|
Plan 55-A
Automatic Telegraph Switching System Plan 55-A was one in a series of store and forward message switching systems developed by Western Union and used from 1948 to 1976 for processing telegrams. It is an automated successor to Plan 51, which commenced service in 1951 in a nationwide network of the U.S. Air Force, but required semi-automatic operation. Based on the technology of punched paper tape storage, the systems of the design were called ''reperforators''. A reperforator performed functions similar to an email message transfer agent (email server), used much later in the Internet, but it used electro-mechanical technology, which preceded the use of semiconductor circuitry and computers. Operation A reperforator switching center received messages via serial communication lines from teleprinters, such as the Teletype Model 28 ASR, or from other switching centers on ''receiving consoles'', each consisting of a paper tape punch feeding tape into a paper tape reader via a storage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, ''programs'', which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. The term computer system may refer to a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation; or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems, including simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, and factory devices like industrial robots. Computers are at the core of general-purpose devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Film
An industrial video is a video that targets industry as its primary audience. An industrial video is a type of sponsored film (such as an educational film) which prioritizes pragmatism over artistic value. While the primary purpose of an educational film is to inform an audience, the purpose of an industrial video can vary depending on the client. Purposes An industrial video may be used for: *Marketing, communicating to potential clients the value of services or products. *Customers, such as a video that explains how to use a product *Fundraising, such as for informing potential investors about the merits of a company, or generating capital for a charitable cause. *Corporations, such as a video that shares a CEO's vision with his employees, or a video that warns employees against improper ethical behavior. Industrial videos have become more prevalent in the market than industrial films because of the lower cost of producing video content. Content creation Like all filmmaking, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point and point-to-multipoint communication, point-to-multipoint configurations. Initially, from 1887 at the earliest, teleprinters were used in telegraphy. Electrical telegraphy had been developed decades earlier in the late 1830s and 1840s, then using simpler Morse key equipment and telegraph operators. The introduction of teleprinters automated much of this work and eventually largely replaced skilled labour, skilled operators versed in Morse code with Data entry clerk, typists and machines communicating faster via Baudot code. With the development of early computers in the 1950s, teleprinters were adapted to allow typed data to be sent to a computer, and responses printed. Some teleprinter models could also be used to create punched tape for Compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Kleinrock
Leonard Kleinrock (born June 13, 1934) is an American computer scientist and Internet pioneer. He is Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Computer Science at UCLA's Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science. Kleinrock made several important contributions to the field of computer science, in particular to the mathematical foundations of data communication in computer networking. He has received numerous prestigious awards. In the early 1960s, Kleinrock pioneered the application of queueing theory to model delays in message switching networks in his Ph.D. thesis, published as a book in 1964. In the late 1960s and 1970s, he played an influential role in the development of the ARPANET. In the 1970s, he applied queueing theory to model and measure the performance of packet switching networks and published several of the standard works on the subject. He supervised graduate students who worked on the communication protocols for the ARPANET including students whose later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
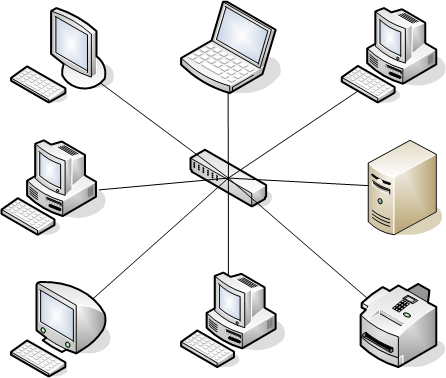
Star Network
A star network is an implementation of a spoke–hub distribution paradigm in computer networks. In a star network, every host is connected to a central hub. In its simplest form, one central hub acts as a conduit to transmit messages. The star network is one of the most common computer network topologies. Network The hub and hosts, and the transmission lines between them, form a graph with the topology of a star. Data on a star network passes through the hub before continuing to its destination. The hub manages and controls all functions of the network. It also acts as a repeater for the data flow. In a typical network the hub can be a network switch, Ethernet hub, wireless access point or a router The star topology reduces the impact of a transmission line failure by independently connecting each host to the hub. Each host may thus communicate with all others by transmitting to, and receiving from, the hub. The failure of a transmission line linking any host to the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teletype Model 28
The Teletype Model 28 is a product line of teleprinters, typing and non-typing tape perforator and tape reperforators, fixed head single contact and pivoted head multi-contact transmitter-distributors, and receiving selector equipment. Regarded as the most rugged machines Teletype Corporation built, this line of teleprinters used an exchangeable type box for printing and sequential selector "Stunt Box" to mechanically initiate non-printing functions within the typing unit of the teleprinter, electrically control functions within the teleprinter and electrically control external equipment. The Teletype Model 28 is more rugged and more expensive than later Teletype Model 32 machines. The Teletype Corporation introduced the Model 28 as a commercial product in 1953 after being originally designed for the United States military. There are three versions of the Model 28 teleprinter: * the Model 28 ASR, (Automatic Send and Receive), which has a built in 5-level paper tape reader and punc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point and point-to-multipoint communication, point-to-multipoint configurations. Initially, from 1887 at the earliest, teleprinters were used in telegraphy. Electrical telegraphy had been developed decades earlier in the late 1830s and 1840s, then using simpler Morse key equipment and telegraph operators. The introduction of teleprinters automated much of this work and eventually largely replaced skilled labour, skilled operators versed in Morse code with Data entry clerk, typists and machines communicating faster via Baudot code. With the development of early computers in the 1950s, teleprinters were adapted to allow typed data to be sent to a computer, and responses printed. Some teleprinter models could also be used to create punched tape for Compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Communication
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels. Serial communication is used for all long-haul communication and most computer networks, where the cost of cable and difficulty of synchronization make parallel communication impractical. Serial computer buses have become more common even at shorter distances, as improved signal integrity and transmission speeds in newer serial technologies have begun to outweigh the parallel bus's advantage of simplicity (no need for serializer and deserializer, or SerDes) and to outstrip its disadvantages (clock skew, interconnect density). The migration from PCI to PCI Express (PCIe) is an example. Modern high speed serial interfaces such as PCIe send data several bits at a time using m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping levels are present in the same crystal, they form a semiconductor junction. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits. Semiconductor devices can display a range of different useful properties, such as passing current more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Store And Forward
Store and forward is a telecommunications technique in which information is sent to an intermediate station where it is kept and sent at a later time to the final destination or to another intermediate station. The intermediate station, or node in a networking context, verifies the integrity of the message before forwarding it. In general, this technique is used in networks with intermittent connectivity, especially in the wilderness or environments requiring high mobility. It may also be preferable in situations when there are long delays in transmission and error rates are variable and high, or if a direct, end-to-end connection is not available. Modern store and forward networking * Store and forward originates with delay-tolerant networks. No real-time services are available for these kinds of networks. * Logistical Networking is a scalable form of store and forward networking that exposes network-embedded buffers on intermediate nodes and allows flexible creation of serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks that consists of Private network, private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, Wireless network, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and Web application, applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), email, electronic mail, internet telephony, streaming media and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |