|
Pleurocidin
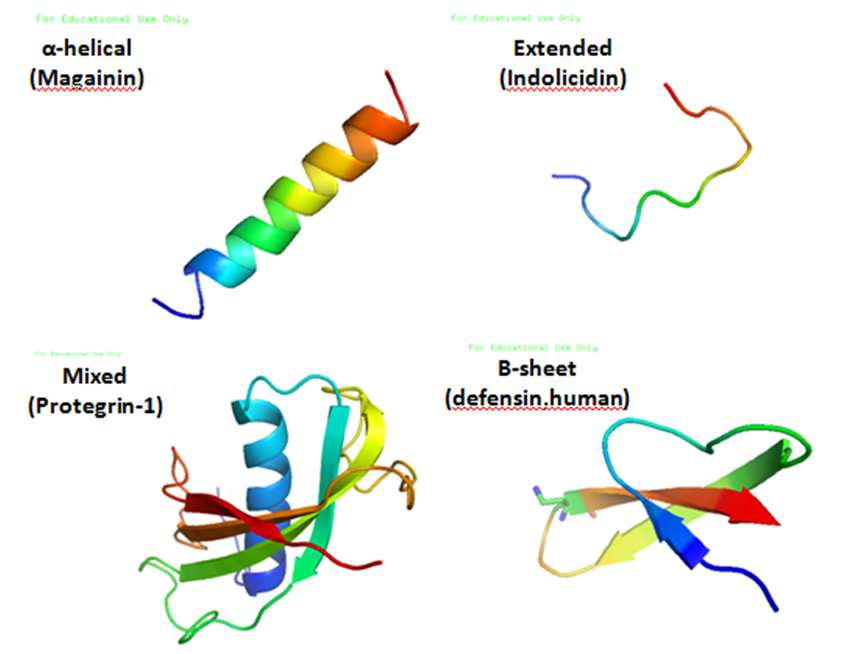
Pleurocidin is an antimicrobial peptide found in the mucus secreted by the skin of the winter flounder (Pleuronectes americanus). It exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Pleurocidin assumes an amphipathic alpha-helical conformation similar to other linear antimicrobial peptides Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for a ... and may play a role in innate host defence. Potential Applications Pleurocidin has been noted for its potential use in food safety, in part due to its heat stable properties and clinically demonstrated effectiveness against common food-borne microorganisms. References {{InterPro content, IPR012515 Protein families Antimicrobial peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Peptide
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antibiotics which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. Antimicrobial peptides are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretion
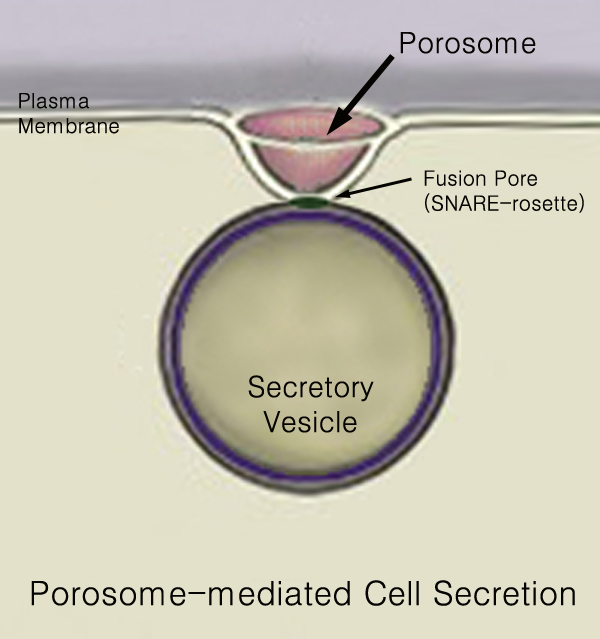
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. '' Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter Flounder
The winter flounder (''Pseudopleuronectes americanus''), also known as the black back, is a right-eyed (" dextral") flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is native to coastal waters of the western north Atlantic coast, from Labrador, Canada to Georgia, United States, although it is less common south of Delaware Bay. It is the most common near-shore (shallow-water) flounder in the waters from Newfoundland down through Massachusetts Bay, reaching a maximum size around 61 cm in length and 2.25 kg in weight. The species grows larger on Georges Bank, where they can reach a length of 70 cm and weight of 3.6 kg. Although winter flounder historically supported large commercial and recreational fisheries, biomass and landings have decreased since the 1980s. Life cycle Winter flounder lay up to 3.3 million demersal, adhesive eggs that are retained within their spawning grounds. Depending on temperature, larvae of approximately 3 mm in length hatch in two to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad-spectrum Antibiotic
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are used when a bacterial infection is suspected but the group of bacteria is unknown (also called empiric therapy) or when infection with multiple groups of bacteria is suspected. This is in contrast to a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, which is effective against only a specific group of bacteria. Although powerful, broad-spectrum antibiotics pose specific risks, particularly the disruption of native, normal bacteria and the development of antimicrobial resistance. An example of a commonly used broad-spectrum antibiotic is ampicillin. Bacterial targets Antibiotics are often grouped by their ability to act on different bacterial groups. Although bacteria are biologically classified using taxonomy, disease-causing bacteria have historically been classified by their m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipathic
An amphiphile (from the Greek αμφις amphis, both, and φιλíα philia, love, friendship), or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic (''water-loving'', polar) and lipophilic (''fat-loving'') properties. Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Common amphiphilic substances are soaps, detergents, and lipoproteins. The phospholipid amphiphiles are the major structural component of cell membranes. Amphiphiles are the basis for a number of areas of research in chemistry and biochemistry, notably that of lipid polymorphism. Organic compounds containing hydrophilic groups at both ends of the molecule are called bolaamphiphilic. The micelles they form in the aggregate are prolate. Structure The lipophilic group is typically a large hydrocarbon moiety, such as a long chain of the form CH3(CH2)n, with n > 4. The hydrophilic group falls into one of the following categories: # charged groups #* anionic. Examples, with the lipophilic part of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Helix
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues earlier along the protein sequence. The alpha helix is also called a classic Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix. The name 3.613-helix is also used for this type of helix, denoting the average number of residues per helical turn, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond. Among types of local structure in proteins, the α-helix is the most extreme and the most predictable from sequence, as well as the most prevalent. Discovery In the early 1930s, William Astbury showed that there were drastic changes in the X-ray fiber diffraction of moist wool or hair fibers upon significant stretching. The data suggested that the unstretched fibers had a coiled molecular structure with a characteristic repeat of ≈. Astbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Conformation
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted just by rotations about formally single bonds (refer to figure on single bond rotation). While any two arrangements of atoms in a molecule that differ by rotation about single bonds can be referred to as different conformations, conformations that correspond to local minima on the potential energy surface are specifically called conformational isomers or conformers. Conformations that correspond to local maxima on the energy surface are the transition states between the local-minimum conformational isomers. Rotations about single bonds involve overcoming a rotational energy barrier to interconvert one conformer to another. If the energy barrier is low, there is free rotation and a sample of the compound exists as a rapidly equilibrating mixture of multiple conformers; if the energy barrier is high enough then there is restricted rotation, a molecule may exist for a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antibiotics which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. Antimicrobial peptides a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Families
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. The most important of these is sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence), since it is the strictest indicator of homology and therefore the clearest indicator of common ancestry. A fairly well developed framework exists for evaluating the significance of similarity between a group of sequences using sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are very unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |