|
Pidima
Pilima, also known as Pidima, is a Wayana village situated on the Litani (Maroni tributary), Litani River in French Guiana. History Pilima was founded by the shaman or ''pïyai'' Pilima, son of former head captain Janomalë. Pilima sometimes clashed with the new head captain of Kawemhakan, Anapaikë, who, according to Pilima, pandered too much to the wishes of the Baptist missionaries. As a reaction to the missionary activities, Pilima started a prophetic movement that had the characteristics of a syncretism, syncretic Christianity, Christian cult: Pilima claimed to be in contact with Aramawali, a great spirit from the heavens who would send "heaven boats" from the sky to gather the Wayana Sola fide, who believed in him, and who would bring them to heaven where they would live an eternal life (Christianity), eternal life. Pilima imitated church rites and attempted to sing songs during ceremonies. A central aspect of the cult was the jumping in the water from a springboard, in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
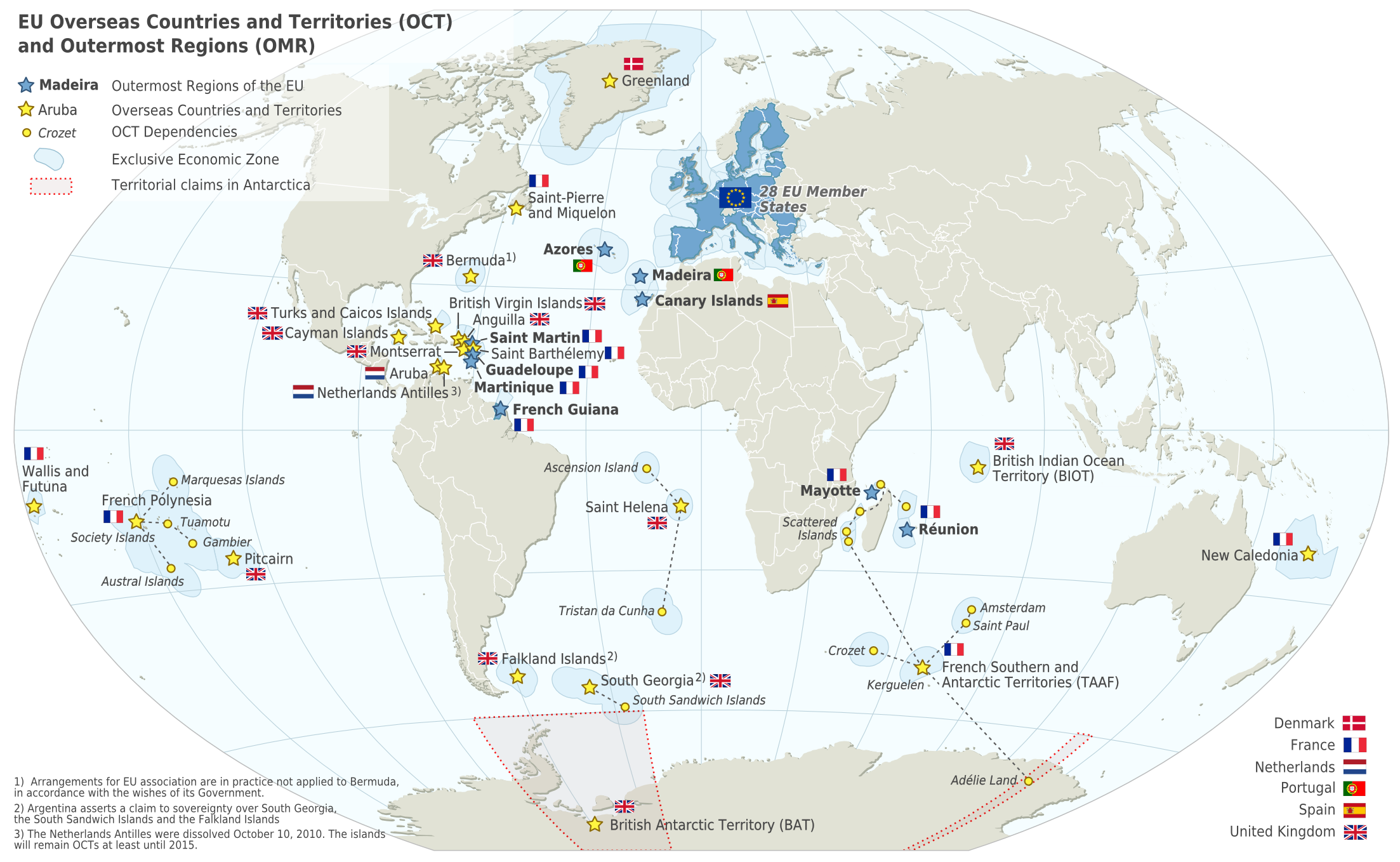
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawemhakan
Kawemhakan, formerly also known as Anapaikë, is a Wayana village in the Sipaliwini District of Suriname. The village lies on the banks of the Lawa River, which forms the border with French Guiana. Name The indigenous name of the village is Kawemhakan, which translates to "high riverbank" in the Wayana language. The village is also known by the name Anapaikë, which is the name of the late granman of the Wayana in Suriname, who died end july 2002. The Baptist missionaries called the village Lawa Station, and many Wayana still refer to the village as "Lawa". History Kawemhakan was founded in 1958, primarily by people who lived in the village of the local chief Janomalë, which was situated further upstream the Lawa River. It was common practice by Wayana to relocate to another village after the death of a chief, but Janomalë's death coincided with the arrival of Baptist missionaries to the area. Both the American missionaries and the Surinamese government wanted to concentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palimino
Palimino is a Wayana village on the Litani River The Litani River (), the classical Leontes (), is an important water resource in southern Lebanon. The river rises in the fertile Beqaa Valley, west of Baalbek, and empties into the Mediterranean Sea north of Tyre. Exceeding in length, the .... Geography Palimino lies about upstream the Litani River from the village of Pëleya and about downstream from the village of Pilima. Notes References * * Indigenous villages in French Guiana Maripasoula Villages in French Guiana {{FrenchGuiana-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptism
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water either partially or completely, traditionally three times, once for each person of the Trinity. The synoptic gospels recount that John the Baptist baptism of Jesus, baptized Jesus., , Baptism is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance (Christian), ordinance in others. Baptism according to the Trinitarian formula, which is done in most mainstream Christian denominations, is seen as being a basis for Christian ecumenism, the concept of unity amongst Christians. Baptism is also called christening, although some reserve the word "christening" for the Infant baptism, baptism of infants. In certain Christian denominations, such as the Catholic Churches, Eastern Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodox Churches, Assyrian Church of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springboard
A springboard or diving board is used for diving and is a board that is itself a spring, i.e. a linear flex-spring, of the cantilever type. Springboards are commonly fixed by a hinge at one end (so they can be flipped up when not in use), and the other end usually hangs over a swimming pool, with a point midway between the hinge and the end resting on an adjustable fulcrum. Springboard materials Modern springboards are made out of a single-piece extrusion of aircraft-grade aluminum. The Maxiflex Model B, the board used in all major competitive diving events, is made out of such aluminum, and is heat treated for a yield strength of . The slip-resistant surface of the board is created using an epoxy resin, finished with a laminate of flint silica and alumina in between the top coats of resin. This thermal-cured resin is aqua-colored to match the water of a clean pool. Adjustment of the spring constant The spring constant of a springboard is usually adjusted by way of a fulcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eternal Life (Christianity)
Eternal life traditionally refers to continued afterlife, life after death, as outlined in Christian eschatology. The Apostles' Creed testifies: "I believe... the resurrection of the body, and life everlasting." In this view, eternal life commences after the Second Coming of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ and the Resurrection of the Dead#Christianity, resurrection of the dead, although in the New Testament's Johannine literature there are references to eternal life commencing in the earthly life of the believer, possibly indicating an inaugurated eschatology. According to mainstream Christian theology, after death but before the Second Coming, the saved live with God in an Intermediate state (Christianity), intermediate state, but after the Second Coming, experience the physical resurrection of the dead and the physical recreation of a the New Earth, New Earth. The Catechism of the Catholic Church states, "By death the soul is separated from the body, but in the resurrectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sola Fide
(or simply ), meaning justification by faith alone, is a soteriological doctrine in Christian theology commonly held to distinguish the Lutheranism, Lutheran and Reformed tradition, Reformed traditions of Protestantism, among others, from the Catholic Church, Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Assyrian Church of the East, Assyrian, Methodist Church, Methodist and Anabaptism, Anabaptist churches. The doctrine asserts that it is on the basis of faith in Christianity, faith alone that believers are made right of sin (such as their transgressions of divine law); and not on the basis of what Paul the Apostle calls "works of the law", which ''sola fide'' proponents interpret as including not only moral, legal or ceremonial requirements but any good works or "works of charity." This forgiveness is known as "Justification (theology), justification". Most Christian denominations including Catholic, Orthodox, Lutheran, Reformed, Anglican and Methodist now subscribe to a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah (Christ (title), Christ) was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Old Testament and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with over 2.3 billion followers, comprising around 28.8% of the world population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories. Christianity remains Christian culture, culturally diverse in its Western Christianity, Western and Eastern Christianity, Eastern branches, and doctrinally diverse concerning Justification (theology), justification and the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thus asserting an underlying unity and allowing for an Inclusivism, inclusive approach to other faiths. While syncretism in art and culture is sometimes likened to eclecticism, in the realm of religion, it specifically denotes a more integrated merging of beliefs into a unified system, distinct from eclecticism, which implies a selective adoption of elements from different traditions without necessarily blending them into a new, cohesive belief system. Etymology The English word is first attested in the early 17th century. It is from Neo-Latin, Modern Latin , drawing on the (), supposedly meaning "Cretan federation". However, this is a spurious etymology derived from the naive idea in Plutarch's 1st- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaman
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as shamanic have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers, and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. Terminology Etymology The Modern English word ''shamanism'' derives from the Russian word , , which itself comes from the word from a Tungusic language – possibly from the southwestern dialect of the Evenki spoken by the Sym Evenki peoples, or from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas Region
The overseas departments and regions of France (, ; DROM) are the five departments and regions of the French Republic which are located outside European France (also known as " metropolitan France"). These overseas entities have exactly the same status as European France's departments and regions. The French Constitution provides that, in general, French laws and regulations (France's civil code, penal code, administrative law, social laws, and tax laws etc.) apply to French overseas departments and regions the same way as in metropolitan France, but can be adapted as needed to suit the region's particular needs. Hence, the local administrations of French overseas departments and regions cannot themselves pass new laws. On occasion, referendums are undertaken to re-assess the sentiment in local status. Since March 2011, the five overseas departments and regions of France are: * French Guiana in South America, a part of The Guianas; * Guadeloupe in the Caribbean Sea, a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |