|
Physarales
Physarales is an order of Amoebozoa in the class Myxomycetes. It contains three families, the Didymiaceae, the Lamprodermataceae, and the Physaraceae. Physarales was circumscribed by Thomas Huston Macbride and published in 1922. Undescribed Family There is evidence of an undescribed family within Physarales that bridges Didymiaceae and Lamprodermataceae, which contains the monotypic genus In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispe ... Tasmaniomyxa. References Myxogastria Amoebozoa orders {{Amoebozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxogastria
Myxogastria/Myxogastrea (myxogastrids, ICZN) or Myxomycetes ( ICN) is a class of slime molds that contains 5 orders, 14 families, 62 genera, and 888 species. They are colloquially known as the ''plasmodial'' or ''acellular'' slime moulds. All species pass through several very different morphologic phases, such as microscopic individual cells, slimy amorphous organisms visible with the naked eye, and conspicuously shaped fruit bodies. Although they are monocellular, they can reach immense widths and weights: in extreme cases they can be up to across and weigh up to . The class Myxogastria is distributed worldwide, but it is more common in temperate regions where it has a higher biodiversity than in polar regions, the subtropics, or the tropics. They are mainly found in open forests, but also in extreme regions such as deserts, under snow blankets, or underwater. They also occur on the bark of trees, sometimes high in the canopy. These are known as cort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
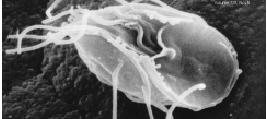
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom (biology), kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup (biology), supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetics, Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoeboz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didymiaceae
Didymiaceae is a family of plasmodial slime molds in the order Physarales Physarales is an order of Amoebozoa in the class Myxomycetes. It contains three families, the Didymiaceae, the Lamprodermataceae, and the Physaraceae. Physarales was circumscribed by Thomas Huston Macbride and published in 1922. Undescr .... Genera The family contains the following four genera: * '' Diderma'' * '' Didymium'' * '' Lepidoderma'' * '' Mucilago'' References Amoebozoa families Myxogastria {{Amoebozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprodermataceae
Lamprodermataceae is a family of slime molds in the order Physarales Physarales is an order of Amoebozoa in the class Myxomycetes. It contains three families, the Didymiaceae, the Lamprodermataceae, and the Physaraceae. Physarales was circumscribed by Thomas Huston Macbride and published in 1922. Undescr .... Genera The family contains the following five genera: *'' Collaria'' Nann.-Bremek *'' Colloderma'' G. Lister *'' Diacheopsis'' Meyl. *'' Elaeomyxa'' Hagelst. *'' Lamproderma'' Rostaf. References {{Authority control Myxogastria Amoebozoa families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physaraceae
Physaraceae is a family of slime molds in the order Physarales. Genera The following genera are members of Physaraceae: *'' Badhamia'' *'' Craterium'' *''Fuligo ''Fuligo'' is a widespread genus of plasmodial slime mold in the family Physaraceae. These organisms are protozoans rather than fungi, but for historical reasons are sometimes treated as part of mycology. Species The following species are accep ...'' *'' Kelleromyxa'' *'' Leocarpus'' *'' Physarella'' *'' Physarina'' *'' Physarum'' *'' Willkommlangea'' References Amoebozoa families {{Amoebozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physarum Psittacinum
''Physarum'' is a genus of mycetozoan slime molds in the family Physaraceae. It contains the following species: *''Physarum albescens'' *''Physarum album'' *''Physarum andinum'' *''Physarum bivalve'' *''Physarum bogoriense'' *''Physarum cinereum'' *''Physarum citrinum'' *''Physarum compressum'' *''Physarum confertum'' *''Physarum conglomeratum'' *''Physarum crateriforme'' *''Physarum daamsii'' *''Physarum didermoides'' *''Physarum digitatum'' *''Physarum flavicomum'' *''Physarum florigerum'' *''Physarum globuliferum'' *''Physarum gyrosum'' *''Physarum hongkongense'' *''Physarum lakhanpalii'' *''Physarum lateritium'' *''Physarum leucophaeum'' *''Physarum loratum'' *''Physarum luteolum'' *''Physarum melleum'' *''Physarum mortonii'' *''Physarum mutabile'' *''Physarum nigripodum'' *''Physarum nucleatum'' *''Physarum oblatum'' *''Physarum plicatum'' *''Physarum polycephalum'' *''Physarum psittacinum'' *''Physarum pulcherrimum'' *''Physarum pusillum'' *''Physarum reniforme'' *''Physaru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Huston Macbride
Thomas Huston Macbride (July 31, 1848 – March 27, 1934) was the tenth president of the University of Iowa, serving from 1914 to 1916. Macbride was a naturalist and botanist, Macbride Hall at the University of Iowa is named for him. He often collaborated with Samuel Calvin. He was the 75th member of the Acacia chapter at the University of Iowa. In 1909, botanist Fred Jay Seaver published ''Macbridella'' a genus of (in fungi family of Melanommataceae), and named in his honour. Then in 1934, botanist Henry Clark Gilbert in the journal of Univ. Iowa Stud. Nat. Hist. circumscribed the genus of Amoebozoa Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In trad ... (from the family Stemonitidaceae), '' Macbrideola''. He noted 'This new genus is named in honor of Dr. Thomas H. Macbride, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follow consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscription (taxonomy)
In biological taxonomy, circumscription is the content of a taxon, that is, the delimitation of which subordinate taxa are parts of that taxon. For example, if we determine that species X, Y, and Z belong in genus A, and species T, U, V, and W belong in genus B, those are our circumscriptions of those two genera. Another systematist might determine that T, U, V, W, X, Y, and Z all belong in genus A. Agreement on circumscriptions is not governed by the Codes of Zoological or Botanical Nomenclature, and must be reached by scientific consensus. A goal of biological taxonomy is to achieve a stable circumscription for every taxon. This goal conflicts, at times, with the goal of achieving a natural classification that reflects the evolutionary history of divergence of groups of organisms. Balancing these two goals is a work in progress, and the circumscriptions of many taxa that had been regarded as stable for decades are in upheaval in the light of rapid developments in molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undescribed Taxon
In taxonomy, an undescribed taxon is a taxon (for example, a species) that has been discovered, but not yet formally described and named. The various Nomenclature Codes specify the requirements for a new taxon to be validly described and named. Until such a description has been published, the taxon has no formal or official name, although a temporary, informal name is often used. A published scientific name may not fulfil the requirements of the Codes for various reasons. For example, if the taxon was not adequately described, its name is called a ''nomen nudum''. It is possible for a taxon to be "undescribed" for an extensive period of time, even if unofficial descriptions are published. An undescribed species may be referred to with the genus name, followed by "sp.", but this abbreviation is also used to label specimens or images that are too incomplete to be identified at the species level. In some cases, there is more than one undescribed species in a genus. In this case, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of Genus, genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |