|
Piccolia Nannaria
''Piccolia nannaria'' is a species of crustose lichen in the class Lecanoromycetes. It is widespread but uncommon in the coastal plain of southeastern North America. Initially thought to be corticolous (bark-dwelling), later collection of the lichen suggest that it may be lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling). Taxonomy The species was first formally described as a new species in 1872 by American lichenologist Edward Tuckerman, as ''Heterothecium nannarium''. The type specimen was collected by Charles Wright in Texas in 1850. Alexander Zahlbruckner proposed a transfer to the genus ''Biatorella'' in 1927. James Lendemer and Sean Beeching transferred the taxon to the genus ''Piccolia'' in 2007. Description ''Piccolia nannaria'' is characterized by its and yellow exterior or thallus. Its , which range in colour from a subtle green to an orange-yellow, are quite tiny, and its asci are , housing numerous minuscule spherical, colourless . Distribution and ecology The lichen is widespre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuck
Tuck may refer to: People * Tuck (surname), including a list of people * Tuck (nickname), a list of people * Tuck (footballer), Portuguese football player and coach João Carlos Novo de Araújo Gonçalves (born 1969) * Hillary Tuck (born 1978), American actress born Hillary Sue Hedges * Tuck Langland, American sculptor * Tuck Woolum, American former college football player and head coach * Trinity the Tuck, American drag queen Fictional characters * Tuck, a pill bug in the 1998 animated film ''A Bug's Life'' * Friar Tuck, one of Robin Hood's Merry Men * Tuck, the family name of characters in the novel ''Tuck Everlasting'' and two film adaptations * Turtle Tuck, in the animated series ''Wonder Pets'' * Tuck, in the animated series ''My Life as a Teenage Robot'' Sports * Back or front tuck, a type of acrobatic flip * One of several dive positions Other uses * Tuck (sewing), a fold or pleat in fabric that is sewn in place * Tuck (sword), also known as an ''estoc'' in French * Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biatorella
''Biatorella'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Biatorellaceae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution. Species The genus ''Biatorella'' includes the following species: * '' Biatorella algerica'' * '' Biatorella algoviae'' * '' Biatorella amabilis'' * ''Biatorella antarctica'' * '' Biatorella australica'' * ''Biatorella austroafrica'' * '' Biatorella camptocarpa'' * ''Biatorella consanguinea'' * '' Biatorella conspurcans'' * ''Biatorella contigua'' * ''Biatorella cyphalea'' * ''Biatorella floridensis'' * ''Biatorella fossarum'' * ''Biatorella germanica'' * ''Biatorella hemisphaerica'' * ''Biatorella praenotata'' * ''Biatorella rappii'' * ''Biatorella rousselii'' * ''Biatorella saxicola'' * ''Biatorella zeorina ''Biatorella'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Biatorellaceae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution. Species The genus ''Biatorella'' includes the following species: * '' Biatorella algerica'' * '' Biatorella algoviae'' * ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Species
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches ( fruticose); flat leaf-like structures ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Fungorum
''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names ( scientific names) in the fungus kingdom. the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. It is somewhat comparable to the International Plant Names Index (IPNI), in which the Royal Botanic Gardens is also involved. A difference is that where IPNI does not indicate correct names, the ''Index Fungorum'' does indicate the status of a name. In the returns from the search page a currently correct name is indicated in green, while others are in blue (a few, aberrant usages of names are indicated in red). All names are linked to pages giving the correct name, with lists of synonyms. ''Index Fungorum'' is one of three nomenclatural repositories recognized by the Nomenclature Committee for Fungi; the others are ''MycoBank'' and '' Fungal Names''. Current names in ''Index Fungorum'' (''Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an association is much larger than the other, it is generally known as the host. In parasitism, the parasite benefits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrhospora Varians
''Pyrrhospora'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Lecanoraceae. The genus was circumscribed by German lichenologist Gustav Wilhelm Körber in 1855, with ''Pyrrhospora quernea'' assigned as the type species. Species *''Pyrrhospora bhutanensis'' *''Pyrrhospora chlororphnia'' *''Pyrrhospora endaurantia'' *''Pyrrhospora fuscisidiata'' *''Pyrrhospora luminescens'' *''Pyrrhospora palmicola'' – Seychelles *''Pyrrhospora quernea'' *''Pyrrhospora rubiginans'' Several species that were once classified in ''Pyrrhospora'' have since been transferred to the genus ''Ramboldia''. These include: *''Pyrrhospora amagiensis'' (now ''Ramboldia amagiensis'') *''Pyrrhospora arandensis'' (now ''Ramboldia arandensis'') *''Pyrrhospora aurantiaca'' (now ''Ramboldia aurantiaca'') *''Pyrrhospora aurea'' (now ''Ramboldia aurea'') *''Pyrrhospora bullata'' (now ''Ramboldia bullata'') *''Pyrrhospora cinnabarina'' (now ''Ramboldia cinnabarina'') *''Pyrrhospora elabens'' (now ''R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
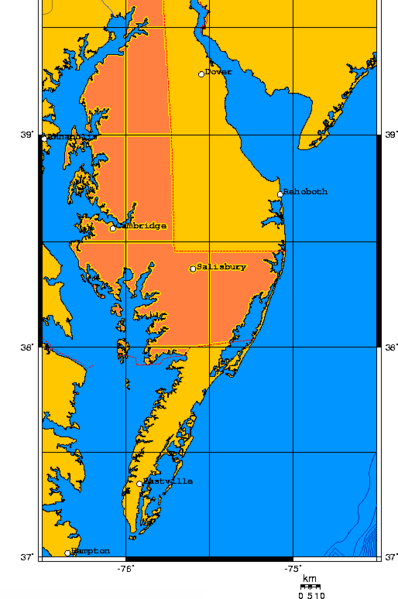
Delmarva Peninsula
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a large peninsula and proposed state on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the vast majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore regions of Maryland and Virginia. The peninsula is long. In width, it ranges from near its center, to at the isthmus on its northern edge, to less near its southern tip of Cape Charles. It is bordered by the Chesapeake Bay on the west, Pocomoke Sound on the southwest, and the Delaware River, Delaware Bay, and the Atlantic Ocean on the east. Etymology In older sources, the peninsula between Delaware Bay and Chesapeake Bay was referred to variously as the Delaware and Chesapeake Peninsula or simply the Chesapeake Peninsula. The toponym ''Delmarva'' is a clipped compound of Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia ( official abbreviation ''VA''), which in turn was modeled after Delmar, a border town named after two of those states. While Delmar was founded and named in 1859 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. Baltimore is the largest city in the state, and the capital is Annapolis, Maryland, Annapolis. Among its occasional nicknames are ''Maryland 400, Old Line State'', the ''Free State'', and the ''Chesapeake Bay State''. It is named after Henrietta Maria, the French-born queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland, who was known then in England as Mary. Before its coastline was explored by Europeans in the 16th century, Maryland was inhabited by several groups of Native Americans – mostly by Algonquian peoples and, to a lesser degree, Iroquoian peoples, Iroquoian and Siouan languages, Siouan. As one of the original Thirteen Colonies of England, Maryland was founded by George Calvert, 1st Baron Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (U
Georgia most commonly refers to: * Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia * Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States Georgia may also refer to: Places Historical states and entities * Related to the country in the Caucasus ** Kingdom of Georgia, a medieval kingdom ** Georgia within the Russian Empire ** Democratic Republic of Georgia, established following the Russian Revolution ** Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, a constituent of the Soviet Union * Related to the US state ** Province of Georgia, one of the thirteen American colonies established by Great Britain in what became the United States ** Georgia in the American Civil War, the State of Georgia within the Confederate States of America. Other places * 359 Georgia, an asteroid * New Georgia, Solomon Islands * South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Canada * Georgia Street, in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada * Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallus
Thallus (plural: thalli), from Latinized Greek (), meaning "a green shoot" or " twig", is the vegetative tissue of some organisms in diverse groups such as algae, fungi, some liverworts, lichens, and the Myxogastria. Many of these organisms were previously known as the thallophytes, a polyphyletic group of distantly related organisms. An organism or structure resembling a thallus is called thalloid, thallodal, thalliform, thalline, or thallose. A thallus usually names the entire body of a multicellular non-moving organism in which there is no organization of the tissues into organs. Even though thalli do not have organized and distinct parts ( leaves, roots, and stems) as do the vascular plants, they may have analogous structures that resemble their vascular "equivalents". The analogous structures have similar function or macroscopic structure, but different microscopic structure; for example, no thallus has vascular tissue. In exceptional cases such as the Lemnoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piccolia
''Piccolia'' is a small genus of crustose lichens in the class Lecanoromycetes. First circumscribed by Italian lichenologist Abramo Bartolommeo Massalongo in 1864, it contains ten species. Due to a lack of molecular data, it has not been assigned to an order or family. Taxonomy Massalongo established the genus, which was initially monotypic, to contain the species ''Piccolia crocea''. He named it for Gregorio Piccoli, an 18th-century naturalist he referred to as "the most eminent investigator of the natural world". In 1927, Alexander Zahlbruckner, an Austrian-Hungarian lichenologist, merged it into the genus ''Biatorella'', based on the fact that they shared a number of characteristics: a crustose thallus, multi-spored asci (the lichen's spore-bearing cells) and apothecia that lack a thalline border. However, Austrian lichenologist Josef Hafellner separated the two genera out again in 1994, arguing that ''Biatorella'' had been rendered "highly heterogenous" by Zahlbruckner's de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxon
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)