|
Phytoecdysteroid
Phytoecdysteroids are plant-derived ecdysteroids. Phytoecdysteroids are a class of chemicals that plants synthesize for defense against phytophagous (plant eating) insects. These compounds are mimics of hormones used by arthropods in the molting process known as ecdysis. It is presumed that these chemicals act as endocrine disruptors for insects, so that when insects eat the plants with these chemicals they may prematurely molt, lose weight, or suffer other metabolic damage and die. Chemically, phytoecdysteroids are classed as triterpenoids, the group of compounds that includes triterpene saponins, phytosterols, and phytoecdysteroids. Plants, but not animals, synthesize phytoecdysteroids from mevalonic acid in the mevalonate pathway of the plant cell using acetyl-CoA as a precursor. Some ecdysteroids, including ecdysone and 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E), are produced by both plants and arthopods. Besides those, over 250 ecdysteroid analog (chemistry), analogs have been identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecdysteroids
Ecdysteroids are arthropod steroid hormones that are mainly responsible for molting (ecdysis), development and, to a lesser extent, reproduction; examples of ecdysteroids include ecdysone, 20-hydroxyecdysone (ecdysterone), turkesterone and 2-deoxyecdysone. These compounds are synthesized in arthropods from dietary cholesterol upon metabolism by the Halloween family of cytochrome P450s. Compounds with ecdysteroid activity in arthropods are not only produced by these animals (''zooecdysteroids''). Phytoecdysteroids also appear in many plants mostly as a protection agents (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivore insects. Fungi also produce a handful of ''mycoecdysteroids''. In addition, synthetic ecdysteroid pesticides such as methoxyfenozide have been produced. Mammals Ecdysterone has been tested on mammals due to the interest in its potential hypertrophic effect. It has been found to increase hypertrophy in rats at a similar level to some anabolic androgenic steroids a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
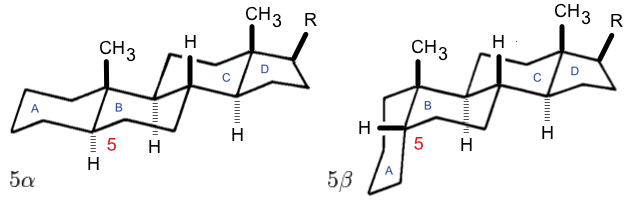
Steroids
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterol: cholesterol (animals), lanosterol ( opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus ( core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four fused rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytochemicals
Phytochemicals are naturally-occurring chemicals present in or extract, extracted from plants. Some phytochemicals are nutrients for the plant, while others are metabolites produced to enhance plant survivability and reproduction. The fields of extracting phytochemicals for manufactured products or applying scientific methods to study phytochemical properties are called ''phytochemistry''. An individual who uses phytochemicals in food chemistry manufacturing or research is a ''phytochemist''. Phytochemicals without a nutrient definition have no confirmed biological activities or proven health benefits when consumed in plant foods. Once phytochemicals in a food enter the digestion process, the fate of individual phytochemicals in the body is unknown due to extensive metabolism of the food in the gastrointestinal tract, producing phytochemical metabolites with different biological properties from those of the parent compound that may have been tested in vitro. Further, the bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Defense Against Herbivory
Plant defense against herbivory or host-plant resistance is a range of adaptations Evolution, evolved by plants which improve their fitness (biology), survival and reproduction by reducing the impact of herbivores. Many plants produce secondary metabolites, known as Heterotelergones, allelochemicals, that influence the behavior, growth, or survival of herbivores. These chemical defenses can act as repellents or toxins to herbivores or reduce plant digestibility. Another defensive strategy of plants is changing their attractiveness. Plant perception (physiology), Plants can sense being touched, and they can respond with strategies to defend against herbivores. Plants alter their appearance by changing their size or quality in a way that prevents overconsumption by large herbivores, reducing the rate at which they are consumed. Other defensive strategies used by plants include escaping or avoiding herbivores at any time in any placefor example, by growing in a location where plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
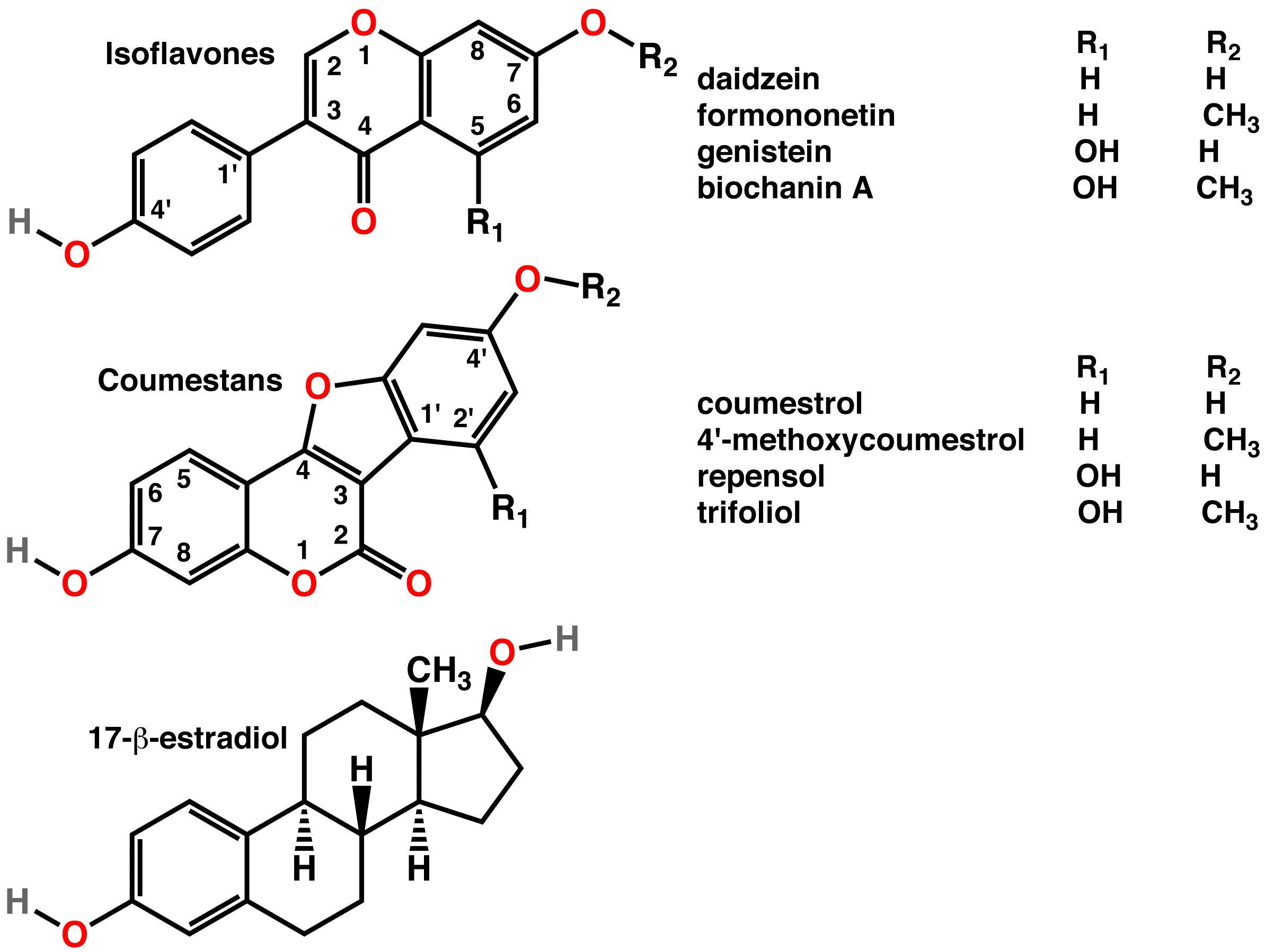
Phytoestrogen
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (a type of estrogen produced by organisms other than humans) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity to estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause both estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soybeans and soy protein concentrate, miso, tempeh, and tofu. Some soy-based infant formulas manufactured with soy protein contain isoflavones. Its name comes from the Greek ''phyto'' ("plant") and ''estrogen'', the hormone which gives fertility to female mammals. The word "estrus" (Greek οίστρος) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoandrogen
Phytoandrogens are substances produced in plants which have effects similar to testosterone in animals. Examples * Triterpenoids from the ''Eucommia ulmoides'' tree can act as phytoandrogens. * Drupanol is a phytoandrogen. Environmental effects Phytoandrogens have been implicated in sex-reversal in fish. See also *Phytoestrogen *Plant hormone Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anat ... References {{Androgen receptor modulators Anabolic–androgenic steroids Phytochemicals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allelochemical
Allelopathy is a biological phenomenon by which an organism produces one or more biochemicals that influence the germination, growth, survival, and reproduction of other organisms. These biochemicals are known as allelochemicals and can have beneficial (positive allelopathy) or detrimental (negative allelopathy) effects on the target organisms and the community. Allelopathy is often used narrowly to describe chemically-mediated competition between plants; however, it is sometimes defined more broadly as chemically-mediated competition between any type of organisms. The original concept developed by Hans Molisch in 1937 seemed focused only on interactions between plants, between microorganisms and between microorganisms and plants. Allelochemicals are a subset of secondary metabolites, which are not directly required for metabolism (i.e. growth, development and reproduction) of the allelopathic organism. Allelopathic interactions are an important factor in determining species dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginsenoside
Ginsenosides or panaxosides are a class of natural product steroid glycosides and triterpene saponins. Compounds in this family are found almost exclusively in the plant genus ''Panax'' (ginseng), which has a long history of use in traditional medicine that has led to the study of pharmacological effects of ginseng compounds. As a class, ginsenosides exhibit a large variety of subtle and difficult-to-characterize biological effects when studied in isolation. Ginsenosides can be isolated from various parts of the plant, though typically from the roots, and can be purified by column chromatography. The chemical profiles of ''Panax'' species are distinct; although Asian ginseng, ''Panax ginseng'', has been most widely studied due to its use in traditional Chinese medicine, there are ginsenosides unique to American ginseng (''Panax quinquefolius'') and Japanese ginseng (''Panax japonicus''). Ginsenoside content also varies significantly due to environmental effects. The leaves and stem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asparagus (genus)
''Asparagus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Asparagoideae. It comprises up to 300 species. Most are evergreen long-lived perennial plants growing from the understory as lianas, bushes or climbing plants. The best-known species is the edible '' Asparagus officinalis'', commonly referred to as just ''asparagus''. Some other members of the genus, such as '' Asparagus densiflorus'', are grown as ornamental plants. Ecology The genus includes a variety of extant forms, occurring from rainforest to semi-desert habitats; many are climbing plants. Most are dispersed by birds. Ornamental species such as '' Asparagus aethiopicus'', '' Asparagus setaceus'' (syn. '' Asparagus plumosus''), and '' Asparagus virgatus'' are finely branched and are misleadingly known as "asparagus fern". In the Macaronesian Islands, several species (such as '' Asparagus umbellatus'' and '' Asparagus scoparius'') grow in moist laurel forest habitat, and preserve the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordyceps
''Cordyceps'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi (sac fungi) that includes over 260 species worldwide, many of which are parasitic. Diverse variants of cordyceps have had more than 1,500 years of use in Chinese medicine. Most ''Cordyceps'' species are endoparasitoids, parasitic mainly on insects and other arthropods (they are thus entomopathogenic fungi); a few are parasitic on other fungi. The generic name ''Cordyceps'' is derived from the ancient Greek κορδύλη ''kordýlē'', meaning "club", and the Latin ''-ceps'', derived from Latin ''caput'', meaning "head". The genus has a worldwide distribution, with most of the known species being from Asia. Taxonomy There are two recognized subgenera: *''Cordyceps'' subgen. ''Cordyceps'' Fr. 1818 *''Cordyceps'' subgen. ''Cordylia'' Tul. & C. Tul. 1865 ''Cordyceps'' sensu stricto are the teleomorphs of several genera of anamorphic, entomopathogenic fungi such as '' Beauveria'' ('' Cordyceps bassiana''), '' Septofusidium'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serratula Coronata
''Serratula'' is a genus of plants in the tribe Cardueae within the family Asteraceae native to Eurasia. Plumeless saw-wort is a common name for plants in this genus. ''Serratula'' as traditionally defined contains at least two groups: one of which is basal within the subtribe Centaureinae and one of which is derived; the former group can be moved to the genus '' Klasea''. Various species contain apigenin, luteolin, quercetin, other flavonoids and ecdysteroids. ; Species ; Formerly includedFlann, C (ed) 2009+ Global Compositae Checklist Numerous species are now considered members of other genera: * '''' * '' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |