|
Pneuma (other)
''Pneuma'' () is an ancient Greek word for "breath", and in a religious context for " spirit". It has various technical meanings for medical writers and philosophers of classical antiquity, particularly in regard to physiology, and is also used in Greek translations of ''ruach'' רוח in the Hebrew Bible, and in the Greek New Testament. In classical philosophy, it is distinguishable from ''psyche'' (), which originally meant "breath of life", but is regularly translated as "spirit" or most often "soul". Presocratics , "air in motion, breath, wind", is equivalent in the material monism of Anaximenes to (, "air") as the element from which all else originated. This usage is the earliest extant occurrence of the term in philosophy. A quotation from Anaximenes observes that "just as our soul (''psyche''), being air (), holds us together, so do breath () and air () encompass the whole world." In this early usage, and are synonymous. Aristotle The "connate pneuma" (''symphuton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
πνεῦμα
''Pneuma'' () is an ancient Greek word for "breathing, breath", and in a religious context for "spirit (animating force), spirit". It has various technical meanings for medical writers and philosophers of classical antiquity, particularly in regard to physiology, and is also used in Greek translations of ''ruach'' :wikt:רוח, רוח in the Hebrew Bible, and in the Novum Testamentum Graece, Greek New Testament. In classical philosophy, it is distinguishable from ''Psyche (psychology)#Etymology, psyche'' (), which originally meant "breath of life", but is regularly translated as "spirit" or most often "soul#Philosophical views, soul". Presocratics , "air in motion, breath, wind", is equivalent in the material monism of Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes to (, "air") as the element from which all else originated. This usage is the earliest extant occurrence of the term in philosophy. A quotation from Anaximenes observes that "just as our soul (''psyche''), being air (), holds us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexis
''Movement of Animals'' (or ''On the Motion of Animals''; Greek Περὶ ζῴων κινήσεως; Latin ''De Motu Animalium'') is one of Aristotle's major texts on biology. It sets out the general principles of animal locomotion In ethology, animal locomotion is any of a variety of methods that animals use to move from one place to another. Some modes of locomotion are (initially) self-propelled, e.g., running, swimming, jumping, flight, flying, hopping, soaring and gli .... Pneuma All animals "possess an inborn spirit (''pneuma sumphuton'') and exercise their strength in virtue of it." (703a10). This inborn spirit is used to explain desire (''orexis''), which is classified as the "central origin (''to meson''), which moves by being itself moved." (703a5-6). Aristotle furthers this idea of being a "middle cause" by furnishing the metaphor of the movement of the elbow, as it relates to the immobility of the shoulder (703a13). The inborn ''pneuma'' is, likewise, tethered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexis
Hexis () is a relatively stable arrangement or disposition, for example a person's health or knowledge or character. It is an Ancient Greek word, important in the philosophy of Aristotle, and because of this it has become a traditional word of philosophy. It stems from a verb related to possession or "having", and Jacob Klein, for example, translates it as "possession". It is more typically translated in modern texts occasionally as "state" (e.g., H. Rackham), but more often as "disposition". General description Joe Sachs translates it as "active condition", in order to make sure that ''hexis'' is not confused with passive conditions of the soul, such as feelings and impulses or mere capacities that belong to us by nature. Sachs points to Aristotle's own distinction, explained for example in '' Categories'' 8b, which distinguishes the word ''diathesis'', normally uncontroversially translated as disposition. In this passage, ''diathesis'' only applies to passive and shallow dispos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penguin Books
Penguin Books Limited is a Germany, German-owned English publishing, publishing house. It was co-founded in 1935 by Allen Lane with his brothers Richard and John, as a line of the publishers the Bodley Head, only becoming a separate company the following year."About Penguin – company history" , Penguin Books. Penguin revolutionised publishing in the 1930s through its inexpensive paperbacks, sold through Woolworths (United Kingdom), Woolworths and other stores for Sixpence (British coin), sixpence, bringing high-quality fiction and non-fiction to the mass market. Its success showed that large audiences existed for several books. It also affected modern British popular culture significantly through its books concerning politics, the arts, and science. Penguin Books is now an imprint (trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeno Of Citium
Zeno of Citium (; , ; c. 334 – c. 262 BC) was a Hellenistic philosophy, Hellenistic philosopher from Kition, Citium (, ), Cyprus. He was the founder of the Stoicism, Stoic school of philosophy, which he taught in Athens from about 300 BC. Based on the moral ideas of the Cynicism (philosophy), Cynics, Stoicism laid great emphasis on good and evil, goodness and calmness, peace of mind gained from living a life of virtue in accordance with nature. It proved very popular, and flourished as one of the Hellenistic philosophy, major schools of philosophy from the Hellenistic period through to the Roman era, and enjoyed revivals in the Renaissance as Neostoicism and in the current era as Modern Stoicism. Life Zeno was born c. 334 BC, in the colony of Kition, Citium in Classical Cyprus, Cyprus. His ancestry is disputed between Phoenician and Greeks, Greek, because Citium contained both Phoenician and Greek inhabitants. While a number of contemporary and modern historians regard Zeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleanthes
Cleanthes (; ; c. 330 BC – c. 230 BC), of Assos, was a Greek Stoic philosopher and boxer who was the successor to Zeno of Citium as the second head ('' scholarch'') of the Stoic school in Athens. Originally a boxer, he came to Athens where he took up philosophy, listening to Zeno's lectures. He supported himself by working as a water-carrier at night. After the death of Zeno, c. 262 BC, he became the head of the school, a post he held for the next 32 years. Cleanthes successfully preserved and developed Zeno's doctrines. He originated new ideas in Stoic physics, and developed Stoicism in accordance with the principles of materialism and pantheism. Among the fragments of Cleanthes' writings which have come down to us, the largest is a ''Hymn to Zeus''. His pupil was Chrysippus who became one of the most important Stoic thinkers. Life Cleanthes was born in Assos in the Troad, about 330 BC. According to Diogenes Laërtius, he was the son of Phanias, and early in life he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meditations
''Meditations'' () is a series of personal writings by Marcus Aurelius, Roman Emperor from 161–180 AD, recording his private notes to himself and ideas on Stoic philosophy. Composition Marcus Aurelius wrote the 12 books of the ''Meditations'' in Koine Greek as a source for his own guidance and self-improvement. It is possible that large portions of the work were written at Sirmium, where he spent much time planning military campaigns from 170–180 AD. A portion of his work was written while he was positioned at Aquincum on campaign in Pannonia, because internal notes reveal that the first book was written when he was campaigning against the Quadi on the river Granova (modern-day Hron in Slovakia) and the second book was written at Carnuntum. It is unlikely that Marcus Aurelius ever intended the writings to be published. The work has no official title, so "Meditations" is one of several titles commonly assigned to the collection. These writings take the form of quotations varyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic particles. In everyday as well as scientific usage, ''matter'' generally includes atoms and anything made up of them, and any particles (or combination of particles) that act as if they have both rest mass and volume. However it does not include massless particles such as photons, or other energy phenomena or waves such as light or heat. Matter exists in various states (also known as phases). These include classical everyday phases such as solid, liquid, and gas – for example water exists as ice, liquid water, and gaseous steam – but other states are possible, including plasma, Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates, and quark–gluon plasma. Usually atoms can be imagined as a nucleus of protons and neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaphysics
Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that examines the basic structure of reality. It is traditionally seen as the study of mind-independent features of the world, but some theorists view it as an inquiry into the conceptual framework of human understanding. Some philosophers, including Aristotle, designate metaphysics as first philosophy to suggest that it is more fundamental than other forms of philosophical inquiry. Metaphysics encompasses a wide range of general and abstract topics. It investigates the nature of existence, the features all entities have in common, and their division into categories of being. An influential division is between particulars and universals. Particulars are individual unique entities, like a specific apple. Universals are general features that different particulars have in common, like the color . Modal metaphysics examines what it means for something to be possible or necessary. Metaphysicians also explore the concepts of space, time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmos
The cosmos (, ; ) is an alternative name for the universe or its nature or order. Usage of the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity. The cosmos is studied in cosmologya broad discipline covering scientific, religious or philosophical aspects of the cosmos and its nature. Religious and philosophical approaches may include the cosmos among spiritual entities or other matters deemed to exist outside the physical universe. Etymology The verb wikt:κοσμέω, κοσμεῖν (''kosmein'') meant generally "to dispose, prepare", but especially "to order and arrange (troops for battle), to set (an army) in array"; also "to establish (a government or regime)", "to adorn, dress" (especially of women). Thus ''kosmos'' meant "ornaments, decoration" (compare ''kosmokomes'' "dressing the hair," and cosmetic). The philosopher Pythagoras used the term ''kosmos'' for the order of the universe. Anaxagoras further introduced the concept of a C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
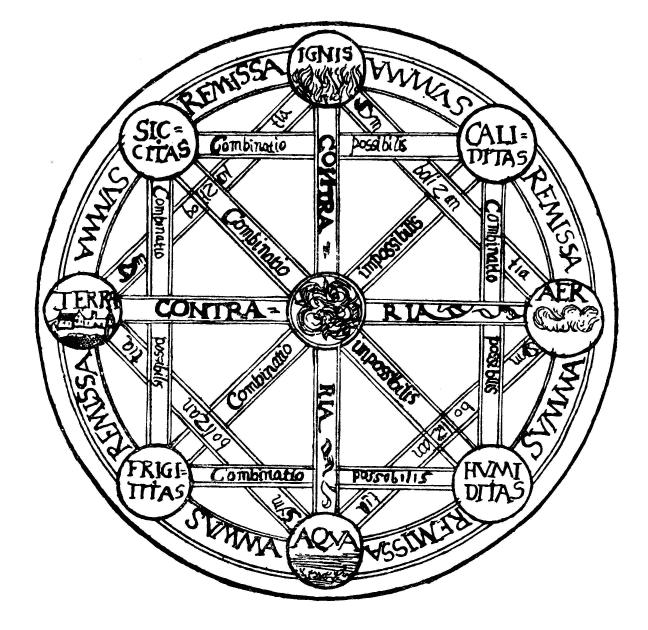
Classical Element
The classical elements typically refer to Earth (classical element), earth, Water (classical element), water, Air (classical element), air, Fire (classical element), fire, and (later) Aether (classical element), aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler Substance theory, substances. Ancient cultures in Ancient Greece, Greece, Angola, Ancient Tibet, Tibet, Ancient India, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personification, personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoicism
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy that flourished in ancient Greece and Rome. The Stoics believed that the universe operated according to reason, ''i.e.'' by a God which is immersed in nature itself. Of all the schools of ancient philosophy, Stoicism made the greatest claim to being utterly systematic. The Stoics provided a unified account of the world, constructed from ideals of logic, monistic physics, and naturalistic ethics. These three ideals constitute virtue which is necessary for 'living a well reasoned life', seeing as they are all parts of a logos, or philosophical discourse, which includes the mind's rational dialogue with itself. Stoicism was founded in the ancient Agora of Athens by Zeno of Citium around 300 BC, and flourished throughout the Greco-Roman world until the 3rd century AD, and among its adherents was Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius. Along with Aristotelian term logic, the system of propositional logic developed by the Stoics was one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |