|
Pithom Stele II.
Pithom (; ; or , and ) was an ancient city of Egypt. References in the Hebrew Bible and ancient Greek and Roman sources exist for this city, but its exact location remains somewhat uncertain. Some scholars identified it as the later archaeological site of Tell el-Maskhuta (). Others identified it as the earlier archaeological site of Tell El Retabeh (). Etymology The English name comes from Hebrew which was taken from the Egyptian toponym ''pr-(j)tm'', "House of Atum". Atum's cult center was in Heliopolis.. Biblical Pithom Pithom is one of the cities which, according to the Book of Exodus , was built for the biblical Pharaoh of the oppression by the forced labour of the Israelites. The other city was Pi-Ramesses. The Septuagint adds a third, "''On'', which is Heliopolis." These cities are called by a term rendered in the Authorized Version "treasure cities" and in the Revised Version "store cities" (). The Septuagint renders it "strong r "fortified"cities." The same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ismailia Governorate
Ismailia () is one of the Canal Zone governorates of Egypt. Located in the northeastern part of the country, its capital is the city of Ismailia. It was named after Ismail Pasha, who as Ottoman Viceroy of Egypt, oversaw the country during the building of the Suez Canal. It is located between the other two Canal governorates; Port Said Governorate, in the Northern part of Egypt and Suez Governorate. Municipal divisions The governorate is divided into municipal divisions, with a total estimated population as of January 2023 of 1,479,511. In the case of Ismailia governorate, there are 4 kism, 5 markaz and 1 new city. The divisions are generally seven: Ismailia which is the capital, Tell El Kebir, Abu Suwir, Qassasin, Fayid, Qantara West and Qantara East. Population According to population estimates, in 2015 the majority of residents in the governorate lived in rural areas, with an urbanization rate of only 45.4%. Out of an estimated 1,479,511 people residing in the gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age. Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations and other peoples.Mark Smith in "The Early History of God: Yahweh and Other Deities of Ancient Israel" states "Despite the long regnant model that the Canaanites and Israelites were people of fundamentally different culture, archaeological data now casts doubt on this view. The material culture of the region exhibits numerous common points between Israelites and Canaanites in the Iron I period (c. 1200–1000 BCE). The record would suggest that the Israelite culture largely overlapped with and derived from Canaanite culture ... In short, Israelite culture was largely Canaanite in nature. Given the information available, one cannot maintain a radical cultural separation between Canaanites and Israelites for the Iron I period." (pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsinoe (Gulf Of Suez)
Arsinoe (), meaning "elevated mind", may refer to: People * Arsinoe of Macedon, mother of Ptolemy I Soter * Apama II or Arsinoe (c. 292 BC–after 249 BC), wife of Magas of Cyrene and mother of Berenice II * Arsinoe, probable mother of Lysimachus or his first wife Nicaea of Macedon * Arsinoe I (305 BC–247 BC) of Egypt * Arsinoe II (316 BC–270 BC) of Egypt * Arsinoe III of Egypt (c. 246 BC–204 BC) * Arsinoe IV of Egypt (died 41 BC), half-sister of Cleopatra VII * Arsinoe (mythology), name of multiple Greek mythological figures Places * Arsinoe (Cilicia) * Arsinoe (Crete) * Arsinoe (Northwest Cyprus) * Arsinoe (Southwest Cyprus) * Arsinoe (Gulf of Suez), a port of Egypt * Arsinoe (Eritrea) * Conope (Greece) or Arsinoe * Ephesus, also called Arsinoe * Faiyum (Egypt), also called Arsinoe or Crocodilopolis, seat of the Roman Catholic titular bishopric Arsinoë in Arcadia * Famagusta (Cyprus) or Arsinoe * Coressia (Greece), called Arsinoe in the Hellenistic period * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitter Lakes
The Great Bitter Lake (; transliterated: ''al-Buḥayrah al-Murra al-Kubrā'') is a large saltwater lake in Egypt which is part of the Suez Canal. Before the canal was built in 1869, the Great Bitter Lake was a dry salt valley or basin. Madl, Pierre (1999)Essay about the phenomenon of Lessepsian Migration, Colloquial Meeting of Marine Biology I, Salzburg, April 1999 (revised in Nov. 2001). References are made to the Great Bitter Lake in the ancient Pyramid Texts. The canal connects the Great Bitter Lake to the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. The canal also connects it to the Small Bitter Lake (; transliterated: al-Buhayrah al-Murra as-Sughra). Ships traveling through the Suez Canal use the Great Bitter Lake as a "passing lane", where they can pass other ships or turn around. Etymology The Modern English and Arabic names are translations of the Greek name (). It was also known in Latin as "dead lake" (). The ancient Egyptian name for the Bitter Lakes region was ''k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly , is about long, and wide at its widest point. It has an average depth of , and in the central Suakin Trough, it reaches its maximum depth of . Approximately 40% of the Red Sea is quite shallow at less than deep and about 25% is less than deep. The extensive shallow shelves are noted for their marine life and corals. More than 1,000 invertebrate species and 200 types of soft and hard coral live in the sea. The Red Sea is the world's northernmost tropical sea and has been designated a Global 200 ecoregion. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river systems by length, longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile has one of the lowest average annual flow rates. About long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt. In pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal Of The Pharaohs
The Canal of the Pharaohs, also called the Ancient Suez Canal or Necho's Canal, is the forerunner of the Suez Canal, constructed in ancient times and kept in use, with intermissions, until being closed in 767 AD for strategic reasons during a rebellion. It followed a different course from its modern counterpart, by linking the Nile to the Red Sea via the Wadi Tumilat. Work began under the pharaohs. According to Darius the Great's Suez Inscriptions and Herodotus, the first opening of the canal was under Persian king Darius the Great, but later ancient authors like Aristotle, Strabo, and Pliny the Elder claim that he failed to complete the work. Another possibility is that it was finished in the Ptolemaic period under Ptolemy II, when engineers solved the problem of overcoming the difference in height through canal locks.Froriep 1986, p. 46 Egyptian and Persian works At least as far back as Aristotle there have been suggestions that perhaps as early as the 12th Dynasty, Pharaoh S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
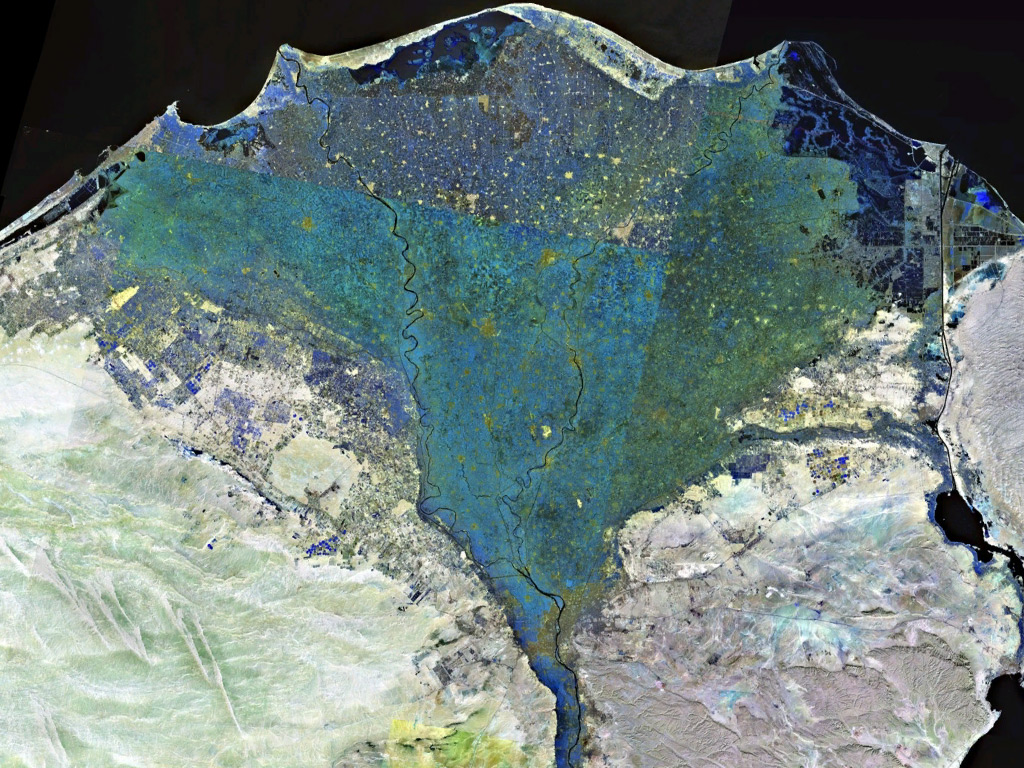
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east; it covers of the Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributary, distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same names. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood management, flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal Of The Pharaohs Map-en
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or river engineering, engineered channel (geography), channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport watercraft, vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers. In most cases, a canal has a series of dams and lock (water transport), locks that create reservoirs of low speed current flow. These reservoirs are referred to as ''slack water levels'', often just called ''levels''. A canal can be called a navigation canal when it parallels a natural river and shares part of the latter's discharge (hydrology), discharges and drainage basin, and leverages its resources by building dams and locks to increase and lengthen its stretches of slack water levels while staying in its valley. A canal can cut across a drainage divide atop a ridge, generally requiring an external water source abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( , "words of the days") is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third section of the Jewish Tanakh, the Ketuvim ("Writings"). It contains a genealogy starting with Adam and a history of ancient Judah and Israel up to the Edict of Cyrus in 539 BC. The book was translated into Greek and divided into two books in the Septuagint in the mid-3rd century BC. In Christian contexts Chronicles is referred to in the plural as the Books of Chronicles, after the Latin name given to the text by Jerome, but is also referred to by its Greek name as the Books of Paralipomenon. In Christian Bibles, they usually follow the two Books of Kings and precede Ezra–Nehemiah, the last history-oriented book of the Protestant Old Testament. Summary The Chronicles narrative begins with Adam, Seth and Enosh, and the story is then carried forward, almos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Kings
The Book of Kings (, ''Sefer (Hebrew), Sēfer Malik, Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of ancient Israel also including the books of Book of Joshua, Joshua, Book of Judges, Judges, and Books of Samuel, Samuel. Biblical commentators believe the Books of Kings mixes legends, folktales, miracle stories and "fictional constructions" in with the annals for the purpose of providing a Theology, theological explanation for the Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), destruction of the Kingdom of Judah by Babylon in c. 586 BC and to provide a foundation for a return from Babylonian captivity, Babylonian exile.Sweeney, p1/ref> The two books of Kings present a history of ancient Israel and Judah, from the death of King David to the release of Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon—a period of some 400 years (). Scholars tend to treat the books as cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |