markings on its back. Around 10% of the examples observed have been found to be host to a new species of red mite which has been named ''Polydiscia deuterosminthurus''. These mites, which ride on the back of their hosts attached just behind the head, are clearly a major burden as they average a third of the length of ''D. bisetosus''. This springtail has been observed on its host plant in May and June but leaves it as the air temperature rises (springtails of this type are especially susceptible to desiccation). Where these creatures (and their parasite Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broom (shrub)
''Cytisus scoparius'' ( syn. ''Sarothamnus scoparius''), the common broom or Scotch broom, is a deciduous leguminous shrub native to western and central Europe. In Great Britain and Ireland, the standard name is broom; this name is also used for other members of the Genisteae tribe, such as French broom or Spanish broom; and the term ''common broom'' is sometimes used for clarification. In other English-speaking countries, the most common name is "Scotch broom" (or Scots broom); however, it is known as English broom in Australia. Though this plant is native to Europe, it has spread to many other parts of the world. Scotch broom is now common in certain areas of North America and South America. This is because people started introducing Scotch broom to different areas of the world. After it was introduced in North America, Scotch broom was frequently planted in gardens. Later, it was used for erosion control along highway cuts and fills. There are other problems with Scotc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genista Hispanica , native to southern France and northern Spain. It is suited for borders, wall and rock gardens, gravelly soils, and coastal situations.
''Genista hispanica'', the Spanish gorse, or anlaga, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae Fabaceae () or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomen ... Subtaxa The following subspecies are accepted: *''Genista hispanica'' subsp. ''hispanica'' *''Genista hispanica'' subsp. ''occidentalis''References hispanica Flora of France[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piggyback
Piggyback, piggy-back, or piggybacking may mean: Transport * Piggyback (transportation), something that is riding on the back of something else Art, entertainment, and media * Splash cymbal piggybacking, mounting a cymbal on top of an already stand-mounted cymbal * "Piggyback" (song), 2017 song by Melanie Martinez * Chapter Nine: The Piggyback, 2022 episode of ''Stranger Things''. Business, finance, and law * Piggy-back (law), shareholder selling rights * Piggybacking, a practice in which a person with bad credit uses the seasoned tradeline of credit of someone else Electronics * Piggyback board, a daughterboard * Piggyback microcontroller, a microcontroller variant with EPROM socket Healthcare * Piggybacking, a second infusion set onto the same intravenous line using a Y-Set (intravenous therapy) * " Piggy-back technique", is a technique in liver transplantation in which the recipient inferior vena cava is preserved. * Vision Correction: The wearing of zero- or ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prothorax
The prothorax is the foremost of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the first pair of legs. Its principal sclerites (exoskeletal plates) are the pronotum (dorsal), the prosternum ( ventral), and the propleuron (lateral) on each side. The prothorax never bears wings in extant insects (except in some cases of atavism), though some fossil groups possessed wing-like projections. All adult insects possess legs on the prothorax, though in a few groups (e.g., the butterfly family Nymphalidae) the forelegs are greatly reduced. In many groups of insects, the pronotum is reduced in size, but in a few it is hypertrophied, such as in all beetles ( Coleoptera). In most treehoppers (family Membracidae, order Hemiptera), the pronotum is expanded into often fantastic shapes that enhance their camouflage or mimicry. Similarly, in the Tetrigidae, the pronotum is extended backward to cover the flight wings, supplanting the function of the tegmina. See also * Glossary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |