|
Piggabeen
Piggabeen is a town located in north-eastern New South Wales, Australia, in the Tweed Shire. Piggabeen adjoins Cobaki Lakes that is situated to the northeast, Cobaki to the South East and Currumbin Valley that is situated approximately to the northwest and across the state border of Queensland. Once predominantly a dairy farming town Piggabeen now mainly consists of acreage homesites and small hobby farms. Piggabeen has a valley that leads northwest towards the Queensland border. Piggabeen and its valley are part of the Tweed Shield Volcano and Caldera that is the largest erosion caldera in the southern hemisphere, with Mount Warning being the extinct volcano A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates ar .... Landmarks located in Piggabeen include the Old Piggabeen Hall and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campbell Hill, New South Wales
Campbell Hill (formerly Mount Campbell) is a mountain located in Piggabeen, New South Wales (NSW), Australia. It is located in the region of the Tweed Shire in the state of New South Wales, in the eastern part of the country, north of the capital, Canberra, approximately from Brisbane and from Surfers Paradise. Campbell Hill is approximately above sea level. Piggabeen is situated in the hinterland approximately 5 km behind the Gold Coast Highway and the Coolangatta Airport, Gold Coast International and Domestic Airport. Piggabeen and its valley adjoins Currumbin Valley in Queensland. The terrain around Campbell Hill is flat to hilly and the mount faces to the northeast. From the top of Campbell Hill you can capture views of the Pacific Ocean, Surfers Paradise, the Gold Coast Airport, the township of Coolangatta, Queensland, Coolangatta that are all within Queensland and also Fingal Head, New South Wales, Fingal Head in New South Wales. Campbell Hill is situated approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currumbin Valley, Queensland
Currumbin Valley is a rural locality in the City of Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia. It borders New South Wales. In the , Currumbin Valley had a population of 1,849 people. Geography Currumbin Valley is in the Gold Coast hinterland of South East Queensland bounded to the south by the Queensland border with New South Wales. The valley is relatively small in size being approximately twenty-four kilometers long and around four kilometers wide. Furthermore, Currumbin Valley provides both rural and residential land but is predominantly rural. Currumbin Valley is a unique part of Australia’s Green Cauldron, being the first valley to the north of the escarpment of the cauldron (the temple of which is Mount Warning) in the Murwillumbah region, to the south. The main road through Currumbin Valley – Currumbin Creek Road extends 20 kilometres west to the Mt Cougal Section of the Springbrook National Park, where it terminates, with a World-Heritage-Listed rainforest walk, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tweed Shire
Tweed Shire is a local government area located in the Northern Rivers region of New South Wales, Australia. It is adjacent to the border with Queensland, where that meets the Tasman Sea. Administered from the town of Murwillumbah, Tweed Shire covers an area of , and has existed as a local government entity since 1947. It was named for the Tweed River. The current mayor of Tweed Shire Council is Cr. Chris Cherry. History The European history of the Tweed Shire began in 1823 when the Tweed River was explored by John Oxley. After sheltering on Cook Island (4 km from the river's mouth), Oxely travelled up river. In 1828, Captain H. J. Rous explored up the river. Settlers began to arrive in 1828, the first of which were the cedar getters, who came to harvest Great Red Cedars and send them back to England. During the height of the cedar logging industry, the Tweed Valley was one of the wealthiest districts in Australia. The Municipality of Murwillumbah was created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
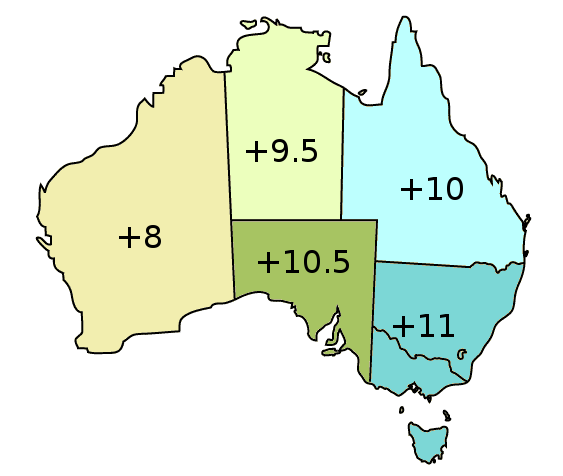
Australian Eastern Standard Time
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Eastern Daylight Time
Each state and territory of Australia determines whether or not to use daylight saving time (DST). However, during World War I and World War II all states and territories had daylight saving by federal law, under the defence power in section 51 of the constitution. In 1968, Tasmania was the first state since the war to adopt daylight saving. In 1971, New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and the Australian Capital Territory also adopted daylight saving, while Western Australia and the Northern Territory did not. Queensland abandoned daylight saving in 1972. Queensland and Western Australia have observed daylight saving over the past 40 years from time to time on a trial basis. New South Wales, the Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, Tasmania and South Australia observe DST every year. This has resulted in three time zones becoming five during the daylight-saving period. South Australia time becomes UTC+10:30, called Central Daylight Time (CDT), possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the states and territories of Australia, Australian state of Queensland, and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of approximately 2.6 million. Brisbane lies at the centre of the South East Queensland metropolitan region, which encompasses a population of around 3.8 million. The Brisbane central business district is situated within a peninsula of the Brisbane River about from its mouth at Moreton Bay, a bay of the Coral Sea. Brisbane is located in the hilly floodplain of the Brisbane River Valley between Moreton Bay and the Taylor Range, Taylor and D'Aguilar Range, D'Aguilar mountain ranges. It sprawls across several local government in Australia, local government areas, most centrally the City of Brisbane, Australia's most populous local government area. The demonym of Brisbane is ''Brisbanite''. The Traditional Owners of the Brisbane a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral District Of Tweed
Tweed is an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales. It is represented by Geoff Provest of The Nationals. It is located in the Tweed valley and eastern Tweed Shire, including Tweed Heads, Kingscliff, Fingal Head, Chinderah, Cudgen, Bogangar, Pottsville and Burringbar. History Tweed was first created with the end of multi-member districts in 1894. In 1904, it was abolished with the reduction in the size of the Legislative Assembly, after Federation. The region was part of Richmond from 1904 to 1913, Byron George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and has been regarded as among the ... from 1913 until 1988 when the district was renamed Murwillumbah. In 1999 the district was renamed Tweed. Members for Tweed Election results References {{Memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Richmond
The Division of Richmond is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales. History The division was proclaimed in 1900, and was one of the original 65 divisions to be contested at the first federal election. The division is named after the area in which it is located, namely the Richmond Valley and Richmond River, which was named in honour of Charles, the fifth Duke of Richmond. Historically, the division has been a rural seat and fairly safe for the National Party (formerly called the Country Party), which held it for all but six years from 1922 to 2004. For 55 of those years, it was held by three generations of the Anthony family—Hubert Lawrence Anthony (a minister in the Fadden and Menzies governments), Doug Anthony (leader of the National Party from 1971 to 1984 and Deputy Prime Minister in the Gorton, McMahon and Fraser governments) and Larry Anthony (a minister in the Howard government)—the first three-generation dynasty in the Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of New South Wales , established_title2 = Establishment , established_date2 = 26 January 1788 , established_title3 = Responsible government , established_date3 = 6 June 1856 , established_title4 = Federation , established_date4 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Wales , demonym = , capital = Sydney , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 128 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Margaret Beazley , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Dominic Perrottet ( Liberal) , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type1 = Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland
) , nickname = Sunshine State , image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Queensland , established_title2 = Separation from New South Wales , established_date2 = 6 June 1859 , established_title3 = Federation of Australia, Federation , established_date3 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Queen Victoria , demonym = , capital = Brisbane , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center_type = Administration , admin_center = Local government areas of Queensland, 77 local government areas , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Australia, Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor of Queensland, Governor , leader_name2 = Jeannette Young , leader_title3 = Premier of Queensland, Premier , leader_name3 = Annastacia Palaszczuk (Australian Labor Party (Queensland Branch), AL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tweed Volcano
Tweed Volcano is a partially eroded Early Miocene shield volcano located in northeastern New South Wales, which formed when this region of Australia passed over the East Australia hotspot around 23 million years ago. Mount Warning, Lamington Plateau and the Border Ranges between New South Wales and Queensland are among the remnants of this volcano that was originally over in diameter and nearly twice the height of Mount Warning today, at . Despite its size, Tweed Volcano was not a supervolcano; other shield volcanoes—such as in the Hawaiian Islands—are much larger. In the 23 million years since the volcano was active, erosion has been extensive, forming a large erosion caldera around the volcanic plug of Mount Warning. Its erosion caldera is the largest in the Southern Hemisphere. Volcanic stratigraphy Lavas from the Tweed Volcano are recognised as part of the Lamington Volcanics. The volcanic stratigraphy of the Tweed Volcano is similar to many other hots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is gone. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur each century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times per century. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2016. More recently, a caldera collapse occurred at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018. Etymology The term ''caldera'' comes from Spanish ', and Latin ', mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |