|
Pindar River
The Pindar River is a river located in Uttarakhand, India. The Pindar originates from Pindari Glacier which is located in Bageshwar district of Kumaon region in Uttarakhand. The source of this river, the Pindar glacier is located at an altitude of . Pindar glacier has relatively easier access and has been documented well for its retreat over 100 years. Pindar river mouth is located at Karnaprayag where it flows into Alaknanda River. Gallery File:Pindari glacier from Zero Point, Uttarakhand, India.jpg, Origin from Pindari Glacier File:Pindari river from Dwali, Uttarakhand, India.jpg, Pindari river from Dwali File:Karnprayag.jpg, Confluence of Alaknanda and Pindar from bottom File:HeadwatersGanges1.jpg, Pinder River (far right) in the map showing The Himalayan headwaters of the Ganges river in Uttarakhand Uttarakhand (, ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2007), is a States and union territories of India, state in North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand (, ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2007), is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. The state is bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the northwest, Tibet to the north, Nepal to the east, Uttar Pradesh to the south and southeast, with a small part touching Haryana in the west. Uttarakhand has a total area of , equal to 1.6% of the total area of India. Dehradun serves as the state capital, with Nainital being the judicial capital. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal division, Garhwal and Kumaon division, Kumaon, with a total of List of districts of Uttarakhand, 13 districts. The forest cover in the state is 45.4% of the state's geographical area. The cultivable area is 16% of the total geographical area. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges and its tributary Yamuna, originate from the Gangotri and Yamunotri glaciers respectively. Ranked 6th among the Top 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumaon Division
Kumaon (; , ; historically romanised as KemāonJames Prinsep (Editor)John McClelland ) is a List of divisions in India, revenue and administrative division in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It spans over the eastern half of the state and is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Nepal, on the south by the state of Uttar Pradesh, and on the west by Garhwal Division, Garhwal. Kumaon comprises six districts of the state: Almora district, Almora, Bageshwar district, Bageshwar, Champawat district, Champawat, Nainital district, Nainital, Pithoragarh district, Pithoragarh and Udham Singh Nagar district, Udham Singh Nagar. Historically known as Manaskhand and then Kurmanchal, the Kumaon region has been ruled by several dynasties over the course of history; most notably the Katyuri kings, Katyuris and the Chand kings, Chands. The Kumaon division was established in 1816, when the British reclaimed this region from the Gorkha Kingdom, Gorkhas, who had annexed the erstwhile Kumaon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bageshwar District
Bageshwar is a district of Uttarakhand state in northern India. The town of Bageshwar is the district headquarters. Prior to its establishment as a district in 1997 it was part of Almora district. Bageshwar district is in Kumaon, and is bounded on the west and northwest by Chamoli District, on the northeast and east by Pithoragarh District, and on the south by Almora District. As of 2011 it is the third least populous district of Uttarakhand (out of 13), after Rudraprayag and Champawat. History The area, that now forms Bageshwar district, was historically known as Danpur, and was ruled by Katyuris during the 7th century AD. After the disintegration of the Katyuri kingdom in the 13th century, the area remained under the rule of Baijnath Katyurs, direct descendants of Katyuri kings. In 1565, king Balo Kalyan Chand annexed Danpur along with Pali, Barahmandal and Mankot to Kumaun. In 1791, Almora, the seat of the Kumaon, was invaded and annexed by the Gorkhas of Nepal. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamoli District
Chamoli district is a district of the Uttarakhand state of India. It is bounded by China's Xizang Autonomous Region to the north, and by the Uttarakhand districts of Pithoragarh district, Pithoragarh and Bageshwar district, Bageshwar to the east, Almora district, Almora to the south, Pauri Garhwal district, Pauri Garhwal to the southwest, Rudraprayag district, Rudraprayag to the west, and Uttarkashi district, Uttarkashi to the northwest. The administrative headquarters of Chamoli district is in Gopeshwar. Chamoli hosts a variety of destinations of pilgrim and tourist interest including Badrinath, Gurudwara Shri Hemkund Sahib, Hemkund Sahib and Valley of Flowers National Park, Valley of Flowers. The Chipko movement was first started in Chamoli. Etymology The name "Chamoli" is derived from the Sanskrit word which stands for "One who wears the moon on his head" denoting the Hindu god Shiva. History The region covered by the district of Chamoli formed part of the Pauri Garhwal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
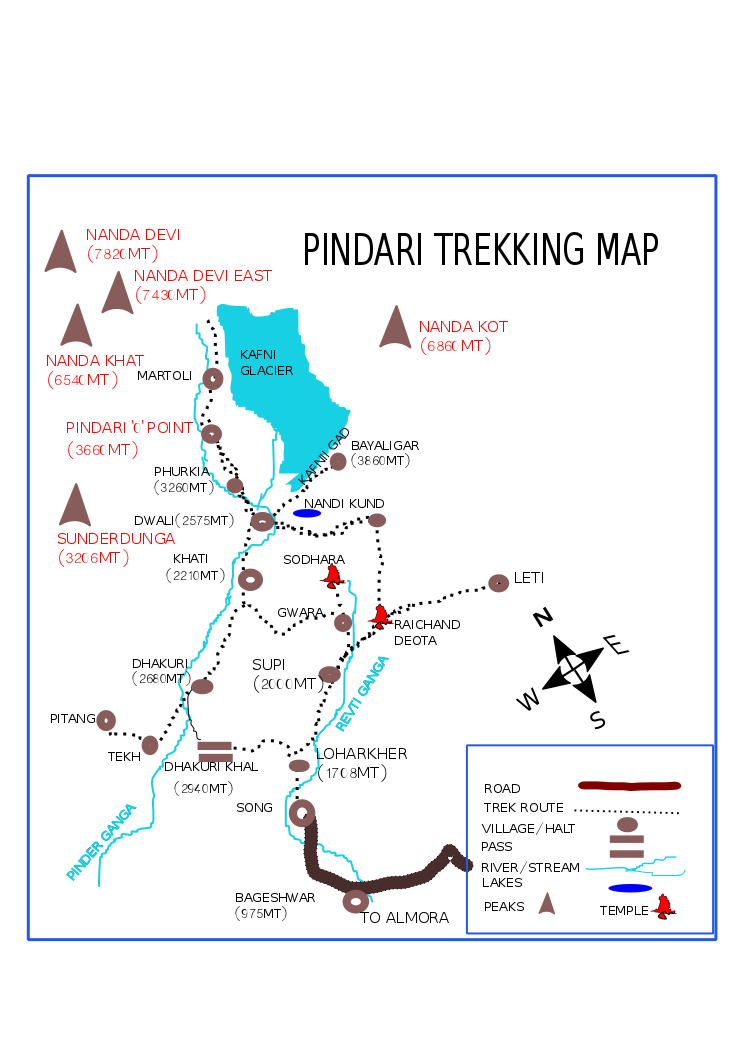
Pindari Glacier
The Pindari Glacier is a glacier found in the upper reaches of the Kumaon Himalayas, to the southeast of Nanda Devi and Nanda Kot. Geography The glacier is about 9 kilometers long and gives rise to the Pindar River which meets the Alakananda at Karnaprayag in the Garhwal district. The trail to reach the glacier crosses the villages of Saung, Loharkhet, crosses over the Dhakuri Pass, continues onto Khati village (the last inhabited village on the trail), Dwali, Phurkia and finally Zero Point, Pindar, the end of the trail. Though most of the trail is along the banks of the Pindari River, the river is mostly hidden until after Khati. The Pindari Glacier trail provides for a round-trip trek that most people find comfortable to complete in 6 days. The Pindari Glacier is also famous for other adventure sports like Ice climbing and Mountain biking. Retreat Several surveys have mapped the retreat of Pindari over the years. The glacier was first surveyed by G.de P.Cotter in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaknanda River
The Alaknanda is a Himalayan river in the Indian state of Uttarakhand and one of the two headstreams of the Ganges, the major river of Northern India and a river considered holy in Hinduism. In hydrology, the Alaknanda is considered the source stream of the Ganges on account of its greater length and discharge; while, in Hindu tradition and culture, the other headstream, the Bhagirathi, is considered the source stream. Course The Alaknanda rises at the confluence and foot of the Satopanth and Bhagirath Kharak glaciers in Uttarakhand. From its origin, it travels to the village of Mana, meets with the Saraswati River, a right bank tributary, and continues downstream through narrow valleys. It reaches the Badrinath valley, arrives at Hanumanchatti, and meets with the Ghrit Ganga, a right bank tributary. From Hanumanchatti, the river goes to Pandukeshwar and flows through wide valleys and steep terrains. At Vishnuprayag it meets Dhauliganga, a left bank tributary, and travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnaprayag
Karnaprayag is a town and municipal board in the Chamoli District in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Karnaprayag is one of the Panch Prayag (five confluences) of Alaknanda River, situated at the confluence of the Alaknanda and Pindar River. Demographics As of the 2001 census, Karnaprayag had a population of 6,976. Males constitute 56% of the population, and females make up 44%. Karnaprayag has an average literacy rate of 76%, higher than the national average of 59.5%. Male literacy is 81%, and female literacy is 69%. 13% of the population is under six years of age. Geography Karnaprayag is located at . It has an average elevation of 860 metres (2,820 feet). The confluence of the Pindar River, which arises from the icy Pindari glacier and the Alaknanda, occurs at Karnaprayag. Overview Karnaprayag is one of five sites where the confluence of rivers occurs. The five prayags are Vishnuprayag, Nandprayag, Karnaprayag, Rudraprayag, and Devprayag. Prayagraj. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges River
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma River, Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna, the lower str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivers Of Uttarakhand
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sediment or alluvium carried by rivers shapes the landscape ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |