|
Pholesobi
Pholesobi, or Pholesobi̇̄ Thoṅje, is a mountain in Nepal. Description Pholesobi is a glaciated double summit in the Nepalese Himalayas. The lower peak is Phole, 6,645 metres. The mountain is situated west of Kangchenjunga and west of Jannu in the Kanchenjunga Conservation Area. Precipitation runoff from the mountain's slopes drains to the Ghunsa River → Tamur River → Kosi River → Ganges. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises 2,000 metres (6,562 ft) above the Kumbhakarna Glacier in . The first ascent of the summit was achieved on October 31, 2024, by Hidesuke Taneishi and Hiroki Yamamoto via the north face.''Inside the Stunning First Ascent of Pholesobi (6,651m)'' Owen Clarke, December 10, 2024, Climbing Magazine, Retri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merra
Merra, or Merrā, is a mountain in Nepal. Description Merra is a glaciated summit in the Nepalese Himalayas. It is situated west-northwest of Kangchenjunga in the Kanchenjunga Conservation Area. Precipitation runoff from the mountain's slopes drains into the Ghunsa River which is a tributary of the Tamur River. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises 2,130 metres (6,988 ft) above the Ghunsa River in . The first ascent of the summit was made on October 18, 2006, by Claus Ostergaard.''Merra Overview'' Nepal Himal Peak Profile, Retrieved April 14, 2025. Climate Based on the , Merra is located in a |
Jannu
Mount Kumbhakarna or Jannu (Limbu: ''Phoktanglungma'') is the 32nd-highest mountain in the world. It is an important western outlier of Kangchenjunga, the world's third-highest peak. Kumbhakarna is a large and steep peak in its own right, and has numerous challenging climbing routes. A subsidiary peak, found on the east face of the mountain, is known as Jannu East. The peak is long known as one of the last unclimbed peaks in the Himalayas and rises to 7,468m. The official name of this peak is Kumbhakarna, but the designation Jannu is still better known. It is called Phoktanglungma by the native population, literally "mountain with shoulders" (''phoktang'' means "shoulder" and ''lungma'' means "mountain"), in the Limbu language, and is sacred in the yuma religion. Location Kumbhakarna is the highest peak of the Kumbhakarna Section of the Kangchenjunga Himal (using H. Adams Carter's classification H. Adams Carter, "Classification of the Himalaya", '' American Alpine Journal'' 59 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Koshi Province
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghunsa
Ghunsa () is a village of Taplejung, Nepal at elevation of 3,475 m and is a major check point for Mt. Kangchenjunga. This village came into attention after the helicopter accident that killed 24 passengers including most prominent figures in conservation work. Inhabitants The local called themselves Gunsa(wa)pa. They can be classified under larger Walung-ngas tribe. The local language spoken by Gunsawa is Ghunsake, a variation of Walungge family, Walungge . Ethnologue. Retrieved 2017-02-14. "Walungge" of Central Tibetan language. Most inhabitants involves themselves in subsistence farming and yak grazing. The main crops grown are maize and potato The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...es. Until recently, many households were semi-nomadic in their quest for capital, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamatari Glacier
The Yamatari glacier valley is located in Taplejung district. The glacier extends from 4050 m and 3900 m. It was formed during the neoglacial age. The glacier have a length of about 10 to 12 km. The Yamatari glacier terminates at and elevation of about 4200 m. Yamatari glacier joins Ghunsa valley at an elevation of about 3500 m just below the settlement at Ghunsa Ghunsa () is a village of Taplejung, Nepal at elevation of 3,475 m and is a major check point for Mt. Kangchenjunga. This village came into attention after the helicopter accident that killed 24 passengers including most prominent figures in conser ... village. References Glaciers of Nepal {{Nepal-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang Himal
Chang Himal, also known as Ramthang Chang or Wedge Peak, is a mountain in Nepal. Description Chang Himal is a glaciated summit in the Nepalese Himalayas. It is situated northwest of Kangchenjunga in the Kanchenjunga Conservation Area. Precipitation runoff from the mountain's slopes drains into the Ghunsa River which is a tributary of the Tamur River. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises 1,820 metres (5,971 ft) above the Kangchenjunga Glacier in . The first ascent of the summit was made on October 5, 1974, by Janez Gradisar, Bojan Pollak, and Michael Smolej via the southwest ridge.''Chang Himal Overview'' Nepal Himal Peak Profile, Retrieved April 12, 2025. The north face was first climbed October 29 – November 2, 2009, by Nick Bullock and Andy Houseman (1800 m, ED+ M6). Climate |
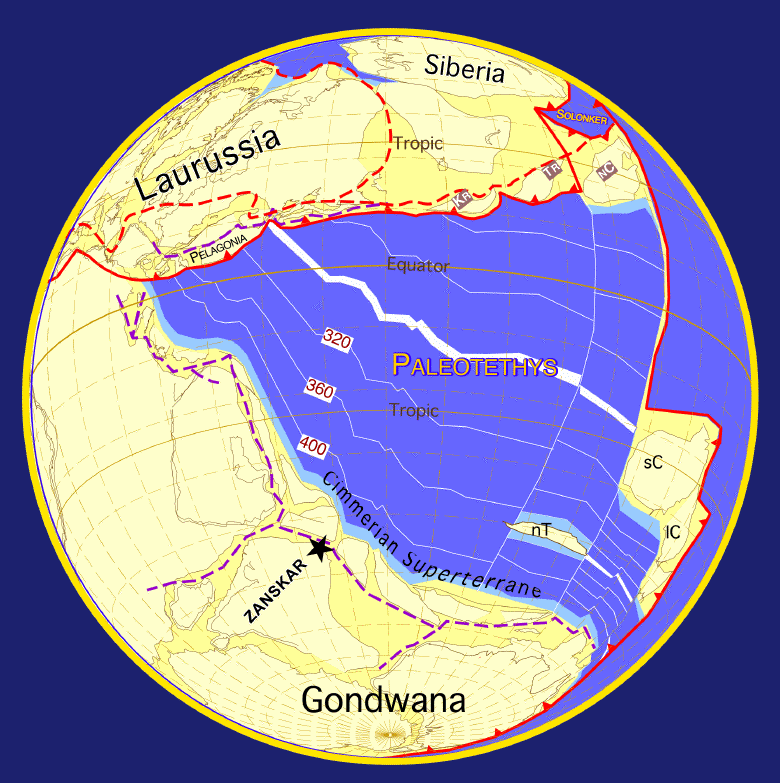
Geology Of The Himalayas
The geology of the Himalayas is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of the immense mountain range formed by plate tectonic forces and sculpted by weathering and erosion. The Himalayas, which stretch over 2400 km between the Namcha Barwa syntaxis at the eastern end of the mountain range and the Nanga Parbat syntaxis at the western end, are the result of an ongoing orogeny — the collision of the continental crust of two tectonic plates, namely, the Indian Plate thrusting into the Eurasian Plate. The Himalaya-Tibet region supplies fresh water for more than one-fifth of the world population, and accounts for a quarter of the global sedimentary budget. Topographically, the belt has many superlatives: the highest rate of uplift (nearly 10 mm/year at Nanga Parbat), the highest relief (8848 m at Mt. Everest Chomolangma), among the highest erosion rates at 2–12 mm/yr, the source of some of the greatest rivers and the highest concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orographic Lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and create clouds and, under the right conditions, precipitation. Orographic lifting can have a number of effects, including precipitation, rain shadowing, leeward winds, and associated clouds. Precipitation Precipitation induced by orographic lift occurs in many places throughout the world. Examples include: * The Mogollon Rim in central Arizona * The western slope of the Sierra Nevada range in California. * The western slope of the Wasatch Range in Utah. Specifically the Little and Big Cottonwood Canyons. * The mountains near Baja California North – specifically La Bocana to Laguna Hanson. * The windward slopes of Khasi and Jayantia Hills (see Mawsynram) in the state of Meghalaya in India. * The Western Highlands of Yemen, which rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region. Many South Asian and Southeast Asian Countries of the Bay of Bengal, countries are dependent on the Bay of Bengal. Geopolitically, the bay is bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka, and the northwesternmost point of Sumatra, Indonesia. Cox's Bazar Beach, Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay. The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of . A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the Ganges–Hooghly River, Hooghly, the Padma River, Padma, the Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |