|
Pluteus Nevadensis
''Pluteus nevadensis'' is a species of fungus in the agaric family Pluteaceae. Described as new to science in 2010, the species is known only from subtropical and pine forests in Mexico, where it grows on rotting pine and oak wood. Fruit bodies (mushrooms) have red-orange caps up to in diameter with a shape ranging from conic, convex, or flattened, depending on their age. The silky yellow stems are up to long. It is similar in appearance to '' Pluteus aurantiorugosus'', with which it shares an orange- or scarlet-colored cap and a yellow stem. ''P. nevadensis'' can be distinguished from this and other superficially similar '' Pluteus'' species by differences in microscopic characteristics. Taxonomy The species was described by Olivia Rodríguez in 2010 in the journal ''Mycotaxon'', based on collections made in 1991. The holotype material was collected on the Colima volcano, in the Municipality of Zapotlán el Grande, at an elevation of . The species was formerly refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in Municipalities of Guerrero, 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the population was recorded that 3,540,685 people who live there. The international sales of their production has gone up, production like fresh mangoes, figs, coconuts, pineapple, avocado, and so much more produce. These sales have really helped Guerrero's economy. These productions have also helped In addition to the capital city, the state's largest cities include Acapulco, Petatlán, Ciudad Altamirano, Guerrero, Ciudad Altamirano, Taxco, Iguala, Ixtapa, Zihuatanejo, anSanto Domingo Today, it is home to a number of indigenous communities, including the Nahuas, Mixtec, Mixtecs, Tlapanec people, Tlapanecs, Amuzgos, and formerly Cuitlatec people, Cuitlatecscopied from article, GuerreroMo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance ( shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
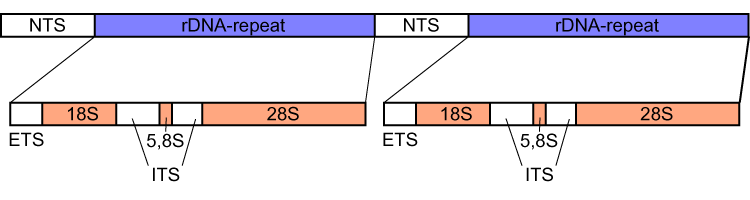
Internal Transcribed Spacer
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. ITS across life domains In bacteria and archaea, there is a single ITS, located between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Conversely, there are two ITSs in eukaryotes: ITS1 is located between 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes, while ITS2 is between 5.8S and 28S (in opisthokonts, or 25S in plants) rRNA genes. ITS1 corresponds to the ITS in bacteria and archaea, while ITS2 originated as an insertion that interrupted the ancestral 23S rRNA gene. Organization In bacteria and archaea, the ITS occurs in one to several copies, as do the flanking 16S and 23S genes. When there are multiple copies, these do not occur adjacent to one another. Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree. History The theoretical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluteus Horakianus
''Pluteus'' is a large genus of fungi with over 300 species. They are wood rotting saprobes with pink spore prints and gills that are free from the stem. The Latin word ''Pluteus'' means ''shed or penthouse''. Characteristics of the genus Characteristics of the ''Pluteus'' genus are: #These fungi grow on wood or wood remains. #The spore powder is deep pink, soon giving a pink tint to the initially pale gills. #The gills are free from the stipe. #There is no volva or ring (exception: the rare recently reclassified North American species ''P. mammillatus'', previously ''Chamaeota sphaerospora''). #Microscopically, they often have abundant, distinctive cystidia. The spores are smooth and roughly egg-shaped. ''Pluteus'' is separated from '' Volvariella'' due to the lack of a volva, and from '' Entoloma'' by growing on wood and by microscopic features (''Entolomas'' have angular spores). Naming The name ''Pluteus'' was established in 1837 by the founding mycologist Elias M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluteus Thompsonii
''Pluteus'' is a large genus of fungi with over 300 species. They are wood rotting saprobes with pink spore prints and gills that are free from the stem. The Latin word ''Pluteus'' means ''shed or penthouse''. Characteristics of the genus Characteristics of the ''Pluteus'' genus are: #These fungi grow on wood or wood remains. #The spore powder is deep pink, soon giving a pink tint to the initially pale gills. #The gills are free from the stipe. #There is no volva or ring (exception: the rare recently reclassified North American species ''P. mammillatus'', previously ''Chamaeota sphaerospora''). #Microscopically, they often have abundant, distinctive cystidia. The spores are smooth and roughly egg-shaped. ''Pluteus'' is separated from '' Volvariella'' due to the lack of a volva, and from '' Entoloma'' by growing on wood and by microscopic features (''Entolomas'' have angular spores). Naming The name ''Pluteus'' was established in 1837 by the founding mycologist Elias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap Cuticle
The pileipellis is the uppermost layer of hyphae in the pileus of a fungal fruit body. It covers the trama, the fleshy tissue of the fruit body. The pileipellis is more or less synonymous with the cuticle, but the cuticle generally describes this layer as a macroscopic feature, while pileipellis refers to this structure as a microscopic layer. Pileipellis type is an important character in the identification of fungi. Pileipellis types include the cutis, trichoderm, epithelium, and hymeniderm types. Types Cutis A cutis is a type of pileipellis characterized by hyphae that are repent, that is, that run parallel to the pileus surface. In an ixocutis, the hyphae are gelatinous. Trichoderm In a trichoderm, the outermost hyphae emerge roughly parallel, like hairs, perpendicular to the cap surface. The prefix "tricho-" comes from a Greek word for "hair". In an ixotrichodermium, the outermost hyphae are gelatinous. Epithelium An epithelium is a pileipellis consisting of rounded ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystidia
A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are often unique to a particular species or genus, they are a useful micromorphological characteristic in the identification of basidiomycetes. In general, the adaptive significance of cystidia is not well understood. Classification of cystidia By position Cystidia may occur on the edge of a lamella (or analogous hymenophoral structure) (cheilocystidia), on the face of a lamella (pleurocystidia), on the surface of the cap (dermatocystidia or pileocystidia), on the margin of the cap (circumcystidia) or on the stipe (caulocystidia). Especially the pleurocystidia and cheilocystidia are important for identification within many genera. Sometimes the cheilocystidia give the gill edge a distinct colour which is visible to the naked eye or wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Section (biology)
In biology a section ( la, sectio) is a taxonomic rank that is applied differently in botany and zoology. In botany Within flora (plants), 'section' refers to a ''botanical'' rank below the genus, but above the species: * Domain > Kingdom > Division > Class > Order > Family > Tribe > Genus > Subgenus > Section > Subsection > Species In zoology Within fauna (animals), 'section' refers to a ''zoological'' rank below the order, but above the family: * Domain > Kingdom > Phylum > Class > Order > Section > Family > Tribe > Genus > Species In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ... In bacteriology The International Code of Nomenclature for Bacteria states that the Section rank is an informal one, between the subgenus and species (as in botany). References Botani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |