|
Plautdietsch
Plautdietsch () or Mennonite Low German is a Low Prussian dialect of East Low German with Dutch influence that developed in the 16th and 17th centuries in the Vistula delta area of Royal Prussia. The word ''Plautdietsch'' translates to "flat (or low) German" (referring to the plains of northern Germany or the simplicity of the language). In other Low German dialects, the word for Low German is usually realised as ''Plattdütsch/Plattdüütsch'' or ''Plattdüütsk'' , – very often also as ''Plattdeutsch'' – but the spelling ''Plautdietsch'' is used to refer specifically to the Vistula variant of the language. Plautdietsch was a Low German dialect like others until it was taken by Mennonite settlers to the southwest of the Russian Empire starting in 1789. From there it evolved and subsequent waves of migration brought it to North America, starting in 1873. In Latin America the first settlement occurred in Argentina in 1877 coming from Russia. Plautdietsch is spoken by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low German
Low German is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language variety, language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian languages, Frisian and English language, English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch language, Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath line, Benrath and Uerdingen line, Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German languages, High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard German, Standard High German, which is based on High German langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Mennonite
The Russian Mennonites ( it. "Russia Mennonites", i.e., Mennonites of or from the Russian Empire are a group of Mennonites who are the descendants of Dutch and North German Anabaptists who settled in the Vistula delta in West Prussia for about 250 years and established colonies in the Russian Empire (present-day Ukraine and Russia's Volga region, Orenburg Governorate, and Western Siberia) beginning in 1789. Since the late 19th century, many of them have immigrated to countries which are located throughout the Western Hemisphere. The rest of them were forcibly relocated, so very few of their descendants currently live in the locations of the original colonies. Russian Mennonites are traditionally multilingual but Plautdietsch (Mennonite Low German) is their first language as well as their lingua franca. In 2014, there were several hundred thousand Russian Mennonites: about 200,000 live in Germany, 74,122 live in Mexico, 150,000 in Bolivia, 40,000 live in Paraguay, 10,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
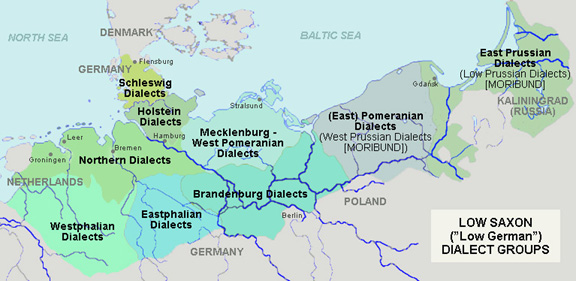
Low Prussian Dialect
Low Prussian (), sometimes known simply as Prussian (''Preußisch''), is a moribund dialect of East Low German that developed in East Prussia. Low Prussian was spoken in East and West Prussia and Danzig up to 1945. In Danzig it formed the basis of the particular city dialect of Danzig German. It developed on a Baltic substrate through the influx of Dutch- and Low German-speaking immigrants. It supplanted Old Prussian, which became extinct in the early 18th century. Simon Dach's poem '' Anke van Tharaw'' was written in Low Prussian. Classification Low Prussian is a Low German dialect formerly spoken in Prussia. It is separated from its only adjacent German dialect, High Prussian, by the Benrath line and the Uerdingen line, the latter dialect being Central German. This was once one of the, if not the hardest linguistic border within the German dialects. Plautdietsch is included within Low Prussian by some observers. Excluding Plautdietsch, Low Prussian can be consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mennonites In Uruguay
Mennonites in Uruguay have been present since 1948. The Mennonites of Uruguay are made up of ethnic Plautdietsch-speaking Russian Mennonites, who are descendants of Friesian, Flemish and Prussian people, as well as Spanish-speaking Uruguayans of all ethnic backgrounds, that converted responding to the missionary efforts of the immigrants. The immigrants belong to a group that is often referred to as Russian Mennonites, because they developed into an ethnic group in the Russian Empire. At the end of the century there were over 1,000 living on Uruguayan territory. Origin The majority of the 1,200 Mennonites who came to Uruguay in the aftermath of World War II lived for about 400 years in the Vistula delta until they were expulsed. A minority came from the region around Lemberg. They spoke and party still speak Plautdietsch, the language which developed in the Vistula delta and which until today unites all conservative "Russian" Mennonites, that have their origin in that regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mennonites In Peru
Mennonites in Peru belong to two quite different groups: converts to the Mennonite faith from different groups of the Peruvian population and very conservative Plautdietsch-speaking ethnic Mennonite Old Colony Mennonites of the so-called Russian Mennonites. Converts to the Mennonite faith are both people who speak Spanish and groups with an indigenous Amerindian background, notably Asháninka. These converts do not differ much from other Protestants in Peru. Russian Mennonites started to settle in Peru in 2015, with two colonies coming from Bolivia and one colony coming from Belize. These Russian Mennonites have their own customs and language (Plautdietsch) and live in colonies. Very Conservative ethnic Mennonites normally do not engage in missionary activities but look for a quiet and remote place where they can live according to their tradition. History Mennonites as a religious group can trace back their roots to the time of the Protestant Reformation. They belonged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mennonite
Mennonites are a group of Anabaptism, Anabaptist Christianity, Christian communities tracing their roots to the epoch of the Radical Reformation. The name ''Mennonites'' is derived from the cleric Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland, part of the Habsburg Netherlands within the Holy Roman Empire, present day Netherlands. Menno Simons became a prominent leader within the wider Anabaptist movement and was a contemporary of Martin Luther (1483–1546) and Philip Melanchthon (1497–1560). Through his writings about the Reformation Simons articulated and formalized the teachings of earlier Swiss Anabaptist founders as well as early teachings of the Mennonites founded on the belief in both the mission and ministry of Jesus. Formal Mennonite beliefs were codified in the Dordrecht Confession of Faith (1632), which affirmed "the baptism of believers only, the washing of the feet as a symbol of servanthood, church discipline, the shunning of the excommunicated, the non-swearing of oaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population of 1,342,153 as of 2021. Manitoba has a widely varied landscape, from arctic tundra and the Hudson Bay coastline in the Northern Region, Manitoba, north to dense Boreal forest of Canada, boreal forest, large freshwater List of lakes of Manitoba, lakes, and prairie grassland in the central and Southern Manitoba, southern regions. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have inhabited what is now Manitoba for thousands of years. In the early 17th century, English and French North American fur trade, fur traders began arriving in the area and establishing settlements. The Kingdom of England secured control of the region in 1673 and created a territory named Rupert's Land, which was placed under the administration of the Hudson's Bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlos Reygadas
Carlos Reygadas Castillo (; born October 10, 1971) is a Mexicans, Mexican filmmaker. Influenced by existentialist art and philosophy, Reygadas' movies feature spiritual journeys into the inner worlds of his main characters, through which themes of love, suffering, death, and life's meaning are explored. Reygadas has been described as "the one-man third wave of Cinema of Mexico, Mexican cinema"; his works are generally considered art films, and are known for their Expressionism, expressionistic cinematography, long takes, and emotionally charged stories. His first and third films, ''Japón (film), Japón'' (2002) and ''Silent Light'' (2007), made him one of Latin America's most prominent writer-directors, with various critics having named ''Silent Light'' as one of the best films of its decade. His films ''Battle in Heaven'' (2005) and ''Post Tenebras Lux (film), Post Tenebras Lux'' (2012) divided critics. He has co-produced other directors such as Amat Escalante (Sangre, Los Bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Low German
East Low German () is a group of Low German dialects spoken in north-eastern Germany as well as by minorities in northern Poland. Together with West Low German dialects, it forms a dialect continuum of the Low German language. Before 1945, the dialect was spoken along the entire then-German-settled Baltic Coast from Mecklenburg, through Pomerania, West Prussia into certain villages of the East Prussian Klaipėda Region. East Pomeranian, Central Pomeranian and West Pomeranian should not be confused with the West Slavic Pomeranian language (). Related languages East Low German belongs to the dialect continuum of the West Germanic languages. It developed from the older Middle Low German. In the West it fades into West Low German. The distinction is usually made referring to the plural endings of the verbs: East Low German endings are based on the old first person ending: -e(n), whereas West Low German endings are based on the old second person ending: -(e)t. The categorizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matt Groening
Matthew Abram Groening ( ; born February 15, 1954) is an American cartoonist, writer, producer, and animator. He is best known as the creator of the television series ''The Simpsons'' (1989–present), ''Futurama'' (1999–2003, 2008–2013, 2023–present), and ''Disenchantment (TV series), Disenchantment'' (2018–2023), and the comic strip ''Life in Hell'' (1977–2012). ''The Simpsons'' is the List of longest-running scripted American primetime television series, longest-running American primetime television series in history, as well as the List of longest-running American television series, longest-running American animated series and sitcom. Born in Portland, Oregon, Groening made his first professional cartoon sale of ''Life in Hell'' to the avant-garde magazine Wet (magazine), ''Wet'' in 1978. At its peak, it was carried in 250 weekly newspapers and caught the attention of American producer James L. Brooks, who contacted Groening in 1985 about adapting it for animated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molotschna
Molotschna Colony or Molochna Colony was a Russian Mennonite settlement in what is now Zaporizhzhia Oblast in Ukraine. Today, the central village, known as Molochansk, has a population less than 10,000. The settlement is named after the Molochna River which forms its western boundary. The land falls mostly within the Tokmatskyi and Chernihivskyi Raions. The nearest large city is Melitopol, southwest of Molochansk. Initially called ''Halbstadt'' (''Half-city''), Molotschna was founded in 1804 by Mennonite settlers from West Prussia and consisted of 57 villages. Known as the New Colony, it was the second and largest Mennonite settlement in the Russian Empire. In the late 19th century, thousands of people left this colony to settle in North America, and later relocated to Latin America, where Mennonites settled in several countries. After many Mennonites left or were deported during and after the last days of World War II, this area became populated largely by Ukrainians. History A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chortitza Colony
Chortitza Colony was a ''volost'', a subdivision of Yekaterinoslav uezd within Yekaterinoslav Governorate in the Russian Empire, now in Ukraine. During the reign of Catherine the Great, the area was annexed by Russia after the liquidation of the Zaporozhian Sich. It was granted to Plautdietsch-speaking settlers (better known as Russian Mennonites) for colonization northwest of Khortytsia Island. The territory of the former colony is now split between the city of Zaporizhzhia and its adjacent Zaporizhzhia Raion, within Zaporizhia it is part of Voznesenskyi and Khortytskyi districts. Chortitza was founded in 1789 by Mennonite settlers of Dutch ancestry from the Vistula delta and consisted of many villages. It was the first of many Mennonite settlements in the Russian Empire. Because the Mennonites living in these villages emigrated or were evacuated or deported at the end of World War II, or emigrated after the collapse of the Soviet Union, few Mennonites are living in the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |