|
Pim Levelt
Willem Johannes Maria (Pim) Levelt (born 17 May 1938) is a Dutch psycholinguist. He is a researcher of human language acquisition and speech production. He developed a comprehensive theory of the cognitive processes involved in the act of speaking, including the significance of the "mental lexicon". Levelt was the founding director of the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics in Nijmegen. He also served as president of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences between 2002 and 2005, of which he has been a member since 1978. Education and career Levelt studied psychology at Leiden University. He worked experimentally for five months under Albert Michotte at the University of Louvain. In 1965, he received his doctorate (cum laude) with John P. van de Geer with a thesis on binocular rivalry. He then spent a year as a postdoctoral fellow at the Harvard Center for Cognitive Studies. Since 1966, Levelt taught and researched at the University of Illinois, the Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Region of Amsterdam, urban area and 2,480,394 in the Amsterdam metropolitan area, metropolitan area. Located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, Dutch province of North Holland, Amsterdam is colloquially referred to as the "Venice of the North", for its canals of Amsterdam, large number of canals, now a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Amsterdam was founded at the mouth of the Amstel River, which was dammed to control flooding. Originally a small fishing village in the 12th century, Amsterdam became a major world port during the Dutch Golden Age of the 17th century, when the Netherlands was an economic powerhouse. Amsterdam was the leading centre for finance and trade, as well as a hub of secular art production. In the 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyman John Harvard (clergyman), John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. Its influence, wealth, and rankings have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world. Harvard was founded and authorized by the Massachusetts General Court, the governing legislature of Colonial history of the United States, colonial-era Massachusetts Bay Colony. While never formally affiliated with any Religious denomination, denomination, Harvard trained Congregationalism in the United States, Congregational clergy until its curriculum and student body were gradually secularized in the 18th century. By the 19th century, Harvard emerged as the most prominent academic and cultural institution among the Boston B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Flemish Academy Of Belgium For Sciences And The Arts
The Royal Flemish Academy of Belgium for Science and the Arts (, , abbr. KVAB) is an independent learned society of science and arts of the Flemish Community in Belgium. It is one of Belgium's numerous academies and traces its origin to 1772 when the Imperial and Royal Academy of Brussels was founded by empress Maria Theresia Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position in her own right. She was the sovereig .... The academy is headquartered in the Academy Palace (''Paleis der Academiën''), Hertogsstraat 1, 1000 Brussels. Mission and goals The mission and goals of the society is the practice and promotion of science and arts in Flanders. To achieve that goal a number of scientific and cultural activities is organized. Also the academy enhances and encourages the collaboration between the Flemish universities, it at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Academy Of Natural Scientists Leopoldina
The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (), in short Leopoldina, is the national academy of Germany, and is located in Halle (Saale). Founded on 1 January 1652, based on academic models in Italy, it was originally named the ''Academia Naturae Curiosorum'' until 1687 when Emperor Leopold I raised it to an academy and named it after himself. It was since known under the German name ''Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina'' until 2007, when it was declared to be Germany's National Academy of Sciences. It is the oldest continuously operating academy of natural sciences worldwide. History ' The Leopoldina was founded in the imperial city of Schweinfurt on 1 January 1652 under the Latin name sometimes translated into English as "Academy of the Curious as to Nature." It was founded by four local physicians – Johann Laurentius Bausch, the first president of the society, Johann Michael Fehr, Georg Balthasar Metzger, and Georg Balthasar Wohlfarth; and was the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academia Europaea
The Academia Europaea is a pan-European Academy of humanities, letters, law, and sciences. The Academia was founded in 1988 as a functioning Europe-wide Academy that encompasses all fields of scholarly inquiry. It acts as co-ordinator of European interests in national research agencies. History The concept of a 'European Academy of Sciences' was raised at a meeting in Paris of the European Ministers of Science in 1985. The initiative was taken by the Royal Society (United Kingdom) which resulted in a meeting in London in June 1986 of Arnold Burgen (United Kingdom), Hubert Curien (France), Umberto Colombo (Italy), David Magnusson (Sweden), Eugen Seibold (Germany) and Ruurd van Lieshout (the Netherlands) – who agreed to the need for a new body. The meeting also included Brian Flowers and John Kendrew. Another, larger meeting took place in October 1986 with participants representing some countries in the Council of Europe and was in support for the development of a Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holland Society Of Sciences
The ''Koninklijke Hollandsche Maatschappij der Wetenschappen'' (Royal Holland Society of Sciences and Humanities), located on the east side of the Spaarne in downtown Haarlem, Netherlands, was established in 1752 and is the oldest society for the sciences in the country. The society has been housed in its present location, called Hodshon Huis, since 1841. Nearby the society is the Teylers Museum, a closely related museum of natural history founded in 1784. In 2002, the society was awarded the predicate "Royal" when it celebrated 250 years of science studies. History of the society and museum The society started as a gentleman's club that met in the Haarlem City Hall to discuss science topics and promote the study of the arts and sciences. They pooled resources to purchase books and specimens for study, which were kept in the town hall until they purchased a building on the Grote Houtstraat (nr. 51, since unrecognizably rebuilt), where the curator of the collection lived. Under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Netherlands Academy Of Sciences
The Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (, KNAW) is an organization dedicated to the advancement of science and literature in the Netherlands. The academy is housed in the Trippenhuis in Amsterdam. In addition to various advisory and administrative functions it operates a number of research institutes and awards many prizes, including the Lorentz Medal in theoretical physics, the Dr Hendrik Muller Prize for Behavioural and Social Science and the Heineken Prizes. Main functions The academy advises the Dutch government on scientific matters. While its advice often pertains to genuine scientific concerns, it also counsels the government on such topics as policy on careers for researchers or the Netherlands' contribution to major international projects. The academy offers solicited and unsolicited advice to parliament, ministries, universities and research institutes, funding agencies and international organizations. * Advising the government on matters related to sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
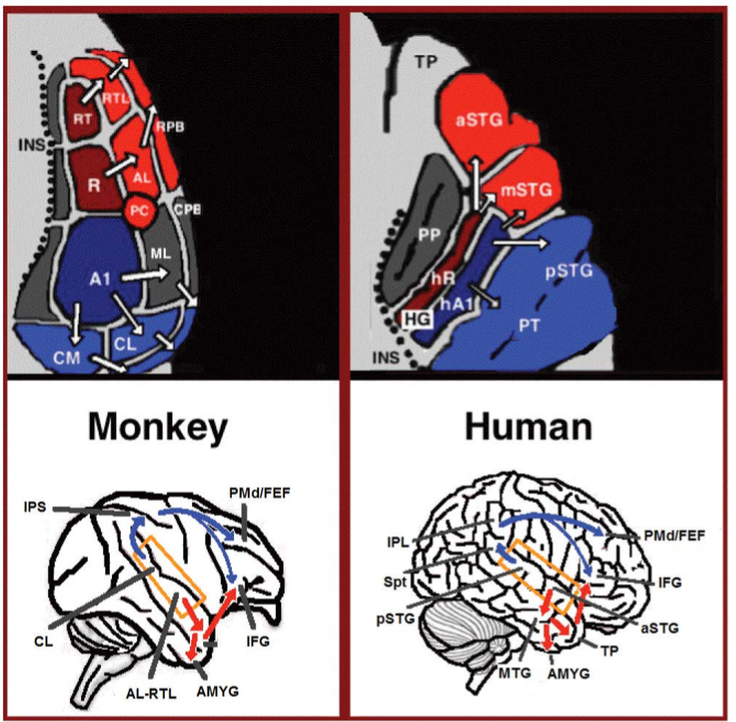
Language Processing
In psycholinguistics, language processing refers to the way humans use words to communicate ideas and feelings, and how such communications are processed and understood. Language processing is considered to be a uniquely human ability that is not produced with the same grammatical understanding or systematicity in even human's closest primate relatives. Throughout the 20th century the dominant model for language processing in the brain was the Geschwind–Lichteim–Wernicke model, which is based primarily on the analysis of brain-damaged patients. However, due to improvements in intra-cortical electrophysiological recordings of monkey and human brains, as well non-invasive techniques such as fMRI, PET, MEG and EEG, an auditory pathway consisting of two parts has been revealed and a two-streams model has been developed. In accordance with this model, there are two pathways that connect the auditory cortex to the frontal lobe, each pathway accounting for different linguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie Van Wetenschappen
The Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (, KNAW) is an organization dedicated to the advancement of science and literature in the Netherlands. The academy is housed in the Trippenhuis in Amsterdam. In addition to various advisory and administrative functions it operates a number of research institutes and awards many prizes, including the Lorentz Medal in theoretical physics, the Dr Hendrik Muller Prize for Behavioural and Social Science and the Heineken Prizes. Main functions The academy advises the Dutch government on scientific matters. While its advice often pertains to genuine scientific concerns, it also counsels the government on such topics as policy on careers for researchers or the Netherlands' contribution to major international projects. The academy offers solicited and unsolicited advice to parliament, ministries, universities and research institutes, funding agencies and international organizations. * Advising the government on matters related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Society
The Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science (; abbreviated MPG) is a formally independent non-governmental and non-profit association of German research institutes. Founded in 1911 as the Kaiser Wilhelm Society, it was renamed to the Max Planck Society in 1948 in honor of its former president, theoretical physicist Max Planck. The society is funded by the federal and state governments of Germany. Mission According to its primary goal, the Max Planck Society supports basic research, fundamental research in the natural science, natural, life science, life and social science, social sciences, the arts and humanities in its 84 (as of January 2024) institutes and research facilities. , the society has a total staff of 24,655 permanent employees, including 6,688 contractually employed scientists, 3,444 doctoral candidates, and 3,203 guest scientists. 44.9% of all employees are female and 57.2% of the scientists are foreign nationals. The society's budget for 2023 was about � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princeton, New Jersey
The Municipality of Princeton is a Borough (New Jersey), borough in Mercer County, New Jersey, United States. It was established on January 1, 2013, through the consolidation of the Borough of Princeton, New Jersey, Borough of Princeton and Princeton Township, New Jersey, Princeton Township, both of which are now defunct. As of the 2020 United States census, the borough's population was 30,681, an increase of 2,109 (+7.4%) from the 2010 United States census, 2010 census combined count of 28,572. In the 2000 United States census, 2000 census, the two communities had a total population of 30,230, with 14,203 residents in the borough and 16,027 in the township. Princeton was founded before the American Revolutionary War. The borough is the home of Princeton University, one of the world's most acclaimed research universities, which bears its name and moved to the community in 1756 from the educational institution's previous location in Newark, New Jersey, Newark. Although its associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Advanced Study
The Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) is an independent center for theoretical research and intellectual inquiry located in Princeton, New Jersey. It has served as the academic home of internationally preeminent scholars, including Albert Einstein, J. Robert Oppenheimer, Emmy Noether, Hermann Weyl, John von Neumann, Michael Walzer, Clifford Geertz and Kurt Gödel, many of whom had emigrated from Europe to the United States. It was founded in 1930 by American educator Abraham Flexner, together with philanthropists Louis Bamberger and Caroline Bamberger Fuld. Despite collaborative ties and neighboring geographic location, the institute, being independent, has "no formal links" with Princeton University. The institute does not charge tuition or fees. Flexner's guiding principle in founding the institute was the pursuit of knowledge for its own sake.Jogalekar. The faculty have no classes to teach. There are no degree programs or experimental facilities at the institute. Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |