|
Platysma
The platysma muscle or platysma is a :wikt:superficial, superficial muscle of the human neck that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid. It covers the anterior surface of the neck superficially. When it contracts, it produces a slight wrinkling of the neck, and a "bowstring" effect on either side of the neck. Etymology First recorded in the period 1685–1695, the word comes via Neo-Latin from Greek language, Greek ''plátysma'', a plate, literally, something wide and flat, equivalent to ''platý(nein)'', to widen, + -''sma'', a variant of the Resultative#Adjectival resultatives, resultative suffix ''-ma''. The botanist William T. Stearn argues that ''platýs'', "in Greek compound words, usually signifies ''broad'', rarely ''flat''," which describes the platysma's broad sheet of muscle. Structure The platysma muscle is a broad sheet of muscle arising from the fascia covering the upper parts of the pectoralis major, pectoralis major muscle and deltoid muscle. Its fibers cross the clavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podochilus
''Podochilus'' is a genus of about 65 species of small, moss-like epiphytic orchids, distributed across China, the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia (Indochina, Indonesia, Philippines, etc.,) New Guinea, Australia and the Solomon Islands. List of species The following is a list of species of ''Podochilus'' accepted by the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families as at January 2019: * ''Podochilus anguinus'' Schltr. * ''Podochilus appendiculatus'' J.J.Sm. * ''Podochilus auriculigerus'' Schltr. * ''Podochilus australiensis'' (F.M.Bailey) Schltr. * ''Podochilus banaensis'' Ormerod * ''Podochilus bancanus'' J.J.Sm. * ''Podochilus bicaudatus'' Schltr. * ''Podochilus bilabiatus'' J.J.Sm. * ''Podochilus bilobulatus'' Schltr. * ''Podochilus bimaculatus'' Schltr. * ''Podochilus cucullatus'' J.J.Sm. * ''Podochilus cultratus'' Lindl. * ''Podochilus cumingii'' Schltr. * ''Podochilus densiflorus'' Blume * ''Podochilus falcatus'' Lindl. * ''Podochilus falcipetalus'' Schltr. * ''Podochil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Branch Of The Facial Nerve
The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a nerve in the neck. It is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It supplies the platysma muscle, among other functions. Structure The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It runs forward beneath the platysma muscle, and forms a series of arches across the side of the neck over the suprahyoid region. One branch descends to join the cervical cutaneous nerve from the cervical plexus The cervical plexus is a nerve plexus of the anterior rami of the first (i.e. upper-most) four cervical spinal nerves C1-C4. The cervical plexus provides motor innervation to some muscles of the neck, and the diaphragm; it provides sensory inne .... Function The lateral part of the cervical branch of the facial nerve supplies the platysma muscle. Additional images File:Lateral head anatomy detail.jpg, Lateral head anatomy detail File:Slide1BAB.JPG, Lateral head anatomy detail. Dissection the newborn File:S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporalis Muscle
In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch so it covers much of the temporal bone.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 98 ''Temporal'' refers to the head's temples. Structure In humans, the temporalis muscle arises from the temporal fossa and the deep part of temporal fascia. This is a very broad area of attachment. It passes medial to the zygomatic arch. It forms a tendon which inserts onto the coronoid process of the mandible, with its insertion extending into the retromolar fossa posterior to the most distal mandibular molar.Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 194 In other mammals, the muscle usually spans the dorsal part of the skull all the way up to the medial line. There, it may be attached to a sagittal cres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing Temporomandibular joint, joints with the cranium's temporal bones. The mandible hosts the lower Human tooth, teeth (their depth delineated by the alveolar process). Many muscles attach to the bone, which also hosts nerves (some connecting to the teeth) and blood vessels. Amongst other functions, the jawbone is essential for chewing food. Owing to the Neolithic Revolution, Neolithic advent of agriculture (), human jaws evolved to be Human jaw shrinkage, smaller. Although it is the strongest bone of the facial skeleton, the mandible tends to deform in old age; it is also subject to Mandibular fracture, fracturing. Surgery allows for the removal of jawbone fragments (or its entirety) as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibular Symphysis
In human anatomy, the facial skeleton of the skull the external surface of the mandible is marked in the median line by a faint ridge, indicating the mandibular symphysis (Latin: ''symphysis menti'') or line of junction where the two lateral halves of the mandible typically fuse in the first year of life (6–9 months after birth). It is not a true symphysis as there is no cartilage between the two sides of the mandible. This ridge divides below and encloses a triangular eminence, the mental protuberance, the base of which is depressed in the center but raised on either side to form the mental tubercle. The lowest (most inferior) end of the mandibular symphysis — the point of the chin — is called the "menton". It serves as the origin for the geniohyoid and the genioglossus muscles. Other animals Solitary mammalian carnivores that rely on a powerful canine bite to subdue their prey have a strong mandibular symphysis, while pack hunters delivering shallow bites have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 1,603,797 in the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The city is the urban core of the Philadelphia metropolitan area (sometimes called the Delaware Valley), the nation's Metropolitan statistical area, seventh-largest metropolitan area and ninth-largest combined statistical area with 6.245 million residents and 7.379 million residents, respectively. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, an English Americans, English Quakers, Quaker and advocate of Freedom of religion, religious freedom, and served as the capital of the Colonial history of the United States, colonial era Province of Pennsylvania. It then played a historic and vital role during the American Revolution and American Revolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saunders (imprint)
Saunders is an American academic publisher based in the United States. It is currently an imprint of Elsevier. Formerly independent, the W. B. Saunders company was acquired by CBS in 1968, who added it to their publishing division Holt, Rinehart & Winston. When CBS left the publishing field in 1986, it sold the academic publishing units to Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. Harcourt was acquired by Reed Elsevier in 2001. . Northern Illinois University Libraries. Retrieved May 2, 2015. W. B. Saunders published the Kinsey Reports
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
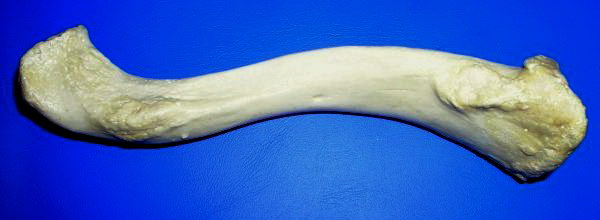
Clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from Latin ''clavicula'' 'little key' because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is Abduction (kinesiology), abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the human arm, arm to the torso, trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the shoulder, human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the # anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis) ( More commonly known as the front delt.) # posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis) ( More commonly known as the rear delt.) # intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis) ( More commonly known as the side delt) The deltoid's fibres are pennate muscle. However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system. It was previously called the deltoideus (plural ''deltoidei'') and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek alphabet, Greek capital letter Delta (letter), delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location. The knowledge of fascial structures is essential in surgery, as they create borders for infectious processes (for example Psoas abscess) and haematoma. An increase in pressure may result in a compartment syndrome, where a prompt fasciotomy may be necessary. For this reason, profound descriptions of fascial structures are available in anatomical literature from the 19th century. Function Fasciae were traditionally thought of as passive structures that transmit mechanical tension generated by muscular activities or external forces throughout the body. An important function of muscle fasciae is to reduce friction of muscular force. In doing so, fasciae provide a supportive and movable wrapping for nerves and blood vessels as they pass thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |