|
Picture Framing Glass
Picture framing glass ("glazing," "conservation glass," "museum quality glass") usually refers to flat glass or acrylic ("plexi") used for framing artwork and for presenting art objects in a display box (also, "conservation framing"). Purpose The primary purpose of glazing in art framing is to clearly exhibit the work while physically protecting it from damaging factors such as light ,humidity, heat, and soiling. Laminated glass and some acrylic may be used to protect against physical damage from glass breakage and to offer protection from a malicious attack. Regular glass as well as some glass surface treatments can also filter some of the damaging ultra-violet radiation (UV) and heat (NIR). Artworks that require protective glazing are those rendered on paper or fabrics (including photographs), which contain pigments and dyes that absorb UV and are susceptible to discoloration. In the case if the framed object or artwork is UV resistant, UV protection can still serve the purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylic Glass
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) is a synthetic polymer derived from methyl methacrylate. It is a transparent thermoplastic, used as an engineering plastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Walcast, Hesalite, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Lucite, PerClax, and Perspex, among several others ( see below). This plastic is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can also be used as a casting resin, in inks and coatings, and for many other purposes. It is often technically classified as a type of glass, in that it is a non-crystalline vitreous substance—hence its occasional historic designation as ''acrylic glass''. History The first acrylic acid was created in 1843. Methacrylic acid, derived from acrylic acid, was formulated in 1865. The reaction between methacrylic acid and methanol results in the ester methyl methacrylate. It was developed in 1928 in several different lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidity affects rate of evaporation of water. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide. When a molecule near the surface absorbs enough energy to overcome the vapor pressure, it will escape and enter the surrounding air as a gas. When evaporation occurs, the energy removed from the vaporized liquid will reduce the temperature of the liquid, resulting in evaporative cooling. On average, only a fraction of the molecules in a liquid have enough heat energy to escape from the liquid. The evaporation will continue until an equilibrium is reached when the evaporation of the liquid is equal to its condensation. In an enclosed environment, a liquid will evaporate unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
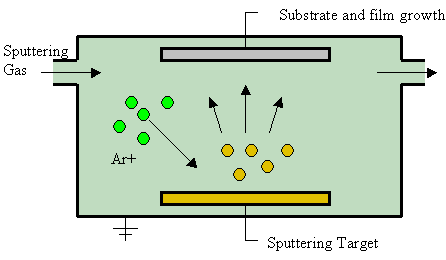
Magnetron Sputtering
Sputter deposition is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method of thin film deposition by the phenomenon of sputtering. This involves ejecting material from a "target" that is a source onto a "substrate" such as a silicon wafer. Resputtering is re-emission of the deposited material during the deposition process by ion or atom bombardment. Sputtered atoms ejected from the target have a wide energy distribution, typically up to tens of eV (100,000 K). The sputtered ions (typically only a small fraction of the ejected particles are ionized — on the order of 1 percent) can ballistically fly from the target in straight lines and impact energetically on the substrates or vacuum chamber (causing resputtering). Alternatively, at higher gas pressures, the ions collide with the gas atoms that act as a moderator and move diffusively, reaching the substrates or vacuum chamber wall and condensing after undergoing a random walk. The entire range from high-energy ballistic impact to low-en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (electromagnetic Radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy—and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy). A notable effect of the absorption of electromagnetic radiation is attenuation of the radiation; attenuation is the gradual reduction of the intensity of light waves as they propagate through a medium. Although the absorption of waves does not usually depend on their intensity (linear absorption), in certain conditions (optics) the medium's transparency changes by a factor that varies as a function of wave intensity, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs. Quantifying absorption Many approaches can potentially quantify radiation absorption, with key examples following. * The absorption coefficient along with some closely related derived quantities * The attenuation coefficient (NB used infrequently with meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
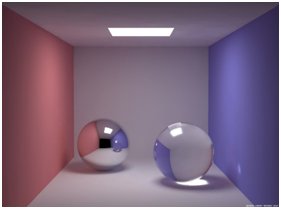
Specular Reflection
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection (physics), reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface. The law of reflection states that a reflected ray (optics), ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surface normal as the incident ray, but on the opposing side of the surface normal in the plane formed by the incident and reflected rays. The earliest known description of this behavior was recorded by Hero of Alexandria (Anno Domini, AD c. 10–70). Later, Ibn al-Haytham, Alhazen gave a complete statement of the law of reflection. He was first to state that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in a same plane perpendicular to reflecting plane. Specular reflection may be contrasted with diffuse reflection, in which light is scattered away from the surface in a range of directions. Law of reflection When light encounters a boundary of a material, it is affected by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called ''diffuse reflections'' and unscattered reflections are called ''specular'' (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering (going back at least as far as Isaac Newton in the 17th century). As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" (not then recognized as electromagnetic in nature) in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering research, noted the connecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Appearance
The visual appearance of objects is given by the way in which they Reflection (physics), reflect and transmit light. The color of objects is determined by the parts of the spectrum of (incident white) light that are reflected or transmitted without being absorbed. Additional appearance attributes are based on the directional distribution of reflected (BRDF) or transmitted light (BTDF) described by attributes like Gloss (material appearance), glossy, shiny versus dull, matte, clear, turbidity, turbid, distinct, etc. Since "visual appearance" is a general concept that includes also various other visual phenomena, such as color, visual texture, visual perception of shape, size, etc., the specific aspects related to how humans see different ''spatial'' distributions of light (absorbed, transmitted and reflected, either regularly or diffusely) have been given the name ''Cesia (visual appearance), cesia''. It marks a difference (but also a relationship) with color, which could be defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specular Reflection
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection (physics), reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface. The law of reflection states that a reflected ray (optics), ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surface normal as the incident ray, but on the opposing side of the surface normal in the plane formed by the incident and reflected rays. The earliest known description of this behavior was recorded by Hero of Alexandria (Anno Domini, AD c. 10–70). Later, Ibn al-Haytham, Alhazen gave a complete statement of the law of reflection. He was first to state that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in a same plane perpendicular to reflecting plane. Specular reflection may be contrasted with diffuse reflection, in which light is scattered away from the surface in a range of directions. Law of reflection When light encounters a boundary of a material, it is affected by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloss (material Appearance)
Gloss is an optical property which indicates how well a surface reflects light in a specular (mirror-like) direction. It is one of the important parameters that are used to describe the visual appearance of an object. Other categories of visual appearance related to the perception of regular or diffuse reflection and transmission of light have been organized under the concept of '' cesia'' in an order system with three variables, including gloss among the involved aspects. The factors that affect gloss are the refractive index of the material, the angle of incident light and the surface texture. Apparent gloss depends on the amount of ''specular'' reflection – light reflected from the surface in an equal amount and the symmetrical angle to the one of incoming light – in comparison with ''diffuse'' reflection – the amount of light scattered into other directions. Theory When light illuminates an object, it interacts with it in a number of ways: * Absorbed within it (l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |