|
Pinkes
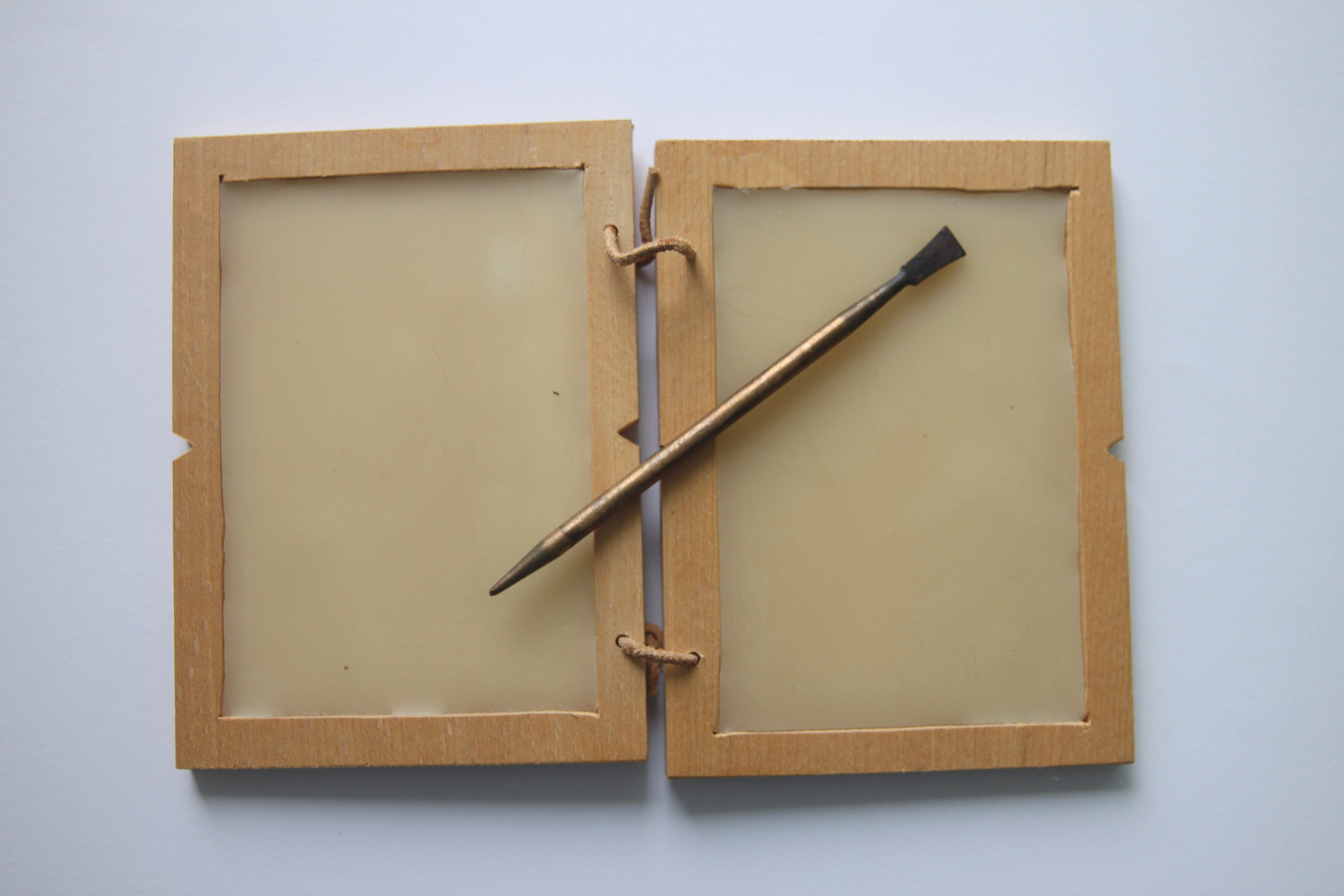
A ''pinkes'' (, plural ''pinkeysim''; , also ''pinkas'', , plural ''pinkasim'') is the ledger of a Jewish community, in which the proceedings of and events relating to the community are recorded. Such record book were used to co-ordinate and document organizations in Jewish towns and villages throughout the early modern period in Europe. Origin The term ''pinkes'' is derived from the Greek word πίναξ, meaning a board or writing-tablet. It originally referred to a physical writing-tablet, as described in the Mishnah, which came in three types: # A tablet covered with dust, primarily used for arithmetical calculations, and large enough to serve as a seat; # A tablet covered with a layer of wax, where writing was done using a stylus A stylus is a writing utensil or tool for scribing or marking into softer materials. Different styluses were used to write in cuneiform by pressing into wet clay, and to scribe or carve into a wax tablet. Very hard styluses are also used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinkas Kehilat Frankfurt De-Oder P1100275
{{disambiguation, given name ...
Pinkas () or Pinchas () may refer to: * A Jewish record book * Pinkas (surname), a Jewish surname * Pinkas Braun (1923–2008), Swiss actor * Pinchas Zukerman (born 1948), Israeli-American violinist, violist and conductor * Pinchas Menachem Justman (1848–1920), Hasidic rabbi and publisher of the Jerusalem Talmud * Pinkas Synagogue, Prague, Czech Republic * ''Pinkas haKehilot'', volume of a book series on Eastern European countries' Jewish communities See also * * Pinka, a river in Central Europe * Pinka, Greater Poland Voivodeship * Phinehas (other) Phinehas was son of Eleazar and grandson of Aaron the High Priest. Phinehas, Pinhas, or Pinchas may also refer to: People *Phinehas, son of Eli, a priest at Shiloh who died with his brother Hophni when the Philistines captured the Ark of the Cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ledger
A ledger is a book or collection of accounts in which accounting transactions are recorded. Each account has: * an opening or brought-forward balance; *a list of transactions, each recorded as either a debit or credit in separate columns (usually with a counter-entry on another page) *and an ending or closing, or carry-forward, balance. Overview The ledger is a permanent summary of all amounts entered in supporting journals (day books) which list individual transactions by date. Usually every transaction, or a total of a series of transactions, flows from a journal to one or more ledgers. Depending on the company's bookkeeping procedures, all journals may be totaled and the totals posted to the relevant ledger each month. At the end of the accounting period, the company's financial statements are generated from summary totals in the ledgers. Ledgers include: * Sales ledger (debtors ledger): records accounts receivable. This ledger records the financial transactions betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly interrelated, as Judaism is their ethnic religion, though it is not practiced by all ethnic Jews. Despite this, religious Jews regard Gerim, converts to Judaism as members of the Jewish nation, pursuant to the Conversion to Judaism, long-standing conversion process. The Israelites emerged from the pre-existing Canaanite peoples to establish Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel and Kingdom of Judah, Judah in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age.John Day (Old Testament scholar), John Day (2005), ''In Search of Pre-Exilic Israel'', Bloomsbury Publishing, pp. 47.5 [48] 'In this sense, the emergence of ancient Israel is viewed not as the cause of the demise of Canaanite culture but as its upshot'. Originally, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date that marks the beginning or end of the period and its extent may vary depending on the area of history being studied. In general, the early modern period is considered to have lasted from around the start of the 16th century to the start of the 19th century (about 1500–1800). In a European context, it is defined as the period following the Middle Ages and preceding the advent of modernity; but the dates of these boundaries are far from universally agreed. In the context of World history (field), global history, the early modern period is often used even in contexts where there is no equivalent "medieval" period. Various events and historical transitions have been proposed as the start of the early modern period, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; , from the verb ''šānā'', "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first written collection of the Jewish oral traditions that are known as the Oral Torah. Having been collected in the 3rd century CE, it is the first work of rabbinic literature, written primarily in Mishnaic Hebrew but also partly in Jewish Palestinian Aramaic. The oldest surviving physical fragments of it are from the 6th to 7th centuries. The Mishnah was literary redaction, redacted by Judah ha-Nasi probably in Beit She'arim (Roman-era Jewish village), Beit Shearim or Sepphoris between the ending of the second century CE and the beginning of the third century. Heinrich Graetz, dissenting, places the Mishnah's compilation in 189 CE (see: H. Graetz, ''History of the Jews'', vol. 6, Philadelphia 1898, p105), and which date follows that penned by Rabbi Abraham ben David in his "Sefer HaKabbalah le-Ravad", or what was then ''anno'' 500 of the Seleucid era. in a time when the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wax Tablet
A wax tablet is a tablet (other), tablet made of wood and covered with a layer of wax, often linked loosely to a cover tablet, as a "double-leaved" diptych. It was used as a reusable and portable writing surface in classical antiquity, antiquity and throughout the Middle Ages. Cicero's letters make passing reference to the use of ''cerae'', and some examples of wax-tablets have been preserved in waterlogged deposits in the Roman Britain, Roman fort at Vindolanda on Hadrian's Wall. Medieval wax tablet books are on display in several European museums. Writing on the wax surface was performed with a pointed instrument, a stylus. A straight-edged spatula-like implement (often placed on the opposite end of the stylus tip) would be used as an eraser. The modern expression of ''"a clean Slate (writing), slate"'' equates to the Latin expression ''"tabula rasa"''. Wax tablets were used for a variety of purposes, from taking down students' or secretaries' notes to recording bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylus
A stylus is a writing utensil or tool for scribing or marking into softer materials. Different styluses were used to write in cuneiform by pressing into wet clay, and to scribe or carve into a wax tablet. Very hard styluses are also used to Engraving, engrave metal, and the slate and stylus system is used to punch out dots to write in Braille. Styluses are held in the hand and thus are usually a narrow elongated shape, similar to a modern ballpoint pen. Many styluses are heavily curved to be held more easily. The word ''stylus'' is also used to describe Stylus (computing), computer styluses used to assist in navigating or providing more precision when using touchscreens. Etymology ''Stylus'' comes from the Latin —the spelling ''stylus'' arose from an erroneous connection with Greek (), 'pillar'.''Oxford Latin Dictionary'', s.v. "stilus" (2012). The Latin word had several meanings, including "a long, sharply pointed piece of metal; the stem of a plant; a pointed instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accounting Journals And Ledgers
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the process of recording and processing information about economic entities, such as businesses and corporations. Accounting measures the results of an organization's economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and regulators. Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants. The terms "accounting" and "financial reporting" are often used interchangeably. Accounting can be divided into several fields including financial accounting, management accounting, tax accounting and cost accounting. Financial accounting focuses on the reporting of an organization's financial information, including the preparation of financial statements, to the external users of the information, such as investors, regulators and suppliers. Management accounting focuses on the measurement, analysis and reporting of information for internal use by management to enhance business op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date that marks the beginning or end of the period and its extent may vary depending on the area of history being studied. In general, the early modern period is considered to have lasted from around the start of the 16th century to the start of the 19th century (about 1500–1800). In a European context, it is defined as the period following the Middle Ages and preceding the advent of modernity; but the dates of these boundaries are far from universally agreed. In the context of World history (field), global history, the early modern period is often used even in contexts where there is no equivalent "medieval" period. Various events and historical transitions have been proposed as the start of the early modern period, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Jews In Europe
The history of the Jews in Europe spans a period of over two thousand years. Jews, a Semitic people descending from the Judeans of Judea in the Southern Levant, Natural History 102:11 (November 1993): 12–19. began migrating to Europe just before the rise of the Roman Empire (27 BCE), although Alexandrian Jews had already migrated to Rome, and some Gentiles had undergone Judaization on a few occasions. A notable early event in the history of the Jews in the Roman Empire was the 63 BCE siege of Jerusalem, where Pompey had interfered in the Hasmonean civil war. Jews have had a significant presence in European cities and countries since the fall of the Roman Empire, including Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, the Netherlands, Germany, Poland, and Russia. In Spain and Portugal in the late fifteenth century, the monarchies forced Jews to either convert to Christianity or leave and they established offices of the Inquisition to enforce Catholic orthodoxy of converted Jews. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |