|
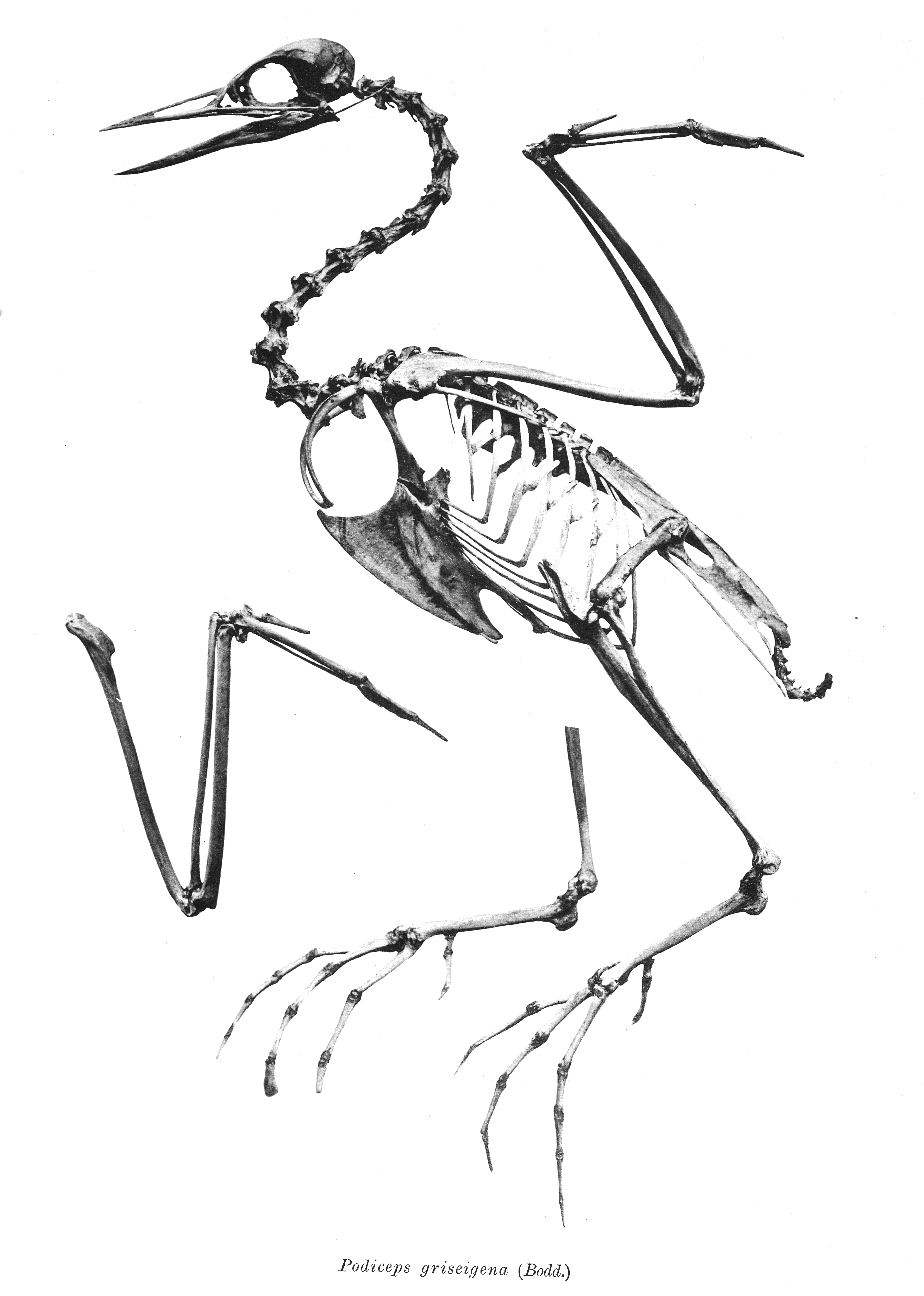
Podiceps Csarnotanus
''Podiceps csarnotanus'' is an extinct species of Upper Pliocene grebe from Hungary. History The species was described by Eugene Kessler in 2009 as part of a series of papers that described fossil material that have been retrieved form the Carpathian Basin. The species name "csarnotanus" is named after the site it was discovered Csarnóta. Description The holotype (MÁFI V. 09. 61. 1) is the distal fragment of the right ulna, which the size of it falls in between the horned grebe (''P. auritus'') and the red-necked grebe (''P. grisegena''). In comparison to the recent species of ''Podiceps'' and the ''Aechmophorus'', the condylus ventralis is elongated and prominent. The condylus dorsalis is rounded, while in modern ''Podiceps'' and ''Aechmophorus'' it just emerges. The cranial surface of the diaphysis is slightly convex, not flat unlike in modern ''Podiceps''. Paleobiology ''P. csarnotanus'' comes from the Carpathian Basin which is located in South Hungary. The locality of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.59 to 1.81 Ma, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well-identified but the exact dates of the start a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condylus Ventralis
A condyle (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. , from ; κόνδυλος knuckle) is the round prominence at the end of a , most often part of a joint – an articulation with another bone. It is one of the markings or features of bones, and can refer to: * On the , in the joint: ** [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2009
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, seashell, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in #Resin, amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of the Cenozoic and the eleventh period of the Phanerozoic. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by Paleogene and Neogene and, despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piacenzian
The Piacenzian is in the international geologic time scale the upper stage (stratigraphy), stage or latest age (geology), age of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 3.6 ± 0.005 year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma and 2.58 Ma (million years ago). The Piacenzian is after the Zanclean and is followed by the Gelasian (part of the Pleistocene). The Piacenzian is roughly coeval with the European land mammal age MN 16, overlaps the late Chapadmalalan and early Uquian South American land mammal age and falls inside the more extensive Blancan North American land mammal age. It also correlates with the Astian, Redonian, Reuverian and Romanian regional stages of Europe, and the Waipipian and Mangapanian stages of New Zealand geologic time scale, New Zealand. Some authorities describe the British Red Crag Formation and Waltonian Stage as late Piacenzian, while others regard them as early Pleistocene. Carbon dioxide levels during the Piacenzian were similar to those of today, making this age, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanclean
The Zanclean is the lowest stage or earliest age on the geologic time scale of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 5.332 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago) and 3.6 ± 0.005 Ma. It is preceded by the Messinian Age of the Miocene Epoch, and followed by the Piacenzian Age. The Zanclean can be correlated with regionally used stages, such as the Opoitian of New Zealand, and the Tabianian or Dacian of Central Europe. It also corresponds to the late Hemphillian to mid-Blancan North American Land Mammal Ages. In California, the Zanclean roughly corresponds to the middle part of the Delmontian stage. Definition The Zanclean Stage was introduced by Giuseppe Seguenza in 1868. It is named after '' Zancle'', the pre- Roman name for the Italian city of Messina on Sicily. The base of the Zanclean (and the Pliocene Series) lies with the top of magnetic chronozone Cr3 (about 100,000 years before the Thvera normal subchronozone C3n.4n). The base is also close to the extinction level of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphysis
The diaphysis (: diaphyses) is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat). It is a middle tubular part composed of compact bone which surrounds a central marrow cavity which contains red or yellow marrow. In diaphysis, primary ossification Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ... occurs. Ewing sarcoma tends to occur at the diaphysis.Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Board Review, Cuccurullo Additional images Illu long bone.jpg File:EpiMetaDiaphyse.jpg, Long bone See also * Epiphysis * Metaphysis References Long bones {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condylus Dorsalis
A condyle (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. , from ; κόνδυλος knuckle) is the round prominence at the end of a , most often part of a joint – an articulation with another bone. It is one of the markings or features of bones, and can refer to: * On the , in the joint: ** [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aechmophorus
''Aechmophorus'' is a genus of birds in the grebe family. Species It has two living representatives breeding in western North America. One prehistoric species has been described from fossil remains: *'' Aechmophorus elasson'' (Late Pliocene of W USA) Although the two living species look very similar, bill shape and coloration, as well as feathering around the scarlet eye of the bird can be used to determine the precise species. Distinguishing features The western grebe has a straight bill with a dull green-yellow color as opposed to the Clark's grebe, which has a slightly upturned, bright orange-yellow bill. In both species the male has a longer and deeper bill than that of the female, making it a distinguishing feature. All species of grebes display the pattern of lobed feet. A tough skin surrounds each toe separately, providing more surface area for effective swimming. This form increases the power of propulsion per stroke and reduces drag when the bird is recovering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grebe
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order (biology), order Podicipediformes (). Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in sea, marine habitats during Bird migration, migration and winter. Most grebes fly, although some flightless species exist, most notably in stable lakes. The order contains a single family (biology), family, the Podicipedidae, which includes 22 species in six extant genus, genera. Although, superficially, they resemble other diving birds such as loons and coots, they are most closely related to flamingos, as supported by morphology (biology), morphological, molecular and paleontology, paleontological data. Many species are monogamy in animals, monogamous and are known for their courtship displays, with the pair performing synchronized dances across the water's surface. The birds build floating vegetative nests where they lay several eggs. About a third of the world's grebes are listed at various levels of conservatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podiceps
''Podiceps'' is a genus of birds in the grebe family. The genus name comes from Latin , "rear-end" and ', "foot", and is a reference to the placement of a grebe's legs towards the rear of its body. It has representatives breeding in all continents except Antarctica. Some species are partially or entirely migratory, moving in winter to the coast or warmer climates. Most species are widespread and overall common, but three South American species each are restricted to a single country; two of them are seriously threatened and a third is already extinct. They breed in vegetated areas of freshwater lakes, nesting on the water's edge, since their legs are set too far back for easy walking. Usually two eggs are laid, and the striped young may be carried on the adult's back. All the genus are excellent swimmers and divers, and pursue their fish prey underwater. Adults have striking breeding plumage, with no difference between the sexes. In winter, the plumage is subdued whites and gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |