|
Pinjore Fort
Pinjore is a town in Panchkula district in the Indian state of Haryana. This residential 'township', located close to Panchkula, Chandigarh, is set over 1,800 feet above the sea level in a valley, overlooking the Sivalik Hills. Pinjore is known for Pinjore Gardens, Asia's best 17th Century Mughal garden, and the Hindustan Machine Tools (HMT) factory. History Etymology The town is named after the five Pandava brothers from Mahabharta, who during the time of their exile had stayed here for some time, hence the name Panchpura which later got corrupted to its current form, Pinjore.Haryana Samvad , Oct 2018, p38-40. Panchpura baoli Panchpura baoli, a has ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Q ... mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
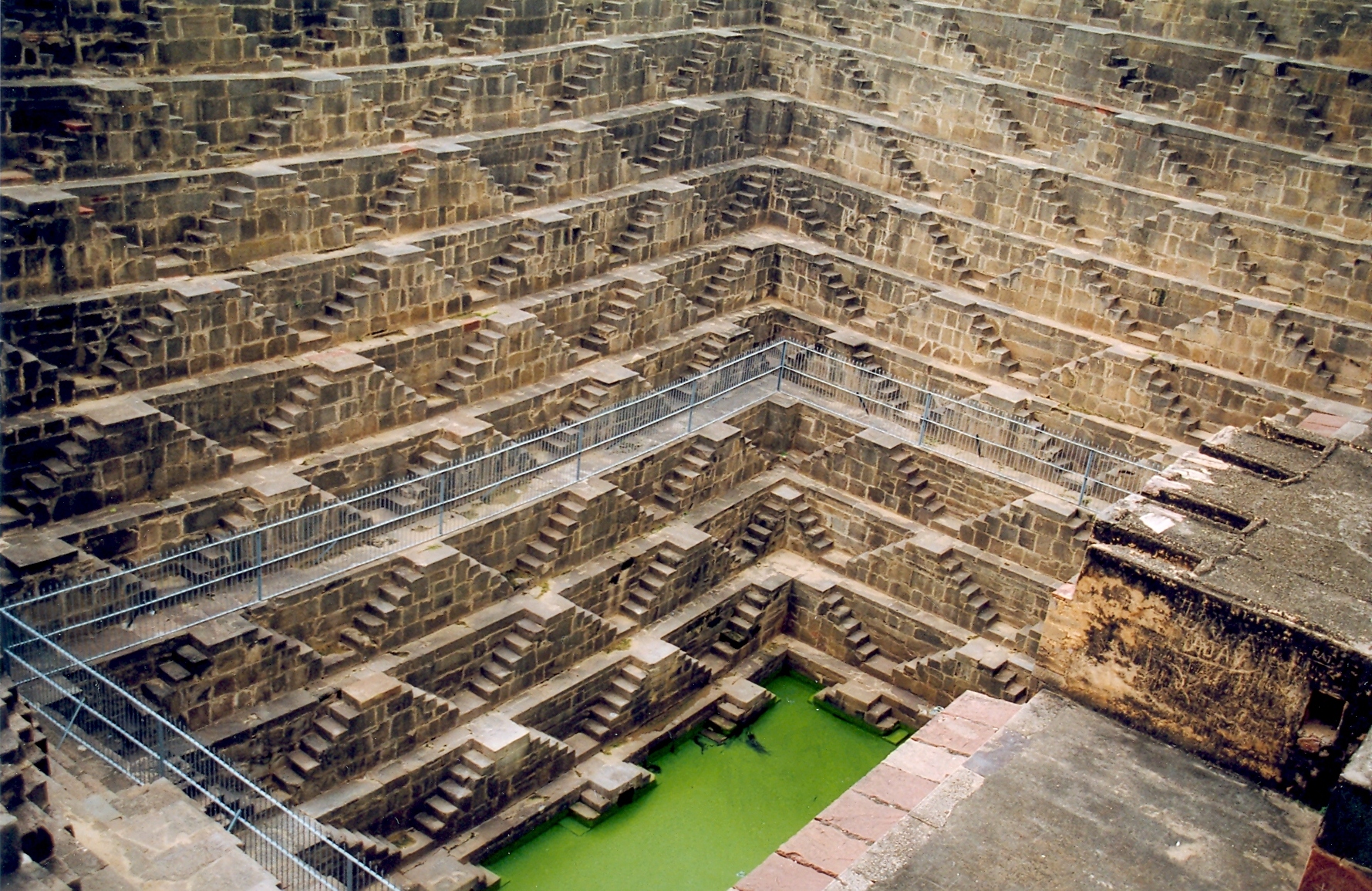
Step Well
Stepwells (also known as vavs or baori) are wells or ponds with a long corridor of steps that descend to the water level. Stepwells played a significant role in defining subterranean architecture in western India from 7th to 19th century. Some stepwells are multi-storeyed and can be accessed by a Persian wheel which is pulled by a bull to bring water to the first or second floor. They are most common in western India and are also found in the other more arid regions of the Indian subcontinent, extending into Pakistan. The construction of stepwells is mainly utilitarian, though they may include embellishments of architectural significance, and be temple tanks. Stepwells are examples of the many types of storage and irrigation tanks that were developed in India, mainly to cope with seasonal fluctuations in water availability. A basic difference between stepwells on the one hand, and tanks and wells on the other, is that stepwells make it easier for people to reach the groundwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acheulean
Acheulean (; also Acheulian and Mode II), from the French ''acheuléen'' after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped " hand axes" associated with ''Homo erectus'' and derived species such as '' Homo heidelbergensis''. Acheulean tools were produced during the Lower Palaeolithic era across Africa and much of West Asia, South Asia, East Asia and Europe, and are typically found with ''Homo erectus'' remains. It is thought that Acheulean technologies first developed about 1.76 million years ago, derived from the more primitive Oldowan technology associated with ''Homo habilis''. The Acheulean includes at least the early part of the Middle Paleolithic. Its end is not well defined, depending on whether Sangoan (also known as "Epi-Acheulean") is included, it may be taken to last until as late as 130,000 years ago. In Europe and Western Asia, early Neanderthals adopted Acheul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Before Present
Before Present (BP) years, or "years before present", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1 January 1950 as the commencement date ( epoch) of the age scale. The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must now account for. In a convention that is not always observed, many sources restrict the use of BP dates to those produced with radiocarbon dating; the alternative notation RCYBP stands for the explicit "radio carbon years before present". Usage The BP scale is sometimes used for dates established by means other than radiocarbon dating, such as stratigraphy. This usage differs from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hominini
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas). The term was originally introduced by Camille Arambourg (1948). Arambourg combined the categories of ''Hominina'' and ''Simiina'' due to Gray (1825) into his new subtribe. Traditionally, chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans were grouped together as pongids. Since Gray's classification, evidence has accumulated from genetic phylogeny confirming that humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas are more closely related to each other than to the orangutan. The former pongids were reassigned to the subfamily Hominidae ("great apes"), which already included humans, but the details of this reassignment remain contested; within Hominini, not every source excludes gorillas, and not every source includes chimpanzees. Humans are the only extant species in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peopling Of India
The peopling of India refers to the migration of ''Homo sapiens'' into the Indian subcontinent. Anatomically modern humans settled India in multiple waves of early migrations, over tens of millennia. The first migrants came with the Coastal Migration/Southern Dispersal 65,000 years ago, whereafter complex migrations within south and southeast Asia took place. West-Asian (Iranian) hunter-gatherers migrated to South Asia after the Last Glacial Period but before the onset of farming. Together with a minor number of ancient South Asian hunter-gatherers they formed the population of the Indus Valley civilisation (IVC). With the decline of the IVC, and the migration of Indo-Europeans, the IVC-people contributed to the formation of both the Ancestral North Indians ("ANI"), who were closely related to contemporary West-Eurasians, and the Ancestral South Indians ("ASI"), who were descended predominantly from the Southeastern Indian hunter gatherers (known as "AASI", who were distantly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaic Humans
A number of varieties of '' Homo'' are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') around 300 ka. Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) from southern Ethiopia ( 195 or 233 ka), the remains from Jebel Irhoud in Morocco (about 315 ka) and Florisbad in South Africa (259 ka) are among the earliest remains of ''Homo sapiens''. The term typically includes '' Homo neanderthalensis'' (430 ± 25 ka), Denisovans, '' Homo rhodesiensis'' (300–125 ka), '' Homo heidelbergensis'' (600–200 ka), '' Homo naledi'', '' Homo ergaster'', '' Homo antecessor'', and ''Homo habilis''. There is no universal consensus on this terminology, and varieties of "archaic humans" are included under the binomial name of either ''Homo sapiens'' or ''Homo erectus'' by some authors. Archaic humans had a brain size averaging 1,200 to 1,400 cubic centimeters, which overlaps with the range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, ( gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Ellcock Pilgrim
(Henry) Guy Ellcock Pilgrim ( Stepney, Barbados, December 24, 1875 – Upton, then in Berkshire, September 15, 1943) was a British geologist and palaeontologist. He was a Fellow of the Royal Society and Superintendent of the Geological Survey of India, and made significant contributions to Cenozoic continental stratigraphy and vertebrate palaeontology. Biography Pilgrim was born the son of Henry Ellcock Pilgrim and Beatrice Lucy Wrenford. After studies at the local Harrison College, he attended University College London where he received his Bachelor of Science in 1901 and Doctor of Science in 1908. He was appointed to the Geological Survey of India in 1902 and promoted to superintendent in 1920, a post he held until his retirement in 1930. He spent much of his retirement at the Department of Geology at the British Museum The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saraswati River
The Sarasvati River () is a deified river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda. As a physical river, in the oldest texts of the Rigveda it is described as a "great and holy river in north-western India," but in the middle and late Rigvedic books it is described as a small river ending in "a terminal lake (samudra)." As the goddess Sarasvati, the other referent for the term "Sarasvati" which developed into an independent identity in post-Vedic times, the river is also described as a powerful river and mighty flood. The Sarasvati is also considered by Hindus to exist in a metaphysical form, in which it formed a confluence with the sacred rivers Ganges and Yamuna, at the Triveni Sangam. According to Michael Witzel, superimposed on the Vedic Sarasvati river is the heavenly river Milky Way, which is seen as "a road to immortality and heavenly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghaggar-Hakra River
The Ghaggar-Hakra River is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season. The river is known as Ghaggar in India, before the Ottu barrage, and as the Hakra in Pakistan, downstream of the barrage, ending in the Thar Desert. In pre-Harappan times the Ghaggar was a tributary of the Sutlej. It is still connected to this paleochannel of the Sutlej, and possibly the Yamuna, which ended in the Nara River, presently a delta channel of the Indus River joining the sea via Sir Creek. The Sutlej changed its course about 8,000-10,000 years ago, leaving the Ghaggar-Hakra as a system of monsoon-fed rivers terminating in the Thar Desert. The Indus Valley civilisation prospered when the monsoons that fed the rivers diminished around 5,000 years ago, and a large number of sites from the Mature Indus Valley Civilisation (2600-1900 BCE) are found along the middle course of the (dried-up) Hakra in Pakistan. Around 4,000 years ago, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
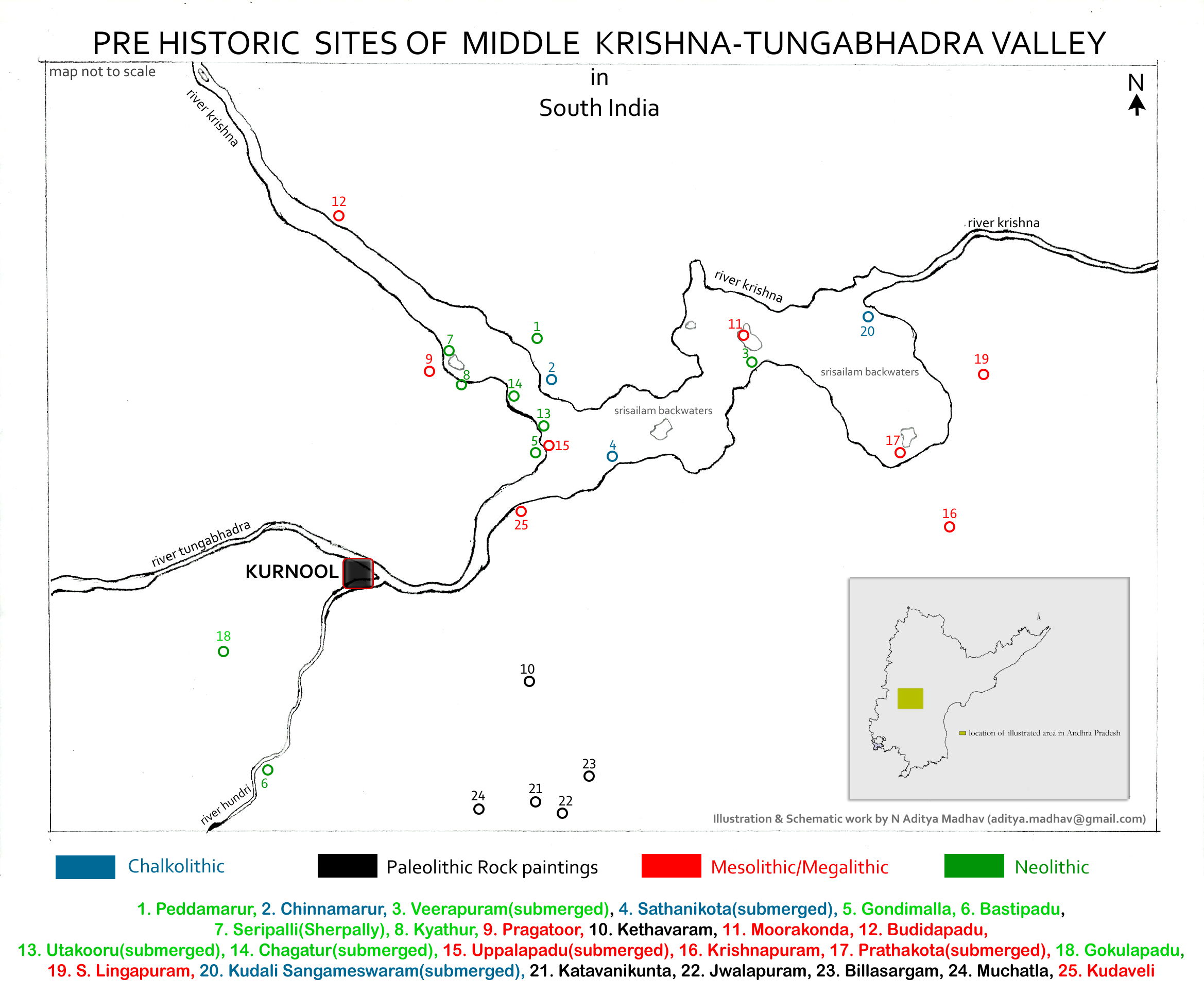
South Asian Stone Age
The South Asian Stone Age covers the Palaeolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic periods in South Asia. Evidence for the most ancient ''Homo sapiens'' in South Asia has been found in the cave sites of Cudappah of India, Batadombalena and Belilena in Sri Lanka. In Mehrgarh, in what is today western Pakistan, the Neolithic began c. 7000 BCE and lasted until 3300 BCE and the first beginnings of the Bronze Age. In South India, the Mesolithic lasted until 3000 BCE, and the Neolithic until 1400 BCE, followed by a Megalithic transitional period mostly skipping the Bronze Age. The Iron Age began roughly simultaneously in North and South India, around c. 1200 to 1000 BCE (Painted Grey Ware culture, Hallur, Paiyampalli). ''Homo erectus'' ''Homo erectus'' lived on the Pothohar Plateau, in upper Punjab, Pakistan along the Soan River (nearby modern-day Rawalpindi) during the Pleistocene Epoch. Soanian sites are found in the Sivalik region across what are now India, Pakistan and Nepal. Biface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)