|
Photike
Photice or Photike () was a city in Epirus in the Roman and Byzantine periods. In the late Middle Ages it was known as Hagios Donatos (Ἅγιος Δονᾶτος). History The city was likely settled since Classical Antiquity, but is only known in later times. It appears in the 6th-century ''Synecdemus'', and according to Procopius of Caesarea, it was restored by Justinian I (). Procopius says that it originally stood in a marshy situation, and that Justinian built a citadel upon a neighbouring height. That citadel was likely named after Saint Donatus; in the lists of Justinian's buildings provided by Procopius, there are two forts of that name in the province of Epirus Vetus. The city is attested as a bishopric, a suffragan see of the Metropolis of Naupaktos, since the Council of Chalcedon in 451. Only a few of its bishops are known: John (at the Council of Chalcedon), Diadochus (signatory of a letter on the murder of Proterius of Alexandria to Emperor Leo I the Thracian), Hila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramythia
Paramythia () is a town and a former municipality in Thesprotia, Epirus, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Souli, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 342.197 km2. The town's population is 2,608 as of the 2021 census. Paramythia acts as a regional hub for several small villages in the Valley of Paramythia and features shops, schools, a gym, a stadium and a medical center. Primary aspects of the economy are agriculture and trade. The town is built on the slopes of Mount Gorilla and overlooks the valley, below. The Castle of Paramythia was built on a hill in one of the highest points of the town during the Byzantine period and today is open to tourists. The A2 motorway (Egnatia Odos), which links Igoumenitsa with Ioannina, goes through the valley north of the town of Paramythia. Name During the Byzantine and much of the Ottoman era the town was known in Greek as ''Agios Donatos'' (), afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay of Vlorë and the Ceraunian Mountains, Acroceraunian Mountains in the north to the Ambracian Gulf and the ruined Roman Empire, Roman city of Nicopolis in the south.. It is currently divided between the Modern regions of Greece, region of Epirus (region), Epirus in northwestern Greece and the counties of Gjirokastër County, Gjirokastër and Vlorë County, Vlorë in southern Albania. The largest city in Epirus is Ioannina, seat of the Greek region of Epirus, with Gjirokastër the largest city in the Albanian part of Epirus. A rugged and mountainous region, Epirus was the north-west area of ancient Greece. It was inhabited by the Greek tribes of the Chaonians, Molossians, and Thesprotians. It was home to the sanctuary of Dodona, the oldest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
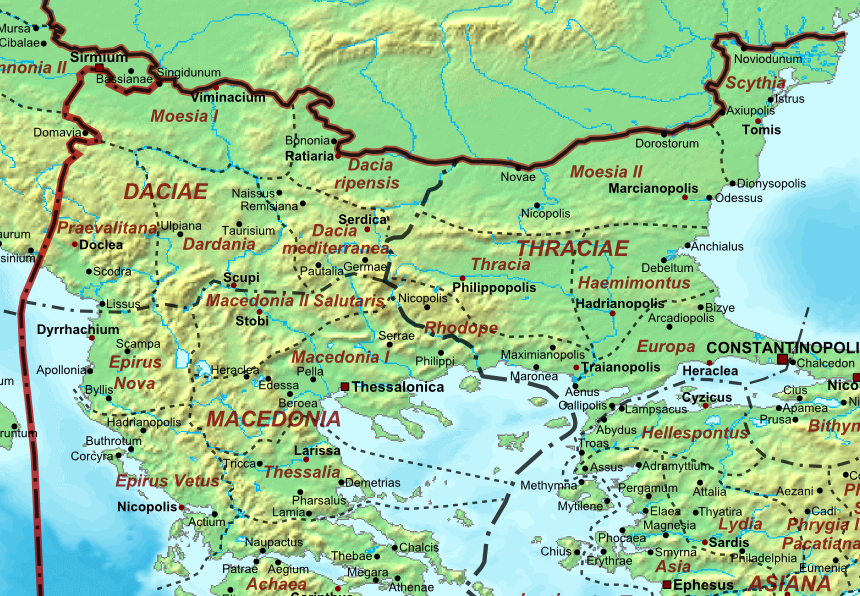
Epirus Vetus
The province of Epirus (, Koine and Medieval Greek: Ἐπαρχία Ἠπείρου, Eparchía Ēpeírou) was a province of the Roman Empire, covering the region of Ancient Epirus. Rome first annexed the region in 167 BC, in the aftermath of the Third Macedonian War, and initially put the region in the larger Roman province of Macedonia, which at the time covered the whole of the Hellenistic world in mainland Europe. In 27 BC, Epirus and Achaea were separated from Macedonia and grouped into the senatorial province of Achaea, with the exception of its northernmost part, which remained part of the province of Macedonia. Under Emperor Trajan, sometime between 103 and 114 AD, Epirus became a separate province, under a '' procurator Augusti''. The new province extended from the Gulf of Aulon (Vlorë) and the Acroceraunian Mountains in the north to the lower course of the Acheloos River in the south, and included the northern Ionian Islands of Corfu, Lefkada, Ithaca, Cephallonia, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolis Of Naupaktos
The Metropolis of Nafpaktos and Agios Vlasios () is a metropolitan see of the Church of Greece. Its seat is the town of Nafpaktos (Naupaktos or Naupactus, in the late Middle Ages known as Lepanto) in southeastern Aetolia-Acarnania, and occupies the municipality of Nafpaktia and the municipal unit of Parakampylia of the Agrinio municipality. The current metropolitan (since 1995) is Hierotheos (Vlachos). History The see of Nafpaktos is attested since the 4th century, and was initially a suffragan of Corinth and later of Athens.Gregory (1991), pp. 1442–1443 Like the rest of Illyricum, Nafpaktos depended on the pope of Rome until 733, when Leo III the Isaurian annexed it to the Patriarchate of Constantinople. Its bishop, Anthony, is attested among the participants of the councils held at Constantinople in 869–70 and 879–80. When Nafpaktos became the seat of the new Byzantine '' thema'' of Nicopolis in the second half of the 9th century, the bishopric was elevated to a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanus II Of Constantinople
Germanus II Nauplius (; died June 1240) was Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople (in exile at Nicaea) from 4 January 1223 until his death in June 1240. He was born at Anaplous in the second half of the 12th century. At the time of the Fourth Crusade in 1204, he served as a deacon in the Hagia Sophia; following the sack of Constantinople, he retired to a monastery at Achyraous.Kazhdan (1991), p. 847. In 1223, he was selected by the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes to fill the seat of the Ecumenical Patriarchate, which had relocated in Nymphaion after the fall of Constantinople in 1204. Germanus II assumed the patriarchal throne on 4 January 1223 and quickly proved himself a valuable ally to Vatatzes. Throughout his patriarchate, Germanus II strove to re-establish his authority as the head of the politically splintered Orthodox world, all the while supporting Vatatzes' in his claim to the Byzantine imperial inheritance. Thus Germanus II clashed with the prelates of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica (Greek Basiliké) was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the ''basilica'' architectural form. Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave flanked by two or more longitudinal aisles, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse at one end, or less frequently at both ends or on the side, usually contained the raised tribunal occupied by the Roman magistrates. The basilica was centrally located in every Roman town, usually adjacent to the forum and often opposite a temple in imperial-era forums. Basilicas were also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aisle
An aisle is a linear space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, in buildings such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, parliaments, courtrooms, theatres, and in long passenger vehicles. An aisle floor may be level or, as in theatres, sloping upward from a stage. Aisles also cross through shops, where they have shelving on either side; warehouses, flanked by storage pallets; and factories, where they separate different work areas. In health clubs, exercise equipment is normally arranged along aisles. They are distinguished from corridors, hallways, walkways, footpaths, pavements (''American English'' sidewalks), trails, paths and open areas of buildings: aisles lie between other open or seating areas, which are all enclosed within a structure. Spaces between buildings are not considered aisles, regardless of their size. The word is related to French ''aile'' (wing). Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keep
A keep is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in castles that were fortified residences, used as a refuge of last resort should the rest of the castle fall to an adversary. The first keeps were made of timber and formed a key part of the motte-and-bailey castles that emerged in Normandy and Anjou during the 10th century; the design spread to England, Portugal, south Italy and Sicily. As a result of the Norman Conquest of England in 1066, use spread into Wales during the second half of the 11th century and into Ireland in the 1170s. The Anglo-Normans and French rulers began to build stone keeps during the 10th and 11th centuries, including Norman keeps, with a square or rectangular design, and circular shell keeps. Stone keeps carried considerable political as well as military importance and could take a decade or more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo I Tocco
Carlo I Tocco was the hereditary Count Palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos from 1376, and ruled as the Despot of Epirus from 1411 until his death on July 4, 1429. Life Carlo I was the son of Count Leonardo I Tocco of Cephalonia and Leukas by Maddalena de' Buondelmonti, sister of Esau de' Buondelmonti, ruler of Ioannina. Leonardo I Tocco, who was count of Cephalonia from 1357 until his death in 1376, as well as duke of Leukas from 1362, was himself the son of Guglielmo Tocco, governor of Corfu for the Angevins, and Margherita Orsini, sister of Nicholas Orsini and John II Orsini, rulers of Epirus and counts of Cephalonia. In this way, Carlo Tocco inherited a claim to Epirus from both the Orsini and the Buondelmonti. Carlo I succeeded his father as count of Cephalonia and duke of Leukas on the latter's death in 1376. He shared power with his brother Leonardo II, who was invested with the island of Zante as appanage in 1399. Expansion in the Morea His marriage to Francesca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Preljubović
Thomas Preljubović (; ) was Despot of Epirus, ruler of the Despotate of Epirus in Ioannina from 1367 to his death in 1384. Thomas was an unpopular ruler and is appraised very negatively by his contemporaries. On December 23, 1384 he was stabbed to death by his guards at dawn. The conspiracy of the faction which overthrew him involved his wife Maria Angelina Doukaina Palaiologina, Maria Angelina who succeeded him. A great deal of his rule was preoccupied with fighting against the Albanians of the Despotate of Arta to his south, the Zenebishi family to his north and the Mazreku (Epirus), Mazreku and other clans to his northwest. Thomas gave himself the self-styled epithet of Albanian-slayer (Greek language, Greek: Αλβανοκτόνος/Αλβανιτόκτονος) after torturing Albanian prisoners in order to terrify his enemies. Life Early years Thomas was the son of ''caesar'' Gregorios Preljub (), the Serbian governor of Medieval Thessaly, Thessaly, who died in late 1355 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos III Palaiologos
Andronikos III Palaiologos (; 25 March 1297 – 15 June 1341), commonly Latinized as Andronicus III Palaeologus, was the Byzantine emperor from 1328 to 1341. He was the son of Michael IX Palaiologos and Rita of Armenia. He was proclaimed co-emperor in his youth, before 1313, and in April 1321 he rebelled against his grandfather, Andronikos II Palaiologos. He was formally crowned co-emperor in February 1325, before ousting his grandfather outright and becoming sole emperor on 24 May 1328. His reign included the last failed attempts to hold back the Ottoman Turks in Bithynia and the defeat at Rusokastro against the Bulgarians, but also the successful recovery of Chios, Lesbos, Phocaea, Thessaly, and Epirus. His early death left a power vacuum that resulted in the disastrous civil war between his widow, Anna of Savoy, and his closest friend and supporter, John VI Kantakouzenos, leading to the establishment of the Serbian Empire and the entry of the Ottoman Empire into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the List of Byzantine usurpers, various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. Modern historians distinguish this later phase of the Roman Empire as Byzantine due to the imperial seat moving from Rome to Byzantium, the Empire's integration of Christianity, and the predominance of Greek instead of Latin. The Byzantine Empire was the direct legal continuation of the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |