|
Piracatinga
''Calophysus macropterus'', known natively as the piracatinga/pirácatina, piranambú, pintadinho, zamurito, water buzzard, or by its popular English name vulture catfish, is a species of catfish (order Siluriformes) of the monotypic genus ''Calophysus'' of the family Pimelodidae. It is sometimes placed in its own family, Calophysidae. Description This species reaches SL, though lengths of have been reported. It originates from the Amazon and Orinoco basins, which encompasses waterways in Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Peru, and Venezuela. The vulture catfish is so named because it is an active scavenger, seeking carcasses in its native waterways to consume in shoals; its feeding action promotes the skeletonization of its food items - they are able to consume all the muscles and viscera from an cadaver within half an hour - though it apparently avoids feeding on cartilage elements, eyeballs, scalps, and limb extremities. Its voracious nature has led to it becoming an important sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Peter Müller
Johannes Peter Müller (14 July 1801 – 28 April 1858) was a German physiologist, comparative anatomist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist, known not only for his discoveries but also for his ability to synthesize knowledge. The paramesonephric duct (Müllerian duct) was named in his honor. Life Early years and education Müller was born in Coblenz. He was the son of a poor shoemaker, and was about to be apprenticed to a saddler when his talents attracted the attention of his teacher, and he prepared himself to become a Roman Catholic Priest. During his college course in Koblenz, he devoted himself to the classics and made his own translations of Aristotle. At first, his intention was to become a priest. When he was eighteen, his love for natural science became dominant, and he turned to medicine, entering the University of Bonn in 1819. There he received his M.D. in 1822. He then studied at the University of Berlin. There, under the influence of G. W. F. Hegel and Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, warm valleys, high-altitude Andean plateaus, and snow-capped peaks, encompassing a wide range of climates and biomes across its regions and cities. It includes part of the Pantanal, the largest tropical wetland in the world, along its eastern border. It is bordered by Brazil to the Bolivia-Brazil border, north and east, Paraguay to the southeast, Argentina to the Argentina-Bolivia border, south, Chile to the Bolivia–Chile border, southwest, and Peru to the west. The seat of government is La Paz, which contains the executive, legislative, and electoral branches of government, while the constitutional capital is Sucre, the seat of the judiciary. The largest city and principal industrial center is Santa Cruz de la Sierra, located on the Geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing Net
A fishing net or fish net is a net (device), net used for fishing. Fishing nets work by serving as an improvised fish trap, and some are indeed rigged as traps (e.g. #Fyke nets, fyke nets). They are usually wide open when deployed (e.g. by casting (fishing), casting or trawling), and then close off when retrieved to engulf and trap fish and other aquatic animals that are larger than the holes/gaps of the net, as well as many unwanted bycatches due to the underwater area a net can cover. Fishing nets are usually meshes formed by knotting a relatively thin thread, and early nets were woven from grasses, vines, flaxes and other fiber crop material, while later woven cotton was used. Modern nets are usually made of artificial polyamides like nylon, although nets of organic polyamides such as wool or silk thread were common until recently and are still used. History Fishing nets have been used widely in the past, including by stone age societies. The oldest known fishing net is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic Pathology
Forensic pathology is pathology that focuses on determining the cause of death by examining a corpse. A post mortem examination is performed by a medical examiner or forensic pathologist, usually during the investigation of criminal law cases and civil law cases in some jurisdictions. Coroners and medical examiners are also frequently asked to confirm the identity of remains. Duties Forensic pathology is an application of medical jurisprudence. A forensic pathologist is a medical doctor who has completed training in anatomical pathology and has subsequently specialized in forensic pathology. The requirements for becoming a "fully qualified" forensic pathologist vary from country to country. Some of the different requirements are discussed below (see ''§ Education''). The forensic pathologist performs autopsies/postmortem examinations with the goal of determining the cause of death as well as the possible manner of death. The autopsy report contains conclusions made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
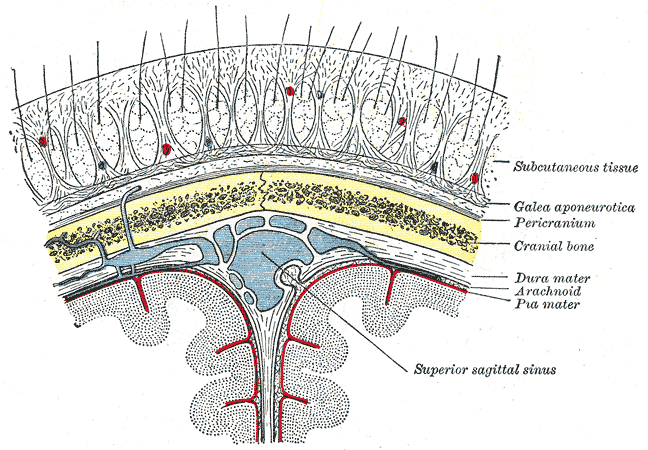
Scalp
The scalp is the area of the head where head hair grows. It is made up of skin, layers of connective and fibrous tissues, and the membrane of the skull. Anatomically, the scalp is part of the epicranium, a collection of structures covering the cranium. The scalp is bordered by the face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. The scientific study of hair and scalp is called trichology. Structure Layers The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can be remembered using the mnemonic 'SCALP': * S: Skin. The skin of the scalp contains numerous hair follicles and sebaceous glands. * C: Connective tissue. A dense subcutaneous layer of fat and fibrous tissue that lies beneath the skin, containing the nerves and vessels of the scalp. * A: Aponeurosis. The epicranial aponeurosis or galea aponeurotica is a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue which anchors the above layers in place. It runs from the frontalis muscle anteriorly to the occipitalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyeball
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system. In higher organisms, the eye is a complex optical Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ... system that collects light from the surrounding environment, regulates its intensity through a Iris (anatomy), diaphragm, Focus (optics), focuses it through an adjustable assembly of Lens (anatomy), lenses to form an image, converts this image into a set of electrical signals, and transmits these signals to the brain through neural pathways that connect the eye via the optic nerve to the visual cortex and other areas of the brain. Eyes with resolving power have come in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans and cyclostomes, it constitutes a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. It usually grows quicker than bone. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadaver
A cadaver, often known as a corpse, is a Death, dead human body. Cadavers are used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue (biology), tissue to repair a defect in a living human being. Students in medical school study and dissect cadavers as a part of their education. Others who study cadavers include archaeologists and arts students. In addition, a cadaver may be used in the development and evaluation of surgical instruments. The term ''cadaver'' is used in courts of law (and, to a lesser extent, also by media outlets such as newspapers) to refer to a dead body, as well as by recovery teams searching for bodies in natural disasters. The word comes from the Latin word ''cadere'' ("to fall"). Related terms include ''cadaverous'' (resembling a cadaver) and ''cadaveric spasm'' (a muscle spasm causing a dead body to twitch or jerk). A cadaver graft (also called “postmortem graft”) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscera
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoaling And Schooling
In biology, any group of fish that stay together for social reasons are shoaling, and if the group is swimming in the same direction in a coordinated manner, they are schooling. In common usage, the terms are sometimes used rather loosely. About one quarter of fish species shoal all their lives, and about one half shoal for part of their lives. Fish derive many benefits from shoaling behaviour including defence against predators (through better predator detection and by diluting the chance of individual capture), enhanced foraging success, and higher success in finding a mate. It is also likely that fish benefit from shoal membership through increased hydrodynamic efficiency. Fish use many traits to choose shoalmates. Generally they prefer larger shoals, shoalmates of their own species, shoalmates similar in size and appearance to themselves, healthy fish, and kin (when recognized). The oddity effect posits that any shoal member that stands out in appearance will be preferen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scavenger
Scavengers are animals that consume Corpse decomposition, dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a herbivorous feeding behavior. Scavengers play an important role in the ecosystem by consuming dead animal and plant material. Decomposer, ''Decomposers'' and detritivores complete this process, by consuming the remains left by scavengers. Scavengers aid in overcoming fluctuations of food resources in the environment. The process and rate of scavenging is affected by both Biotic component, biotic and Abiotic component, abiotic factors, such as carcass size, habitat, temperature, and seasons. Etymology Scavenger is an alteration of ''scavager,'' from Middle English ''skawager'' meaning "customs collector", from ''skawage'' meaning "customs", from Old North French ''escauwage'' meaning "inspection", from ''schauwer'' meaning "to inspect", of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |